Are you looking to understand what a port is in a server? At rental-server.net, we provide straightforward explanations and solutions for server-related topics. This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about server ports, their types, and how they function, helping you choose the right server solutions for your needs. Explore rental-server.net today for expert advice and the best server rental options.
1. Understanding Server Ports: The Basics
What is a port in a server? A port is a virtual point where network connections start and end, facilitating communication between different applications and services. It acts like a doorway, directing network traffic to the correct process or application running on a server.
Think of a server’s IP address as a building’s street address. The port number, then, is like an apartment number within that building. Each application or service uses a specific port to send and receive data. This ensures that when data arrives at the server, it’s routed to the correct application. For instance, web traffic typically uses port 80 (HTTP) or port 443 (HTTPS).
2. Why Are Server Ports Important?
Why are server ports important? Server ports are essential for enabling multiple applications and services to run simultaneously on a single server without interfering with each other.
Without ports, all network traffic would arrive at a single point, making it impossible to differentiate between different types of data. Ports allow servers to handle multiple requests concurrently, improving efficiency and performance. They also play a critical role in security by enabling firewalls to control which types of traffic are allowed to enter or exit the server. According to a study by the SANS Institute, proper port management is crucial for maintaining a secure network environment.
3. Types of Port Numbers: A Detailed Overview
What are the different types of port numbers and their uses? Port numbers are categorized into three main ranges: Well-Known Ports, Registered Ports, and Dynamic/Private Ports. Each type serves a specific purpose in network communication.
3.1. Well-Known Ports (0 to 1023)
What are Well-Known Ports? Well-Known Ports, ranging from 0 to 1023, are reserved for common services and applications. These ports are controlled by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and are typically used by system-level processes.
Common examples include:
- Port 20 and 21: File Transfer Protocol (FTP) for data transfer.
- Port 22: Secure Shell (SSH) for secure remote access.
- Port 25: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) for email sending.
- Port 53: Domain Name System (DNS) for domain name resolution.
- Port 80: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) for standard web traffic.
- Port 110: Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) for email retrieval.
- Port 143: Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) for email management.
- Port 443: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) for secure web traffic.
These ports are critical for standard internet operations. IANA maintains a comprehensive list of these ports to ensure consistent usage across different systems.
3.2. Registered Ports (1024 to 49151)
What are Registered Ports? Registered Ports, ranging from 1024 to 49151, are assigned to specific applications and services by IANA. Software vendors and developers can register their applications to use these ports.
These ports are often used for proprietary applications and services. While they are not as strictly controlled as Well-Known Ports, registration helps prevent conflicts and ensures that services can operate reliably.
3.3. Dynamic/Private Ports (49152 to 65535)
What are Dynamic/Private Ports? Dynamic or Private Ports, ranging from 49152 to 65535, are used for temporary or private connections. These ports are not assigned by IANA and can be used by any application without registration.
They are typically used for client-side connections when a client initiates a connection to a server. Once the connection is closed, the port becomes available for reuse. This range provides a large pool of ports that can be dynamically allocated, ensuring that applications have the resources they need for communication.
4. TCP vs. UDP: Understanding Port Protocols
What are TCP and UDP? Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are two fundamental protocols that use port numbers to manage network traffic. They offer different approaches to data transmission, each with its own advantages and use cases.
4.1. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
What is TCP? TCP is a connection-oriented protocol that provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of data. It establishes a connection between the sender and receiver before transmitting data, ensuring that all packets arrive in the correct order and without errors.
TCP is commonly used for applications that require high reliability, such as:
- Web browsing (HTTP/HTTPS)
- Email (SMTP, IMAP, POP3)
- File transfer (FTP)
- Secure Shell (SSH)
The reliability of TCP comes at the cost of increased overhead, as it requires additional steps for connection establishment and error checking.
4.2. User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
What is UDP? UDP is a connectionless protocol that provides a faster, but less reliable, method of data transmission. It does not establish a connection before sending data and does not guarantee that packets will arrive in order or without errors.
UDP is commonly used for applications that require low latency and can tolerate some data loss, such as:
- Online gaming
- Video streaming
- Voice over IP (VoIP)
- Domain Name System (DNS)
The lack of overhead in UDP makes it ideal for real-time applications where speed is more important than reliability.
