Safari can’t find the server errors can be frustrating, especially when your internet connection appears stable, but with rental-server.net’s guide, understanding and fixing this issue becomes simple, ensuring uninterrupted browsing, and we offer solutions ranging from DNS settings to server configurations. By exploring various server options and hosting solutions, rental-server.net helps you optimize your online presence with dedicated servers, VPS hosting, and cloud solutions.
1. What Does “Safari Can’t Find the Server” Actually Mean?
The “Safari can’t find the server” error means Safari is unable to connect to the web server hosting the website you’re trying to visit. This can be due to various reasons, from DNS issues to website problems.
Understanding the Technical Background
Safari, like other web browsers, relies on a Domain Name System (DNS) to translate domain names (like rental-server.net) into IP addresses, which are necessary for locating web servers, according to RFC 1034. If Safari can’t resolve the domain name to an IP address or can’t connect to the server at that IP address, it will display the “Safari can’t find the server” error. This could be due to:
- DNS resolution failure: The DNS server is not responding, or the domain name is not correctly configured.
- Server downtime: The web server is offline or experiencing technical issues.
- Network connectivity problems: There’s an issue with your internet connection preventing Safari from reaching the server.
- Firewall or security software: Security software is blocking Safari’s access to the server.
Common Scenarios Where This Error Occurs
- Website is down: The server hosting the website is temporarily unavailable due to maintenance or an unexpected outage.
- Incorrect URL: A typo in the web address can lead to Safari not finding the server.
- DNS server issues: Problems with your DNS server can prevent Safari from resolving the website’s domain name.
- Network configuration errors: Incorrect network settings on your Mac can interfere with Safari’s ability to connect to servers.
 Safari Error
Safari Error
2. What Are the Potential Causes of Safari’s Connection Issues?
Safari’s connection issues can stem from a variety of factors, ranging from simple user errors to complex network configurations and server-side problems, according to Cisco’s guide on network troubleshooting. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Client-Side Issues
- Incorrect URL: A common mistake is typing the URL incorrectly. Even a small typo can prevent Safari from finding the server. Always double-check the web address for accuracy.
- Browser Cache and Cookies: Over time, Safari accumulates cached data and cookies that can become corrupted or outdated. This can interfere with the browser’s ability to connect to certain websites. Clearing the cache and cookies can often resolve these issues.
- Browser Extensions: Some browser extensions can interfere with Safari’s network connections. These extensions might modify network requests, block content, or introduce conflicts that prevent Safari from finding the server.
- Outdated Browser: Using an outdated version of Safari can lead to compatibility issues with modern web servers and security protocols. Ensure that you’re running the latest version of Safari to benefit from bug fixes and security updates.
- Firewall and Security Software: Firewalls and security software can sometimes block Safari’s access to certain websites or servers. These programs might misidentify legitimate traffic as malicious and prevent Safari from connecting.
- VPN and Proxy Settings: VPNs and proxy servers can alter Safari’s network configuration and introduce connectivity issues. If you’re using a VPN or proxy, try disabling it to see if it resolves the “Safari can’t find the server” error.
Network-Related Issues
- Internet Connection Problems: A faulty internet connection is one of the most common reasons for Safari’s connection issues. Ensure that your internet connection is stable and that you can access other websites without problems.
- DNS Server Issues: Safari relies on DNS servers to translate domain names into IP addresses. If the DNS server is not responding or is providing incorrect information, Safari won’t be able to find the server.
- Router Problems: Issues with your router, such as incorrect settings or outdated firmware, can interfere with Safari’s ability to connect to the internet. Restarting your router and updating its firmware can often resolve these problems.
- DHCP Lease Issues: Your computer obtains its IP address and other network settings from a DHCP server. If the DHCP lease expires or there’s a problem with the DHCP server, Safari may not be able to connect to the internet. Renewing the DHCP lease can resolve these issues.
Server-Side Issues
- Website Downtime: The web server hosting the website may be temporarily unavailable due to maintenance or an unexpected outage. In this case, the “Safari can’t find the server” error is not caused by any problem on your end.
- Server Configuration Errors: Incorrect server configurations can prevent Safari from connecting to the website. These errors might involve DNS settings, firewall rules, or other server-side configurations.
- Geographical Restrictions: Some websites restrict access based on the user’s geographical location. If you’re trying to access a website that’s not available in your region, Safari will display the “Safari can’t find the server” error.
