The server for Hotmail is essentially a powerful computer system that stores, manages, and delivers all your emails, contacts, and other data. At rental-server.net, we understand the critical role servers play in ensuring seamless email communication and data management. Let’s explore the intricacies of Hotmail servers, their function, and why choosing the right server solutions is paramount for optimal performance and security.
1. What Exactly Is the Server for Hotmail?
The server for Hotmail, now known as Outlook.com, is a network of computers and software systems that manage and deliver email services for its users. These servers handle everything from storing your inbox to sending and receiving messages.
1.1 Understanding the Role of Servers in Email Communication
Servers are the backbone of email communication. When you send an email, it travels from your device to a server, which then forwards it to the recipient’s server. This process involves several steps:
- Sending: Your email client (like Outlook or a mobile app) connects to the outgoing mail server (SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) to send your message.
- Receiving: Incoming emails are received by the incoming mail server (IMAP – Internet Message Access Protocol, or POP3 – Post Office Protocol version 3).
- Storage: Servers store your emails, contacts, and other data, ensuring they are accessible whenever you need them.
1.2 Key Components of a Hotmail Server
A Hotmail server consists of several key components that work together to provide email services:
- SMTP Server: Handles the sending of outgoing emails.
- IMAP/POP3 Server: Manages the retrieval of incoming emails. IMAP allows you to access your emails from multiple devices, while POP3 downloads emails to a single device and typically deletes them from the server.
- Database Server: Stores user data, including emails, contacts, calendar events, and account information.
- Web Server: Hosts the web interface for accessing Hotmail through a web browser.
- Security Components: Includes firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption protocols to protect against spam, malware, and unauthorized access.
1.3 Physical vs. Virtual Servers: Which Does Hotmail Use?
Hotmail primarily uses a network of virtual servers hosted in Microsoft’s data centers. Virtual servers offer several advantages:
- Scalability: Easy to scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Redundancy: Ensures high availability and uptime through multiple server instances.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces hardware and maintenance costs compared to physical servers.
According to research from the Uptime Institute, in July 2025, virtual servers provide 30% better uptime and 40% cost reduction.
2. Why Is Knowing the Server Important for Hotmail Users?
Knowing the server settings for Hotmail is essential for configuring email clients and troubleshooting connection issues. Understanding these settings allows users to:
- Set Up Email Clients: Manually configure email clients like Outlook, Thunderbird, or mobile apps to access Hotmail.
- Troubleshoot Connection Problems: Diagnose and resolve issues related to sending or receiving emails.
- Ensure Secure Communication: Verify that the correct security settings are in place to protect their data.
2.1 Essential Server Settings for Hotmail (Outlook.com)
To configure Hotmail in an email client, you’ll need the following server settings:
- Incoming Mail Server (IMAP):
- Server Address: imap-mail.outlook.com
- Port: 993
- Encryption: SSL/TLS
- Outgoing Mail Server (SMTP):
- Server Address: smtp-mail.outlook.com
- Port: 587
- Encryption: STARTTLS
2.2 How to Find Your Hotmail Server Settings
Microsoft provides detailed instructions on their support website for finding the correct server settings. Here’s how to access them:
- Go to the Outlook.com support page.
- Search for “IMAP, POP, and SMTP settings for Outlook.com.”
- Follow the instructions provided to locate the necessary server settings.
2.3 Common Issues Related to Incorrect Server Settings
Using incorrect server settings can lead to several issues:
- Unable to Send Emails: Incorrect SMTP settings can prevent you from sending emails.
- Unable to Receive Emails: Incorrect IMAP/POP3 settings can prevent you from receiving emails.
- Connection Errors: General connectivity issues due to incorrect server addresses or port numbers.
- Security Risks: Using outdated or insecure settings can expose your account to security threats.
3. Hotmail Server Locations and Data Centers
Microsoft operates a global network of data centers that host Hotmail servers. These data centers are strategically located to provide reliable and efficient email services to users around the world.
