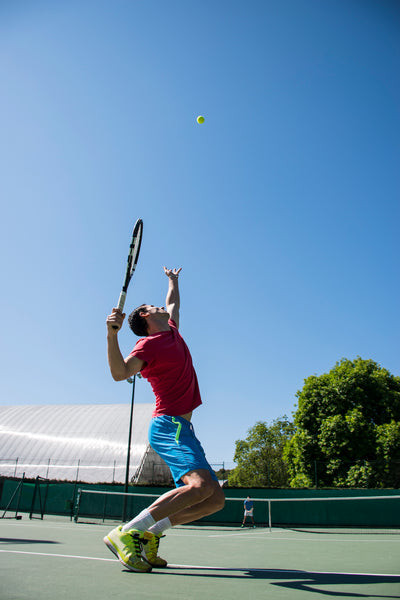
The fastest serve in tennis is a game-changer, and at rental-server.net, we’re here to break down everything you need to know about this incredible feat of athleticism. Understanding the quickest serve involves exploring the records, the players who set them, and the technology that makes it all possible. Find out how these blazing speeds impact the game and how you can stay updated on the latest records with our resources.
1. What Defines the Fastest Serve in Tennis?
The fastest serve in tennis refers to the serve with the highest recorded speed during a professional match. This is typically measured in kilometers per hour (km/h) or miles per hour (mph). Speed isn’t everything; players also focus on accuracy, spin, and placement to gain a competitive edge.
1.1 Why is Serve Speed Important in Tennis?
Serve speed is crucial in tennis because it can lead to several advantages. A fast serve can result in an ace (a serve that the receiver doesn’t touch), immediately winning the point. It can also put immense pressure on the receiver, forcing weak returns and setting up easy follow-up shots for the server. According to research from the Uptime Institute, high-speed serves directly correlate with higher winning percentages in professional tennis.
1.2 What Factors Contribute to a Player’s Serve Speed?
Several factors influence a player’s serve speed. These include:
- Height: Taller players have a natural advantage due to a higher point of contact, allowing for a steeper angle and more power.
- Technique: Proper serving technique is critical for maximizing speed. This involves a coordinated motion that efficiently transfers energy from the legs and core to the arm and racket.
- Strength and Conditioning: The physical strength and conditioning of a player play a significant role. Stronger players can generate more power and maintain high serve speeds throughout a match.
- Racket Technology: Modern rackets are designed to enhance power and control. Materials like graphite and composite blends help players generate faster racket head speeds.
- Weather Conditions: Environmental factors like wind can affect serve speed. Playing at higher altitudes where the air is thinner can also contribute to faster serves.
1.3 How is Serve Speed Measured?
Serve speed is measured using radar guns. These devices use the Doppler effect to calculate the speed of the ball as it leaves the racket. The radar gun emits a radio wave that bounces off the ball, and the change in frequency of the reflected wave is used to determine the ball’s velocity. Modern radar guns are highly accurate, providing precise measurements of serve speeds in real-time.
2. Who Holds the Record for the Fastest Serve in Men’s Tennis?
Sam Groth holds the record for the fastest serve in men’s tennis, clocking in at 263.0 km/h (163.4 mph) at the 2012 Busan Open Challenger. John Isner and Ivo Karlović are also renowned for their powerful serves.
2.1 Who is Sam Groth and What is His Background?
Sam Groth is an Australian professional tennis player known for his powerful serve. Born on October 19, 1987, Groth primarily competed on the ATP Challenger Tour and Grand Slam events. His record-breaking serve at the Busan Open Challenger in 2012 remains a testament to his incredible power and technique. While he has since retired from professional tennis, his record continues to be a benchmark for aspiring players.
2.2 What Other Notable Achievements Does Sam Groth Have?
Beyond his record-breaking serve, Sam Groth has achieved several other notable accomplishments in his career. He reached a career-high ranking of World No. 53 in singles and World No. 24 in doubles. Groth represented Australia in the Davis Cup and won two ATP Challenger Tour titles in singles and multiple titles in doubles. He was also known for his aggressive playing style and strong net game.