3. How to Troubleshoot “Safari Can’t Find the Server” Step-by-Step?
Troubleshooting “Safari can’t find the server” requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the underlying cause. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you diagnose and fix the problem:
Initial Checks
-
Verify the URL:
- Double-check the web address for typos or errors. Even a small mistake can prevent Safari from finding the server.
- Try accessing the website using its IP address directly. If this works, it indicates a DNS resolution issue.
-
Check Your Internet Connection:
- Ensure that your internet connection is stable and that you can access other websites without problems.
- Restart your modem and router to refresh your network connection.
-
Test with Another Browser:
- Try accessing the website using another browser, such as Chrome or Firefox.
- If the website loads in another browser, it suggests that the problem is specific to Safari.
-
Clear Safari’s Cache and Cookies:
- Cached data and cookies can sometimes interfere with Safari’s ability to connect to websites.
- To clear the cache and cookies, go to Safari > Settings > Privacy > Manage Website Data and click “Remove All.”
-
Disable Browser Extensions:
- Browser extensions can sometimes interfere with Safari’s network connections.
- Disable all extensions and try accessing the website again. If the website loads, enable the extensions one by one to identify the problematic one.
Advanced Troubleshooting
-
Check DNS Settings:
- Safari relies on DNS servers to translate domain names into IP addresses.
- If the DNS server is not responding or is providing incorrect information, Safari won’t be able to find the server.
- To change your DNS settings, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, click “Details,” and then go to the “DNS” tab.
- Add Google’s Public DNS servers (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare’s DNS servers (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1) to the list.
-
Renew DHCP Lease:
- Your computer obtains its IP address and other network settings from a DHCP server.
- If the DHCP lease expires or there’s a problem with the DHCP server, Safari may not be able to connect to the internet.
- To renew the DHCP lease, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, click “Details,” go to the “TCP/IP” tab, and click “Renew DHCP Lease.”
-
Check Firewall and Security Software:
- Firewalls and security software can sometimes block Safari’s access to certain websites or servers.
- Temporarily disable your firewall and security software to see if it resolves the issue.
- If the website loads with the firewall and security software disabled, configure them to allow Safari’s traffic.
-
Check VPN and Proxy Settings:
- VPNs and proxy servers can alter Safari’s network configuration and introduce connectivity issues.
- Disable your VPN and proxy settings to see if it resolves the “Safari can’t find the server” error.
- To disable proxy settings, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, click “Details,” go to the “Proxies” tab, and uncheck any enabled proxy protocols.
-
Update Safari and macOS:
- Using an outdated version of Safari or macOS can lead to compatibility issues with modern web servers and security protocols.
- Ensure that you’re running the latest versions of Safari and macOS to benefit from bug fixes and security updates.
- To update Safari, go to the App Store and check for available updates.
- To update macOS, go to System Settings > General > Software Update.
Server-Side Checks
-
Check Website Status:
- The web server hosting the website may be temporarily unavailable due to maintenance or an unexpected outage.
- Use online tools like Down for Everyone or Just Me to check if the website is down for everyone or just you.
-
Contact Website Support:
- If the website is down for everyone, there’s nothing you can do on your end.
- Contact the website’s support team to inquire about the outage and get an estimated time for when the website will be back online.
 Safari Settings
Safari Settings
4. What Role Does DNS Play in Website Accessibility?
DNS (Domain Name System) is crucial for website accessibility because it translates human-readable domain names (like rental-server.net) into IP addresses, which computers use to locate web servers, according to How DNS Works. Without DNS, users would have to remember and enter complex IP addresses to access websites.
How DNS Works
- DNS Query: When you type a domain name into your browser, the browser sends a DNS query to a DNS resolver, which is typically provided by your internet service provider (ISP).
- Recursive Search: The DNS resolver starts a recursive search to find the IP address associated with the domain name. It first checks its cache, and if the information is not there, it queries a root DNS server.
- Root Server: The root server directs the resolver to a top-level domain (TLD) server, such as .com or .net.
- TLD Server: The TLD server directs the resolver to the authoritative DNS server for the domain name.
- Authoritative Server: The authoritative DNS server contains the IP address for the domain name. It sends the IP address back to the DNS resolver.
- DNS Resolution: The DNS resolver sends the IP address to your browser.
- Website Access: Your browser uses the IP address to connect to the web server hosting the website and retrieve the content.