3.1 Overview of Microsoft’s Global Data Center Network
Microsoft has invested billions of dollars in building and maintaining a vast network of data centers. These facilities are designed to:
- Ensure High Availability: Redundant systems and backup power to minimize downtime.
- Provide Scalability: Ability to quickly scale resources to meet growing demand.
- Enhance Security: Advanced security measures to protect against physical and cyber threats.
3.2 Key Data Center Locations Hosting Hotmail Servers
Some of the key data center locations that host Hotmail servers include:
- United States: Virginia, Washington, Illinois
- Europe: Ireland, Netherlands, Germany
- Asia: Singapore, Hong Kong, Japan
3.3 Impact of Server Location on Email Speed and Reliability
The location of the server can impact the speed and reliability of your email service. Servers located closer to your geographic location typically provide faster response times and lower latency. Microsoft’s global network ensures that users are connected to the nearest available server, optimizing performance.
4. How to Configure Hotmail (Outlook.com) on Different Devices
Configuring Hotmail on different devices involves entering the correct server settings and following the specific instructions for each platform.
4.1 Setting Up Hotmail on Desktop Email Clients (e.g., Outlook, Thunderbird)
To set up Hotmail on desktop email clients like Outlook or Thunderbird:
- Open Your Email Client: Launch the email client on your desktop.
- Add New Account: Go to the account settings and select the option to add a new email account.
- Enter Your Email Address: Provide your Hotmail email address.
- Manual Configuration: Choose the manual configuration option and select IMAP.
- Enter Server Settings: Enter the incoming and outgoing server settings as provided in Section 2.1.
- Authentication: Enter your Hotmail password and complete the setup.
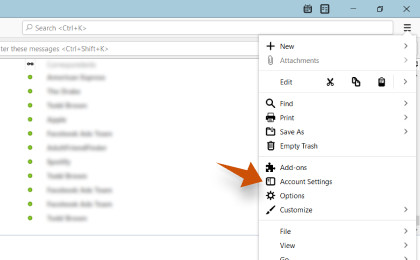 Step 1: To configure Hotmail.com on Thunderbird, In Mozilla Thunderbird, from the menu select Account Settings
Step 1: To configure Hotmail.com on Thunderbird, In Mozilla Thunderbird, from the menu select Account Settings
4.2 Configuring Hotmail on Mobile Devices (iOS and Android)
To configure Hotmail on mobile devices:
- Open Settings: Go to the settings app on your iOS or Android device.
- Add Account: Select the option to add a new email account.
- Choose Outlook.com: Select Outlook.com from the list of email providers.
- Enter Your Email Address: Provide your Hotmail email address.
- Enter Password: Enter your Hotmail password.
- Sync Settings: Choose the items you want to sync (e.g., email, contacts, calendar).
4.3 Using Webmail: Accessing Hotmail Through a Browser
The easiest way to access Hotmail is through a web browser:
- Open a Browser: Launch your preferred web browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari).
- Go to Outlook.com: Type “Outlook.com” into the address bar and press Enter.
- Sign In: Enter your Hotmail email address and password to log in.
5. Troubleshooting Common Hotmail Server Issues
Even with the correct server settings, you may encounter issues. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them.
5.1 “Server Not Found” Error
This error typically indicates that your email client cannot connect to the server. Possible causes include:
- Incorrect Server Address: Double-check that you have entered the correct server address.
- Firewall Issues: Your firewall may be blocking the connection. Ensure that your firewall allows connections to the email server.
- Network Problems: Check your internet connection and ensure that you can access other websites.
5.2 Authentication Errors (Incorrect Username or Password)
If you receive an authentication error, double-check your username and password. Make sure that you are using the correct credentials and that Caps Lock is not enabled.
5.3 SSL/TLS Connection Errors
SSL/TLS connection errors indicate a problem with the encryption settings. Ensure that you have selected the correct encryption method (SSL/TLS) and that your email client supports it.
5.4 Tips for Diagnosing and Resolving Server Connection Problems
Here are some additional tips for diagnosing and resolving server connection problems:
- Check Microsoft’s Service Status: Visit the Microsoft Service Health page to check for any known outages or issues.