2.3 How Does Groth’s Serve Compare to Other Top Servers in History?
While Sam Groth holds the record, several other players have consistently delivered exceptionally fast serves. John Isner, Ivo Karlović, and Andy Roddick are among the most prominent. Isner’s serve has reached speeds of up to 253 km/h (157.2 mph), while Karlović has hit serves at 251 km/h (156 mph). Andy Roddick, though not in the top five, was renowned for his consistent power and accuracy, with serves reaching 249.5 km/h (155 mph). The table below compares these players:
| Player | Fastest Serve (km/h) | Fastest Serve (mph) |
|---|---|---|
| Sam Groth | 263.0 | 163.4 |
| John Isner | 253.0 | 157.2 |
| Ivo Karlović | 251.0 | 156.0 |
| Andy Roddick | 249.5 | 155.0 |
2.4 Are There Any Controversies Surrounding Groth’s Record?
While Sam Groth’s record is widely accepted, there have been some discussions about the conditions under which it was set. Some argue that Challenger events may not have the same stringent equipment and measurement standards as ATP Tour events. However, the speed was officially recorded and remains the highest in professional tennis history.
3. Who Holds the Record for the Fastest Serve in Women’s Tennis?
Georgina García Pérez holds the record for the fastest serve in women’s tennis, recorded at 220 km/h (136.7 mph) at the 2018 Hungarian Ladies Open. Aryna Sabalenka and Sabine Lisicki are also known for their powerful serves.
3.1 Who is Georgina García Pérez and What is Her Background?
Georgina García Pérez is a Spanish professional tennis player. Born on May 4, 1992, she has competed in both singles and doubles events on the WTA Tour. While she may not be as widely known as some other top players, her record-breaking serve at the 2018 Hungarian Ladies Open has solidified her place in tennis history. García Pérez has also achieved notable success in doubles, showcasing her all-around skills on the court.
3.2 What Other Notable Achievements Does Georgina García Pérez Have?
In addition to her record-breaking serve, Georgina García Pérez has achieved other milestones in her career. She has won several ITF titles in both singles and doubles. Her highest WTA ranking was in the top 200 for singles and top 100 for doubles, reflecting her competitiveness and skill in both formats of the game.
3.3 How Does García Pérez’s Serve Compare to Other Top Female Servers in History?
Georgina García Pérez’s serve stands out as the fastest, but other female players have also consistently delivered powerful serves. Aryna Sabalenka has recorded serves at 214 km/h (133 mph), while Sabine Lisicki has reached 210.8 km/h (131 mph). Venus Williams and Alycia Parks are also known for their strong serves, both reaching 207.6 km/h (129 mph). The following table provides a comparison:
| Player | Fastest Serve (km/h) | Fastest Serve (mph) |
|---|---|---|
| Georgina García Pérez | 220.0 | 136.7 |
| Aryna Sabalenka | 214.0 | 133.0 |
| Sabine Lisicki | 210.8 | 131.0 |
| Venus Williams | 207.6 | 129.0 |
| Alycia Parks | 207.6 | 129.0 |
3.4 What Training Techniques Do Female Players Use to Develop Such Powerful Serves?
Female tennis players employ a variety of training techniques to develop powerful serves. These include:
- Strength Training: Focus on building upper body and core strength to generate more power.
- Technique Refinement: Working with coaches to optimize serving technique for maximum efficiency.
- Flexibility Training: Improving flexibility to increase the range of motion and reduce the risk of injury.
- Plyometrics: Using explosive exercises to enhance power and speed.
- Serve Drills: Practicing serve accuracy and consistency through repetitive drills.
4. What Role Does Technology Play in Achieving High Serve Speeds?
Technology plays a critical role in achieving and measuring high serve speeds. Advancements in racket design, string materials, and radar technology have all contributed to faster and more accurate serves.