Impact of DNS Issues on Safari
- Incorrect DNS Settings: If your DNS settings are incorrect or outdated, Safari may not be able to resolve domain names to IP addresses, resulting in the “Safari can’t find the server” error.
- DNS Server Downtime: If the DNS server is experiencing downtime or technical issues, Safari won’t be able to resolve domain names, preventing you from accessing websites.
- DNS Cache Poisoning: In rare cases, the DNS cache can be poisoned with incorrect information, leading Safari to connect to the wrong server or display the “Safari can’t find the server” error.
Troubleshooting DNS-Related Issues in Safari
-
Flush DNS Cache:
- Clearing the DNS cache can remove outdated or corrupted DNS records, allowing Safari to fetch fresh information from the DNS server.
- To flush the DNS cache on macOS, open the Terminal application and run the command
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder.
-
Change DNS Servers:
- If you’re experiencing DNS-related issues, try changing your DNS servers to a reliable public DNS server like Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
- To change your DNS servers, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, click “Details,” and then go to the “DNS” tab.
-
Check DNS Records:
- Use online tools like MXToolbox or Google Admin Toolbox Dig to check the DNS records for the website you’re trying to access.
- Ensure that the DNS records are correctly configured and that the domain name is resolving to the correct IP address.
5. How to Clear Safari’s Cache and Cookies Effectively?
Clearing Safari’s cache and cookies is an effective way to resolve various browsing issues, including the “Safari can’t find the server” error. Here’s how to do it:
Steps to Clear Cache and Cookies
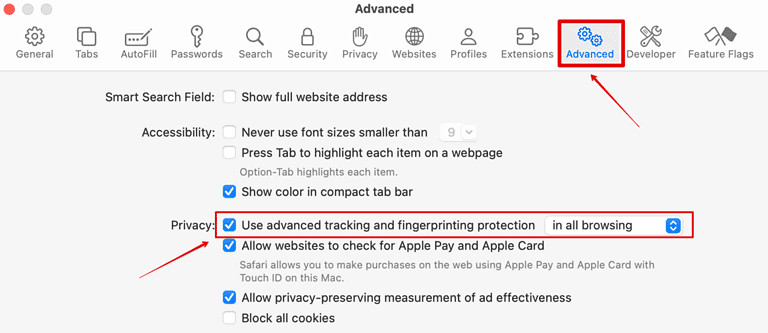
-
Open Safari Settings:
- Click on the “Safari” menu in the top-left corner of the screen and select “Settings.”
-
Go to the Privacy Tab:
- In the Settings window, click on the “Privacy” tab.
-
Manage Website Data:
- Click on the “Manage Website Data” button. This will open a window displaying all the websites that have stored data on your computer.
-
Remove All Data:
- To clear all cache and cookies, click on the “Remove All” button.
- A confirmation dialog will appear, asking if you’re sure you want to remove the data. Click on “Remove Now” to confirm.
-
Clear History (Optional):
- To further clean up Safari, you can also clear your browsing history.
- Click on the “History” menu in the top menu bar and select “Clear History.”
- Choose the desired time range for clearing your history and click on “Clear History.”
Why Clear Cache and Cookies?
- Resolves Connection Issues: Outdated or corrupted cached data and cookies can interfere with Safari’s ability to connect to websites. Clearing them can resolve the “Safari can’t find the server” error.
- Improves Performance: Clearing the cache and cookies can improve Safari’s performance by removing unnecessary data and freeing up storage space.
- Enhances Privacy: Clearing cookies can enhance your privacy by removing tracking data that websites use to monitor your browsing activity.
Alternative Method: Private Browsing
- Safari’s Private Browsing mode prevents the browser from saving your browsing history, cookies, and cache.
- To open a Private Browsing window, click on the “File” menu in the top menu bar and select “New Private Window.”
- Using Private Browsing can help you determine if the “Safari can’t find the server” error is caused by cached data or cookies. If the website loads in Private Browsing mode, it suggests that clearing the cache and cookies will resolve the issue.
6. How Do Browser Extensions Impact Connectivity?
Browser extensions can significantly impact Safari’s connectivity by modifying network requests, blocking content, or introducing conflicts that prevent Safari from finding the server, according to Web Browser Extensions and Security.
Common Issues Caused by Extensions
- Content Blocking: Extensions designed to block ads, trackers, or other types of content can sometimes block legitimate website content, leading to the “Safari can’t find the server” error.