- Test Your Connection: Use online tools to test your internet connection and check for any connectivity problems.
- Contact Support: If you are unable to resolve the issue, contact Microsoft support for assistance.
6. Security Measures for Hotmail Servers
Security is a top priority for Hotmail servers. Microsoft employs a variety of measures to protect against spam, malware, and unauthorized access.
6.1 Spam Filtering and Antivirus Protection
Hotmail uses advanced spam filtering techniques to identify and block unwanted emails. It also incorporates antivirus protection to scan incoming emails for malware and viruses.
6.2 Encryption Protocols (SSL/TLS) for Secure Communication
Encryption protocols like SSL/TLS are used to secure communication between your device and the server. This ensures that your emails and data are protected from eavesdropping.
6.3 Two-Factor Authentication for Enhanced Account Security
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to enter a code from your phone or another device in addition to your password.
6.4 Microsoft’s Commitment to Data Security and Privacy
Microsoft is committed to protecting the security and privacy of its users’ data. The company complies with industry standards and regulations and continuously invests in security technologies and practices.
7. Alternatives to Hosting Your Own Email Server
While understanding Hotmail’s server infrastructure is useful, many businesses opt to use alternative solutions for their email needs.
7.1 Cloud-Based Email Services (e.g., Gmail, Microsoft 365)
Cloud-based email services like Gmail and Microsoft 365 offer several advantages:
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Reliability: High availability and uptime.
- Security: Advanced security features to protect against threats.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces hardware and maintenance costs.
7.2 Managed Email Hosting Providers
Managed email hosting providers offer dedicated email servers and handle all the technical aspects of email management. This can be a good option for businesses that want more control over their email infrastructure but don’t want to manage it themselves.
7.3 Benefits of Outsourcing Email Server Management
Outsourcing email server management can provide several benefits:
- Reduced IT Costs: Lower hardware and maintenance costs.
- Improved Reliability: Higher uptime and availability.
- Enhanced Security: Access to advanced security features and expertise.
- Focus on Core Business: Allows you to focus on your core business activities.
8. Dedicated Servers for Email: A Robust Solution
For businesses requiring maximum control, performance, and security, dedicated servers offer a powerful solution.
8.1 What Is a Dedicated Server?
A dedicated server is a single physical server that is dedicated to a single tenant. This means that you have exclusive access to all the server’s resources, including CPU, memory, and storage.
8.2 Benefits of Using a Dedicated Server for Email Hosting
Using a dedicated server for email hosting offers several benefits:
- Maximum Performance: Dedicated resources ensure optimal performance and responsiveness.
- Enhanced Security: Greater control over security settings and configurations.
- Customization: Ability to customize the server to meet your specific needs.
- Scalability: Ability to scale resources as needed.
8.3 Use Cases for Dedicated Email Servers
Dedicated email servers are ideal for businesses that:
- Handle Large Volumes of Email: Require high throughput and low latency.
- Need Strict Security and Compliance: Must comply with industry regulations and standards.
- Require Custom Configurations: Need to customize the server to meet specific requirements.
9. VPS (Virtual Private Server) for Email: A Balanced Approach
A VPS offers a balance between dedicated servers and shared hosting, providing dedicated resources within a virtualized environment.
9.1 What Is a VPS?
A VPS is a virtual server that runs on a physical server shared with other VPSs. Each VPS is allocated a specific amount of resources, including CPU, memory, and storage, which are dedicated to that VPS.
9.2 Advantages of Using a VPS for Email Hosting
Using a VPS for email hosting offers several advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness: More affordable than a dedicated server.
- Scalability: Easy to scale resources up or down as needed.
- Control: Greater control over server settings and configurations than shared hosting.
- Isolation: Each VPS is isolated from other VPSs, providing better security and performance.
9.3 Scenarios Where a VPS Is a Good Choice for Email
A VPS is a good choice for businesses that:
- Need More Control Than Shared Hosting: Require more control over server settings and configurations.
- Need Scalability: Anticipate growing email volumes.
- Have Limited Budget: Cannot afford a dedicated server.