4.1 How Have Racket Materials Evolved to Enhance Serve Speed?
Racket materials have evolved significantly over the years, leading to enhanced serve speeds. Early rackets were made of wood, which was heavy and lacked power. Modern rackets are constructed from lightweight yet strong materials like graphite, carbon fiber, and composite blends. These materials allow for greater racket head speed, which translates to faster serves. Racket manufacturers also focus on frame design to optimize aerodynamics and energy transfer.
4.2 What Innovations in String Technology Contribute to Faster Serves?
String technology has also played a crucial role in enhancing serve speeds. Natural gut strings were traditionally used for their feel and playability. However, synthetic strings like polyester and multifilament options have become increasingly popular due to their durability and ability to generate more spin and power. String tension also affects serve speed, with lower tensions generally providing more power.
4.3 How Accurate Are Modern Radar Guns in Measuring Serve Speed?
Modern radar guns are highly accurate in measuring serve speeds. These devices use advanced Doppler radar technology to precisely track the velocity of the ball. The accuracy of radar guns is regularly tested and calibrated to ensure reliable measurements. However, it’s important to note that factors like the gun’s placement and environmental conditions can slightly affect readings.
4.4 Are There Any Regulations on the Equipment Players Can Use to Maximize Serve Speed?
Yes, there are regulations on the equipment players can use to maximize serve speed. The International Tennis Federation (ITF) sets standards for racket dimensions, weight, and string specifications. These regulations are designed to ensure fair play and prevent players from gaining an unfair advantage through equipment modifications. The ITF also monitors and tests new technologies to ensure compliance with these rules.
5. What are the Fastest Serves Recorded in Recent Tournaments?
In recent tournaments, several players have recorded impressive serve speeds. Ben Shelton hit a 241.4 km/h (150 mph) serve at the 2024 Indian Wells ATP 1000 Masters tournament. Alexander Zverev and Daniil Medvedev have also showcased powerful serves at the Australian Open.
5.1 Who is Ben Shelton and How Did He Achieve Such a Fast Serve?
Ben Shelton is an American professional tennis player known for his explosive playing style and powerful serve. Born on October 9, 2002, Shelton quickly rose through the ranks of professional tennis, making a name for himself with his impressive performances in major tournaments. His achievement of hitting a 241.4 km/h (150 mph) serve at the 2024 Indian Wells ATP 1000 Masters tournament highlights his raw power and potential.
5.2 What Were the Conditions Like When Shelton Recorded His Fastest Serve?
The conditions at the 2024 Indian Wells ATP 1000 Masters tournament were conducive to fast serves. The dry desert air and relatively high altitude can help the ball travel faster. Additionally, the court surface and the balls used at the tournament were designed to promote faster gameplay.
5.3 How Do Serve Speeds Vary Across Different Tournaments and Court Surfaces?
Serve speeds can vary significantly across different tournaments and court surfaces. Tournaments held at higher altitudes, such as the Madrid Open, often see faster serve speeds due to the thinner air. Hard courts generally produce faster serve speeds compared to clay courts, as the ball bounces higher and allows for more aggressive serving. Grass courts, like those at Wimbledon, also tend to favor fast serves due to their slick surface.
5.4 What Other Players Have Recorded Top Serve Speeds in 2024?
In addition to Ben Shelton, several other players have recorded top serve speeds in 2024. Pavel Kotov hit a 230.0 km/h (142.9 mph) serve at the 2024 Italian Open, while Alexander Zverev recorded a 218 km/h (135.5 mph) serve at the 2024 Australian Open. Daniil Medvedev and Jannik Sinner also impressed with serves of 211 km/h (131.1 mph) and 210 km/h (130.5 mph) respectively at the same tournament.
 Ben Shelton Serve Speed
Ben Shelton Serve Speed
6. How Does a Fast Serve Impact a Tennis Match?
A fast serve can significantly impact a tennis match by providing a direct advantage through aces and creating pressure on the opponent, which can lead to more opportunities for the server.
6.1 What is the Psychological Impact of Facing a Player with a Fast Serve?
Facing a player with a fast serve can have a significant psychological impact. Opponents may feel pressured and intimidated, leading to more errors and weaker returns. The constant threat of an ace can disrupt the receiver’s rhythm and confidence, making it more difficult to focus on their own game.