- Network Interception: Some extensions intercept network requests to modify them or inject additional code. This can interfere with Safari’s ability to connect to the server.
- Resource Consumption: Extensions can consume significant system resources, such as memory and CPU, which can slow down Safari and lead to connectivity issues.
- Compatibility Issues: Extensions may not be compatible with certain websites or with each other, leading to conflicts that prevent Safari from finding the server.
Identifying Problematic Extensions
-
Disable All Extensions:
- To disable all extensions, go to Safari > Settings > Extensions and uncheck the box next to each extension.
-
Test Website Connectivity:
- Try accessing the website again after disabling all extensions.
- If the website loads, it indicates that one or more extensions were causing the problem.
-
Enable Extensions One by One:
- Enable the extensions one by one, testing the website after enabling each extension.
- When the website stops loading, the last extension you enabled is the problematic one.
-
Remove or Update Problematic Extensions:
- Remove the problematic extension or check for updates.
- Updating the extension may resolve compatibility issues and fix bugs that were causing the connectivity problems.
Managing Extensions Effectively
- Install Extensions from Trusted Sources: Only install extensions from the Mac App Store or from trusted developers to minimize the risk of installing malicious or poorly coded extensions.
- Read Extension Reviews: Before installing an extension, read reviews from other users to see if they have experienced any problems with the extension.
- Keep Extensions Updated: Regularly check for updates to your extensions to ensure that you have the latest bug fixes and security updates.
- Disable Unnecessary Extensions: Disable extensions that you don’t use regularly to reduce the risk of conflicts and improve Safari’s performance.
 Details Settings
Details Settings
7. What Network Settings Should You Verify on Your Mac?
Verifying your Mac’s network settings is essential for troubleshooting connectivity issues like “Safari can’t find the server.” Here are the key network settings to check:
Key Network Settings
-
IP Address:
- Your IP address is your computer’s unique identifier on the network.
- Ensure that your computer has a valid IP address and that it’s not conflicting with another device on the network.
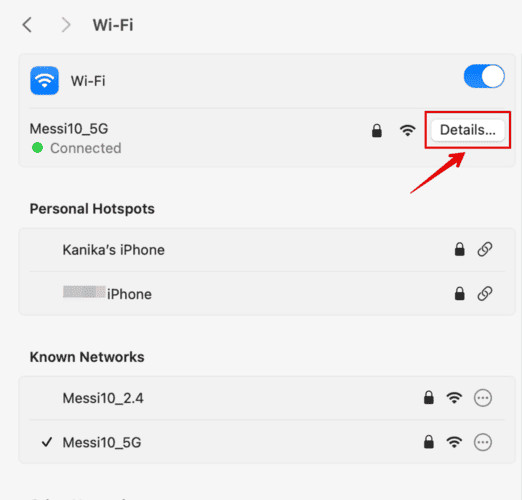
- To check your IP address, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, and look for the “IP Address” field.
-
Subnet Mask:
- The subnet mask defines the range of IP addresses that are considered to be on the same network as your computer.
- Ensure that your subnet mask is correctly configured and that it matches the subnet mask of your network.
- To check your subnet mask, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, and look for the “Subnet Mask” field.
-
Router Address:
- The router address is the IP address of your router, which serves as the gateway between your computer and the internet.
- Ensure that your router address is correctly configured and that your computer can communicate with the router.
- To check your router address, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, and look for the “Router” field.
-
DNS Servers:
- DNS servers translate domain names into IP addresses, allowing you to access websites by their names instead of their IP addresses.
- Ensure that your DNS servers are correctly configured and that they’re responding to DNS queries.
- To check your DNS servers, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, click “Details,” and then go to the “DNS” tab.
-
Proxy Settings:
- Proxy servers act as intermediaries between your computer and the internet, routing your traffic through a different server.
- Ensure that your proxy settings are correctly configured and that you’re not using a proxy server unnecessarily.
- To check your proxy settings, go to System Settings > Network, select your active network connection, click “Details,” and then go to the “Proxies” tab.
Troubleshooting Network Settings
- Automatic Configuration: In most cases, your network settings should be configured automatically using DHCP. Ensure that your network connection is set to “Using DHCP” in the System Settings > Network panel.
- Manual Configuration: If you’re using a static IP address or custom DNS servers, double-check that all the settings are entered correctly.