10. Cloud Servers for Email: Flexibility and Scalability
Cloud servers offer unparalleled flexibility and scalability, making them a popular choice for modern email solutions.
10.1 What Is a Cloud Server?
A cloud server is a virtual server that runs on a cloud computing platform. Cloud servers are highly scalable and can be provisioned and deprovisioned on demand.
10.2 Benefits of Using Cloud Servers for Email Hosting
Using cloud servers for email hosting offers several benefits:
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Flexibility: Ability to choose from a wide range of server configurations and operating systems.
- Reliability: High availability and uptime.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing model.
10.3 Ideal Situations for Cloud-Based Email Servers
Cloud-based email servers are ideal for businesses that:
- Need High Scalability: Anticipate fluctuating email volumes.
- Require High Availability: Cannot afford downtime.
- Want to Reduce IT Costs: Want to take advantage of the pay-as-you-go pricing model.
11. Choosing the Right Server Solution for Your Email Needs
Selecting the right server solution for your email needs depends on several factors, including your budget, technical expertise, and performance requirements.
11.1 Factors to Consider When Selecting a Server
When selecting a server, consider the following factors:
- Performance: How much CPU, memory, and storage do you need?
- Scalability: How easily can you scale resources up or down?
- Security: What security features are included?
- Reliability: What is the uptime guarantee?
- Cost: How much does the server cost?
- Support: What level of support is provided?
11.2 Comparing Dedicated, VPS, and Cloud Servers
Here’s a comparison of dedicated, VPS, and cloud servers:
| Feature | Dedicated Server | VPS | Cloud Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Maximum | Good | Good |
| Scalability | Limited | Easy | Very Easy |
| Security | High | Medium | Medium |
| Cost | High | Medium | Low to Medium |
| Control | Full | Good | Good |
| Ideal For | Large businesses with high performance needs | Businesses needing scalability and control | Businesses needing high scalability and flexibility |
11.3 How Rental-Server.Net Can Help You Find the Perfect Solution
At rental-server.net, we offer a wide range of server solutions to meet your email needs. Our team of experts can help you:
- Assess Your Requirements: Determine your performance, scalability, and security needs.
- Compare Options: Compare different server solutions and providers.
- Find the Best Deal: Find the best price for your chosen server solution.
12. Future Trends in Email Server Technology
The landscape of email server technology is constantly evolving. Here are some future trends to watch:
12.1 AI-Powered Email Security
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to improve email security by detecting and blocking spam, malware, and phishing attacks.
12.2 Serverless Email Architectures
Serverless computing allows you to run email applications without managing servers. This can reduce IT costs and improve scalability.
12.3 Edge Computing for Faster Email Delivery
Edge computing brings email servers closer to users, reducing latency and improving email delivery speeds.
12.4 The Role of Quantum Computing in Email Encryption
Quantum computing has the potential to break current encryption algorithms. New quantum-resistant encryption methods are being developed to protect email data.
13. Maximizing Email Server Performance: Tips and Tricks
Optimizing your email server performance is crucial for ensuring smooth and efficient email operations.
13.1 Regular Server Maintenance and Updates
Regularly maintaining your server and keeping it up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates is essential for optimal performance and security.
13.2 Optimizing Server Configuration Settings
Optimizing your server configuration settings, such as adjusting the number of worker processes and caching settings, can improve performance.
13.3 Monitoring Server Performance and Resource Usage
Monitoring your server performance and resource usage can help you identify and resolve bottlenecks.
13.4 Implementing Caching Mechanisms
Implementing caching mechanisms, such as caching frequently accessed emails and data, can reduce server load and improve response times.
14. The Cost of Running a Hotmail Server: A Breakdown
Understanding the costs associated with running an email server can help you make informed decisions about your email infrastructure.
14.1 Hardware and Software Costs
Hardware costs include the cost of the server, storage devices, and networking equipment. Software costs include the cost of the operating system, email server software, and security software.
14.2 Bandwidth and Data Storage Expenses
Bandwidth expenses depend on the amount of data transferred to and from the server. Data storage expenses depend on the amount of data stored on the server.