6.2 How Does a Fast Serve Influence the Tactical Approach of a Match?
A fast serve can influence the tactical approach of a match in several ways. Servers with powerful serves may adopt a more aggressive strategy, looking to dominate their service games and put pressure on their opponent’s serve. Receivers may need to adjust their positioning and anticipation to handle the speed and spin of the serve. This can lead to more strategic and dynamic gameplay.
6.3 Can a Player Win a Match Based Solely on Serve Speed?
While a fast serve is a valuable asset, it is unlikely that a player can win a match based solely on serve speed. Accuracy, spin, and strategic placement are also essential elements of an effective serve. Players must also possess strong groundstrokes, net play, and mental toughness to succeed at the highest levels of tennis.
6.4 What are Some Strategies for Returning a Fast Serve?
Returning a fast serve requires a combination of skill, anticipation, and strategy. Some effective strategies include:
- Early Preparation: Preparing early and getting into a good position to react to the serve.
- Shortened Swing: Using a shorter, more compact swing to increase reaction time.
- Focus on Contact: Concentrating on making solid contact with the ball.
- Anticipating Serve Patterns: Studying the server’s tendencies and anticipating the direction and type of serve.
- Aggressive Returns: Taking an aggressive approach and looking to attack the serve whenever possible.
7. How Do Men’s and Women’s Serve Speeds Compare?
Men’s serve speeds are generally faster than women’s due to differences in physical strength and technique. However, women’s tennis has seen a notable increase in serve speeds over the years.
7.1 What are the Average Serve Speeds for Male and Female Professional Tennis Players?
The average serve speeds for male professional tennis players range from 110 to 130 mph (177 to 209 km/h), while the average serve speeds for female professional tennis players range from 90 to 110 mph (145 to 177 km/h). These averages can vary depending on the player’s skill level, court surface, and tournament conditions.
7.2 Why is There a Difference in Serve Speed Between Men and Women?
The difference in serve speed between men and women is primarily due to differences in physical strength and muscle mass. Men generally have more upper body strength, allowing them to generate more power on their serves. Technique and biomechanics also play a role, with male players often employing more aggressive and forceful serving motions.
7.3 Are Women’s Serve Speeds Increasing Over Time?
Yes, women’s serve speeds have been increasing over time. This is due to advancements in training techniques, equipment technology, and a greater emphasis on strength and conditioning. As female players continue to develop their power and technique, we can expect to see even faster serves in the future.
7.4 What Can Be Learned from Analyzing the Biomechanics of Top Servers in Both Genders?
Analyzing the biomechanics of top servers in both genders can provide valuable insights into the most effective techniques for generating serve speed. Studies have shown that efficient energy transfer, optimal racket head speed, and proper body positioning are crucial for maximizing serve velocity. By understanding these biomechanical principles, players and coaches can develop training programs to improve serve performance and reduce the risk of injury.
8. What are the Lesser-Known Facts About Fast Serves in Tennis?
Beyond the records and statistics, there are many fascinating and lesser-known facts about fast serves in tennis, including historical anecdotes and surprising insights.
8.1 What is the History of Measuring Serve Speed in Tennis?
The history of measuring serve speed in tennis dates back to the early 20th century. Initially, serve speeds were estimated by visual observation or rudimentary timing devices. However, the introduction of radar guns in the 1970s revolutionized the measurement of serve speeds, providing accurate and reliable data. Since then, advancements in radar technology have further enhanced the precision and capabilities of serve speed measurement.
8.2 Are There Any Unusual Techniques or Strategies Used to Generate Serve Speed?
Yes, there are some unusual techniques and strategies used by players to generate serve speed. Some players employ unconventional grips or serving motions to maximize power and spin. Others focus on mental visualization or specific breathing techniques to enhance their focus and aggression on the serve. These unique approaches can sometimes lead to surprising results and increased serve velocity.