- Network Diagnostics: macOS includes a Network Diagnostics tool that can help you identify and troubleshoot network problems. To run the Network Diagnostics tool, go to System Settings > Network and click the “Assist me…” button.
8. How to Determine if a Website Is Down for Everyone or Just You?
Determining whether a website is down for everyone or just you is a crucial step in troubleshooting the “Safari can’t find the server” error. If the website is down for everyone, the problem is likely on the server-side, and there’s nothing you can do on your end, according to Website Monitoring.
Online Tools
-
Down for Everyone or Just Me:
- Down for Everyone or Just Me is a simple online tool that checks the status of a website and tells you whether it’s down for everyone or just you.
- Enter the URL of the website you’re trying to access and click the “or just me?” button.
- The tool will display a message indicating whether the website is up or down.
-
Is It Down Right Now:
- Is It Down Right Now is another online tool that checks the status of a website and provides additional information, such as the website’s response time and uptime history.
- Enter the URL of the website you’re trying to access and click the “Check” button.
- The tool will display a detailed report about the website’s status.
Other Methods
-
Check Social Media:
- Search for the website on social media platforms like Twitter or Facebook to see if other users are reporting problems.
- If many users are reporting that the website is down, it’s likely a server-side issue.
-
Contact Website Support:
- If you’re still unsure whether the website is down for everyone or just you, contact the website’s support team to inquire about the status of the website.
- The support team may be able to provide you with more information about the outage and an estimated time for when the website will be back online.
-
Use a VPN:
- Connect to a VPN server in a different location and try accessing the website again.
- If the website loads through the VPN, it suggests that the problem is related to your network or geographical location.
Interpreting the Results
- Website Is Down for Everyone: If the online tools and social media reports indicate that the website is down for everyone, there’s likely a server-side issue, and you’ll need to wait for the website to be back online.
- Website Is Down Just for You: If the online tools and social media reports indicate that the website is up, the problem is likely on your end, and you’ll need to troubleshoot your network settings, browser settings, or other client-side issues.
9. How Does a VPN or Proxy Server Affect Safari’s Connectivity?
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and proxy servers can significantly affect Safari’s connectivity by altering network configurations and introducing potential issues.
How VPNs Work
A VPN creates an encrypted connection between your device and a remote server, masking your IP address and encrypting your internet traffic. This can enhance your privacy and security, but it can also introduce connectivity issues.
How Proxy Servers Work
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, routing your traffic through a different server. This can be used to bypass geographical restrictions, improve performance, or filter content.
Potential Issues
-
Connectivity Problems:
- VPNs and proxy servers can sometimes cause connectivity problems due to misconfigurations, server downtime, or compatibility issues.
- If you’re experiencing the “Safari can’t find the server” error, try disabling your VPN or proxy server to see if it resolves the issue.
-
Slow Performance:
- VPNs and proxy servers can slow down your internet connection due to the added overhead of encryption and routing your traffic through an intermediary server.
- If you’re experiencing slow performance, try disabling your VPN or proxy server to see if it improves your browsing speed.
-
Geographical Restrictions:
- Some websites block traffic from certain VPN or proxy server IP addresses, leading to the “Safari can’t find the server” error.
- If you’re trying to access a website that’s blocked by your VPN or proxy server, try connecting to a different server or disabling the VPN or proxy server altogether.
-
DNS Leaks:
- VPNs and proxy servers can sometimes leak your DNS queries, revealing your true IP address and location to the websites you visit.
- To prevent DNS leaks, ensure that your VPN or proxy server is properly configured to use its own DNS servers.
-
Security Risks:
- Using untrusted VPN or proxy servers can expose you to security risks, such as malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches.
- Only use VPN or proxy servers from trusted providers and ensure that your connection is encrypted.
Troubleshooting VPN and Proxy Issues
-
Disable VPN or Proxy:
- The first step in troubleshooting VPN or proxy issues is to disable the VPN or proxy server and try accessing the website again.
- If the website loads without the VPN or proxy server, it indicates that the VPN or proxy server was causing the problem.
-
Check VPN or Proxy Settings:
- Ensure that your VPN or proxy settings are correctly configured and that you’re using the correct server address, port number, and authentication credentials.
-
Try a Different Server:
- If you’re using a VPN, try connecting to a different server in a different location to see if it resolves the issue.
-
Contact VPN or Proxy Support:
- If you’re still experiencing problems with your VPN or proxy server, contact the provider’s support team for assistance.