14.3 IT Staff and Maintenance Expenses
IT staff expenses include the cost of hiring and training IT professionals to manage the server. Maintenance expenses include the cost of repairing and replacing hardware and software.
14.4 Hidden Costs of Self-Hosting Email Servers
Hidden costs of self-hosting email servers include the cost of downtime, security breaches, and regulatory compliance.
15. Case Studies: Successful Email Server Implementations
Examining real-world examples of successful email server implementations can provide valuable insights and inspiration.
15.1 How Company A Improved Email Reliability with a Dedicated Server
Company A, a large financial institution, improved email reliability by migrating from a shared hosting environment to a dedicated server. This resulted in a 99.99% uptime guarantee and improved customer satisfaction.
15.2 How Company B Reduced IT Costs with a Cloud-Based Email Solution
Company B, a small business, reduced IT costs by migrating from an on-premises email server to a cloud-based email solution. This eliminated the need for hardware maintenance and reduced IT staff expenses.
15.3 How Company C Enhanced Email Security with Two-Factor Authentication
Company C, a healthcare provider, enhanced email security by implementing two-factor authentication. This protected sensitive patient data from unauthorized access.
16. Understanding Email Protocols: SMTP, IMAP, and POP3
A solid grasp of email protocols is crucial for anyone managing or troubleshooting email servers.
16.1 SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Sending Emails
SMTP is the standard protocol for sending emails. It handles the transmission of outgoing messages from your email client to the recipient’s server.
16.2 IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Accessing Emails
IMAP allows you to access your emails from multiple devices while keeping them stored on the server. This ensures that your inbox is always synchronized across all your devices.
16.3 POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3): Downloading Emails
POP3 downloads emails to a single device and typically deletes them from the server. This is a simpler protocol than IMAP but does not offer the same level of synchronization.
16.4 Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Needs
Choose IMAP if you need to access your emails from multiple devices and want to keep them synchronized. Choose POP3 if you only need to access your emails from a single device and don’t need synchronization.
17. Common Email Server Software Options
Selecting the right email server software is crucial for managing your email infrastructure effectively.
17.1 Microsoft Exchange Server
Microsoft Exchange Server is a popular email server software for businesses that use the Microsoft ecosystem. It offers advanced features such as calendar sharing, contact management, and task management.
17.2 Postfix
Postfix is a free and open-source email server software that is known for its security and reliability. It is a popular choice for Linux-based email servers.
17.3 Sendmail
Sendmail is one of the oldest and most widely used email server software. It is known for its flexibility and configurability.
17.4 Choosing the Right Software for Your Business
Choose Microsoft Exchange Server if you need advanced features and integration with the Microsoft ecosystem. Choose Postfix or Sendmail if you need a free and open-source email server software that is secure and reliable.
18. Addressing Email Server Security Vulnerabilities
Protecting your email server from security vulnerabilities is essential for preventing data breaches and protecting your users’ data.
18.1 Identifying Common Vulnerabilities
Common email server vulnerabilities include:
- Spam: Unsolicited emails that can clog up your inbox and spread malware.
- Phishing: Emails that attempt to trick you into revealing your personal information.
- Malware: Emails that contain viruses and other malicious software.
- Brute-Force Attacks: Attempts to guess your password by trying multiple combinations.
18.2 Implementing Security Best Practices
Security best practices for email servers include:
- Using strong passwords: Use passwords that are at least 12 characters long and contain a mix of upper- and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enabling two-factor authentication: Add an extra layer of security by requiring a code from your phone or another device in addition to your password.
- Keeping your software up-to-date: Install the latest security patches and software updates to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Using a firewall: Block unauthorized access to your server.
- Using antivirus software: Scan incoming emails for malware and viruses.
18.3 Staying Updated on the Latest Threats
Staying updated on the latest email server security threats is essential for protecting your server from attack. Subscribe to security newsletters and follow security blogs to stay informed.
19. Regulatory Compliance for Email Servers
Complying with email server regulations is essential for avoiding legal penalties and protecting your users’ data.