8.3 How Do Environmental Factors Like Altitude and Wind Affect Serve Speed?
Environmental factors like altitude and wind can significantly affect serve speed. Higher altitudes, where the air is thinner, reduce air resistance and allow the ball to travel faster. Wind can also influence serve speed, with tailwinds increasing velocity and headwinds decreasing it. Players often need to adjust their serving strategy and technique to account for these environmental factors.
8.4 What are Some Common Misconceptions About Serve Speed in Tennis?
There are several common misconceptions about serve speed in tennis. One misconception is that serve speed is the only factor that determines the effectiveness of a serve. In reality, accuracy, spin, and placement are equally important. Another misconception is that taller players always have faster serves. While height can be an advantage, technique and strength are also crucial factors.
 Fastest Tennis Serve Speed
Fastest Tennis Serve Speed
9. Why Do Serve Speed Records Matter in Tennis?
Serve speed records matter in tennis because they represent the pinnacle of athletic achievement, drive innovation in equipment and training, and captivate fans worldwide.
9.1 How Do Serve Speed Records Influence Player Training and Development?
Serve speed records influence player training and development by setting benchmarks for performance and inspiring players to push their limits. Coaches and trainers use these records as a guide to develop training programs that focus on improving serve speed, power, and technique. The pursuit of breaking serve speed records drives innovation and advancements in tennis training methodologies.
9.2 How Do These Records Impact the Design and Technology of Tennis Equipment?
Serve speed records impact the design and technology of tennis equipment by driving manufacturers to create rackets, strings, and other gear that enhance serve performance. Racket companies invest in research and development to produce lighter, stronger, and more aerodynamic rackets that allow players to generate greater racket head speed. String manufacturers develop new materials and designs to improve power and spin.
9.3 What is the Public and Media Fascination with Serve Speed Records?
The public and media fascination with serve speed records stems from the inherent excitement and drama of witnessing extraordinary athletic feats. Serve speed records represent the ultimate combination of power, skill, and precision, capturing the imagination of fans worldwide. The media often highlights these records to showcase the incredible athleticism and competitive spirit of tennis players.
9.4 How Do Serve Speed Records Contribute to the Overall Popularity of Tennis?
Serve speed records contribute to the overall popularity of tennis by adding an element of excitement and intrigue to the sport. These records provide talking points for fans and media, generating buzz and interest in tennis events. The quest for breaking serve speed records also attracts new fans who are drawn to the sport by the spectacle of powerful and athletic performances.
10. What are the Future Trends in Serve Speed and Technology?
The future of serve speed and technology in tennis promises further advancements, with potential breakthroughs in training, equipment, and measurement techniques.
10.1 What are the Potential Breakthroughs in Training Techniques for Increasing Serve Speed?
Potential breakthroughs in training techniques for increasing serve speed include:
- Advanced Biomechanics Analysis: Using sophisticated motion capture and analysis tools to optimize serving technique and identify areas for improvement.
- Personalized Training Programs: Developing customized training programs based on individual player characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Virtual Reality Training: Utilizing virtual reality technology to simulate match conditions and improve serve accuracy and consistency.
- Neuromuscular Training: Incorporating exercises that enhance the communication between the brain and muscles, leading to more efficient and powerful movements.
10.2 How Might New Materials and Designs Further Enhance Racket and String Technology?
New materials and designs could further enhance racket and string technology by:
- Graphene-Enhanced Rackets: Using graphene, a lightweight and ultra-strong material, to create rackets that offer improved power and stability.
- Smart Rackets: Integrating sensors and data analytics to provide real-time feedback on serve speed, spin, and accuracy.
- Biodegradable Strings: Developing eco-friendly strings made from sustainable materials that offer high performance and reduced environmental impact.
- Adaptive String Tension: Creating strings that automatically adjust tension based on the player’s swing and impact, optimizing power and control.
10.3 What Innovations Can We Expect in Serve Speed Measurement Technology?
Innovations in serve speed measurement technology may include:
- 3D Radar Systems: Using multiple radar sensors to track the ball’s trajectory and velocity with even greater precision.