10. When Should You Consider Contacting Your ISP for Support?
Contacting your ISP (Internet Service Provider) for support should be considered when you’ve exhausted all other troubleshooting steps and suspect that the problem lies with your internet connection or their network infrastructure.
Common Scenarios
-
Widespread Connectivity Issues:
- If you’re experiencing connectivity issues with multiple websites and devices, it’s likely a problem with your internet connection.
- Contact your ISP to report the issue and inquire about any known outages or maintenance activities in your area.
-
Intermittent Connection Problems:
- If your internet connection is dropping frequently or experiencing intermittent slowdowns, it could be a sign of a problem with your ISP’s network.
- Contact your ISP to troubleshoot the issue and ensure that your connection is stable and reliable.
-
Slow Speeds:
- If you’re consistently experiencing slow internet speeds, even when no one else is using your network, it could be a problem with your ISP’s service.
- Contact your ISP to test your connection speed and troubleshoot any potential issues.
-
DNS Issues:
- If you’ve tried changing your DNS servers and flushing your DNS cache, but you’re still experiencing DNS-related issues, it could be a problem with your ISP’s DNS servers.
- Contact your ISP to report the issue and inquire about the status of their DNS servers.
-
Equipment Problems:
- If you suspect that there’s a problem with your modem or router, contact your ISP to troubleshoot the issue and replace any faulty equipment.
Before Contacting Your ISP
-
Gather Information:
- Before contacting your ISP, gather as much information as possible about the issue, including when it started, what websites or services are affected, and what troubleshooting steps you’ve already taken.
-
Check Your Account:
- Ensure that your account is in good standing and that you’ve paid your bill on time.
-
Have Your Account Information Ready:
- When you call your ISP, be prepared to provide your account number, address, and other identifying information.
What to Expect When Contacting Your ISP
- Troubleshooting Steps: Your ISP may ask you to perform some basic troubleshooting steps, such as restarting your modem and router, checking your cables, and testing your connection speed.
- Technician Visit: If the issue cannot be resolved over the phone, your ISP may schedule a technician to visit your home and troubleshoot the problem in person.
- Escalation: If your issue is not resolved to your satisfaction, ask to speak to a supervisor or escalate the issue to a higher level of support.
At rental-server.net, we understand the importance of reliable server connections. While we specialize in providing top-notch dedicated server, VPS hosting, and cloud solutions, we hope this guide helps you resolve Safari’s connectivity issues and ensures seamless browsing.
Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States
Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000
Website: rental-server.net
FAQ: Safari Can’t Find the Server
- Why does Safari say it can’t find the server?
Safari displays “Safari can’t find the server” when it’s unable to connect to the web server hosting the website you’re trying to visit, which could be due to DNS issues, server downtime, or network problems. - How do I fix Safari when it can’t find the server?
You can fix it by checking your internet connection, verifying the URL, clearing Safari’s cache and cookies, disabling browser extensions, and ensuring your DNS settings are correct. - What does it mean when a server cannot be found?
When a server cannot be found, it means your computer or browser is unable to locate the server hosting the website or service you’re trying to access, usually due to network issues or server problems. - How do I reset my Safari browser?
To reset Safari, clear its history, cache, and cookies by going to Safari > Settings > Privacy > Manage Website Data > Remove All, and then clear the history under the History menu. - How do I clear the DNS cache on my Mac?
To clear the DNS cache on your Mac, open Terminal and run the commandsudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder. - Can a VPN cause Safari to not find the server?
Yes, a VPN can cause Safari to not find the server if the VPN server is experiencing downtime, is misconfigured, or is blocking traffic to the website you’re trying to access. - How do I change my DNS settings on a Mac?
Change your DNS settings by going to System Settings > Network, selecting your active network connection, clicking “Details,” going to the “DNS” tab, and adding new DNS server addresses. - What should I do if a website is down for everyone?
If a website is down for everyone, there’s nothing you can do but wait for the website’s administrators to resolve the issue; you can also check their social media for updates. - How do browser extensions affect Safari’s connectivity?
Browser extensions can affect Safari’s connectivity by modifying network requests, blocking content, or introducing conflicts that prevent Safari from finding the server. - When should I contact my ISP for Safari connectivity issues?
Contact your ISP when you’ve tried all other troubleshooting steps and suspect the problem is with your internet connection, such as widespread connectivity issues, intermittent problems, or slow speeds.