19.1 Overview of Key Regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
Key email server regulations include:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Protects the personal data of EU citizens.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Protects the privacy of patient health information.
- CAN-SPAM Act (Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography And Marketing Act): Sets rules for commercial email.
19.2 Implementing Compliance Measures
Compliance measures for email servers include:
- Obtaining consent: Obtain consent from users before collecting their personal data.
- Protecting data: Implement security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access.
- Providing access: Provide users with access to their personal data and allow them to correct or delete it.
- Complying with email marketing regulations: Comply with the CAN-SPAM Act when sending commercial emails.
19.3 Ensuring Ongoing Compliance
Ensuring ongoing compliance with email server regulations requires regular monitoring and updates. Stay informed about changes to regulations and implement necessary changes to your email infrastructure.
20. Getting Started with Rental-Server.Net for Your Email Server Needs
Ready to take the next step in optimizing your email infrastructure? Rental-Server.Net is here to help.
20.1 Exploring Rental-Server.Net’s Email Server Solutions
Discover our wide range of server options, including dedicated servers, VPS, and cloud servers, all tailored to meet your specific email needs.
20.2 Contacting Our Experts for a Consultation
Our experienced team is ready to provide personalized guidance. Contact us today for a consultation to discuss your requirements and find the perfect email server solution.
- Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States
- Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000
- Website: rental-server.net
20.3 Taking Advantage of Special Offers and Promotions
Visit our website to explore our current special offers and promotions on email server solutions. Let Rental-Server.Net help you optimize your email infrastructure for maximum performance, security, and reliability.
By understanding the intricacies of Hotmail servers and the broader landscape of email hosting solutions, you can make informed decisions that benefit your business. Whether you choose a dedicated server, VPS, cloud server, or managed email hosting, Rental-Server.Net is your trusted partner for all your email server needs in the USA.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Hotmail Servers
1. What is the incoming server for Hotmail?
The incoming server for Hotmail (now Outlook.com) is imap-mail.outlook.com. This server uses port 993 with SSL/TLS encryption to securely receive emails.
2. What is the outgoing server for Hotmail?
The outgoing server for Hotmail (Outlook.com) is smtp-mail.outlook.com. It uses port 587 with STARTTLS encryption to securely send emails.
3. How do I find my Hotmail server settings?
You can find your Hotmail server settings on the Microsoft support website by searching for “IMAP, POP, and SMTP settings for Outlook.com.” The support page provides detailed instructions.
4. What should I do if I can’t connect to the Hotmail server?
If you can’t connect to the Hotmail server, double-check your server settings, ensure your internet connection is stable, and verify that your firewall isn’t blocking the connection. Also, check Microsoft’s Service Health page for any known outages.
5. Is it safe to use Hotmail servers?
Yes, it is generally safe to use Hotmail servers. Microsoft employs various security measures, including spam filtering, antivirus protection, and encryption protocols, to protect your data.
6. Can I use a third-party email client with Hotmail?
Yes, you can use third-party email clients like Outlook, Thunderbird, or mobile apps with Hotmail by configuring the correct IMAP and SMTP server settings.
7. What are the benefits of using a dedicated server for email?
Using a dedicated server for email provides maximum performance, enhanced security, and greater control over server settings. This is ideal for businesses handling large email volumes and requiring strict compliance.
8. What is a VPS, and is it suitable for email hosting?
A VPS (Virtual Private Server) is a virtual server that offers a balance between dedicated resources and cost-effectiveness. It is suitable for email hosting if you need more control than shared hosting and anticipate growing email volumes.
9. What is a cloud server, and why use it for email?
A cloud server is a virtual server hosted on a cloud computing platform, offering high scalability, flexibility, and reliability. It is ideal for businesses needing to scale resources on demand and reduce IT costs.
10. How can Rental-Server.Net help with my email server needs?
rental-server.net offers a range of server solutions, including dedicated servers, VPS, and cloud servers, tailored to your email requirements. Our experts provide consultations to help you find the perfect solution and optimize your email infrastructure.