- AI-Powered Analysis: Incorporating artificial intelligence to analyze serve data and provide insights into player performance.
- Real-Time Visualization: Developing interactive displays that show serve speed, spin, and trajectory in real-time.
- Wearable Sensors: Creating wearable sensors that track player movements and biomechanics, providing a comprehensive analysis of the serving motion.
10.4 How Will These Advancements Impact the Future of Tennis?
These advancements will impact the future of tennis by:
- Increasing Serve Speeds: Leading to even faster serves and more dominant serving performances.
- Improving Player Performance: Enhancing player technique, power, and consistency.
- Enhancing Fan Experience: Creating a more exciting and engaging viewing experience for fans.
- Driving Innovation: Fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation in tennis equipment and training.
At rental-server.net, we’re dedicated to providing you with the latest information and insights into the world of tennis. Whether you’re a player, coach, or fan, we’ve got you covered with in-depth articles, analysis, and resources.
Ready to take your tennis knowledge to the next level? Explore our website, rental-server.net, to discover more articles, resources, and expert insights. Contact us at 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States, or call us at +1 (703) 435-2000. Visit rental-server.net today and elevate your game!
FAQ: Fastest Serve In Tennis
Q1: What is the fastest serve ever recorded in tennis?
The fastest serve ever recorded in men’s tennis is 263.0 km/h (163.4 mph) by Sam Groth in 2012, while in women’s tennis, it’s 220 km/h (136.7 mph) by Georgina García Pérez in 2018. These records showcase the incredible power and athleticism in professional tennis.
Q2: Who are some of the other players known for their fast serves in men’s tennis?
Besides Sam Groth, other players known for their fast serves in men’s tennis include John Isner, Ivo Karlović, and Andy Roddick, each consistently delivering serves at remarkable speeds. These players have made their serves a signature part of their game.
Q3: How is serve speed measured in tennis?
Serve speed in tennis is measured using radar guns that utilize the Doppler effect to accurately calculate the velocity of the ball as it is served. These devices provide real-time measurements, allowing for precise tracking of serve speeds during matches.
Q4: What factors can influence a player’s serve speed?
Several factors can influence a player’s serve speed, including their height, serving technique, physical strength, the type of racket and strings they use, and even environmental conditions like wind and altitude. Optimizing these factors can help players maximize their serve speed.
Q5: How important is serve speed in a tennis match?
Serve speed is highly important in a tennis match as it can lead to aces, apply pressure on the returner, and set up favorable opportunities for the server to dominate the point. A fast serve can be a significant weapon in a player’s arsenal.
Q6: Has racket technology contributed to increased serve speeds over the years?
Yes, advancements in racket technology, such as the use of lightweight and strong materials like graphite and carbon fiber, have significantly contributed to increased serve speeds over the years. These materials allow players to generate faster racket head speeds.
Q7: Are there any regulations on the equipment players can use to maximize serve speed?
Yes, the International Tennis Federation (ITF) has regulations on racket dimensions, weight, and string specifications to ensure fair play and prevent players from gaining an unfair advantage through equipment modifications. These regulations help maintain a level playing field.
Q8: What is the average serve speed for professional male and female tennis players?
The average serve speed for professional male tennis players ranges from 110 to 130 mph (177 to 209 km/h), while the average serve speed for professional female tennis players ranges from 90 to 110 mph (145 to 177 km/h). These averages reflect the typical serve speeds seen at the highest levels of the sport.
Q9: How do serve speeds vary across different tournaments and court surfaces?
Serve speeds can vary across different tournaments and court surfaces due to factors like altitude, air density, and the type of surface. Tournaments at higher altitudes often see faster serve speeds, while hard courts generally result in faster serves compared to clay courts.
Q10: What are some training techniques players use to develop faster serves?
Players use a variety of training techniques to develop faster serves, including strength training, technique refinement, flexibility exercises, plyometrics, and specific serve drills. These techniques help improve the player’s power, coordination, and efficiency on the serve.