5. How Do Ports Work? A Practical Example
How do ports work in practice? Imagine you’re browsing a website on your computer. When you type a URL into your browser, your computer sends a request to the web server hosting the website. This request includes the server’s IP address and the port number for HTTP (port 80) or HTTPS (port 443).
The server receives the request and uses the port number to direct the traffic to the web server application. The web server processes the request and sends the website data back to your computer, using a dynamic port on your computer as the source port and port 80 or 443 on the server as the destination port. Your computer then displays the website in your browser.
This process illustrates how ports enable communication between different applications and services over a network.
6. Common Port Numbers and Their Uses
What are some commonly used ports? Here’s a table of common port numbers and their associated networking protocols:
| Port Number | Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 20, 21 | FTP | File Transfer Protocol for data transfer |
| 22 | SSH | Secure Shell for secure remote access |
| 25 | SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol for email sending |
| 53 | DNS | Domain Name System for domain name resolution |
| 80 | HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol for standard web traffic |
| 110 | POP3 | Post Office Protocol version 3 for email retrieval |
| 143 | IMAP | Internet Message Access Protocol for email management |
| 443 | HTTPS | Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure for secure web traffic |
| 3389 | RDP | Remote Desktop Protocol for remote access to Windows systems |
| 8080 | HTTP Alternate | Alternative HTTP port, often used for testing or development |
Understanding these common port numbers can help you troubleshoot network issues and configure your server settings effectively.
7. Port Scanning: Understanding the Risks
What is port scanning? Port scanning is a technique used to identify open ports on a server or network. It involves sending requests to different ports to see which ones respond, indicating that a service is listening on that port.
While port scanning can be used for legitimate purposes, such as network security assessments, it is also a common method used by attackers to find potential vulnerabilities. By identifying open ports, attackers can determine which services are running on a server and look for known exploits. According to a report by Verizon, port scanning is often the first step in a cyberattack.
8. How Do Firewalls Protect Ports?
How do firewalls protect ports? Firewalls act as a barrier between a network and the outside world, controlling which traffic is allowed to enter or exit the network. They use rules to filter traffic based on IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols.
Firewalls can be configured to block specific ports, preventing unauthorized access to services running on those ports. For example, a firewall might be configured to block port 22 (SSH) from all IP addresses except for a specific range used by administrators. This prevents attackers from gaining remote access to the server via SSH.
Firewalls are an essential component of network security and play a critical role in protecting servers from attack. They should be properly configured and regularly updated to ensure that they provide effective protection against the latest threats.
9. Troubleshooting Common Port Issues
What are some common port issues and how can they be resolved? Port conflicts and blocked ports are common issues that can prevent applications and services from functioning correctly. Here are some troubleshooting steps:
9.1. Port Conflicts
What are port conflicts? Port conflicts occur when two or more applications try to use the same port number. This can prevent one or both applications from starting or functioning correctly.
Troubleshooting:
- Identify the conflicting applications: Use command-line tools like
netstat(Windows) orlsof(Linux) to identify which applications are using the conflicting port. - Reconfigure the applications: Change the port number used by one of the applications to a different, unused port.
- Restart the applications: Restart the applications to apply the changes.
9.2. Blocked Ports
What are blocked ports? Blocked ports occur when a firewall or other network device prevents traffic from reaching a specific port. This can prevent applications from communicating with each other.
Troubleshooting:
- Check the firewall rules: Review the firewall rules to ensure that the necessary ports are open for the applications to communicate.
- Test the port connectivity: Use tools like
telnetornc(netcat) to test whether a port is reachable from another device on the network. - Contact your network administrator: If you are unable to resolve the issue, contact your network administrator for assistance.
10. Optimizing Port Usage for Server Performance
How can port usage be optimized for server performance? Efficient port management can significantly improve server performance and security. Here are some best practices:
10.1. Minimize Open Ports
Why should open ports be minimized? Only open the ports that are necessary for the services running on the server. Closing unnecessary ports reduces the attack surface and minimizes the risk of vulnerabilities.
10.2. Use Strong Firewall Rules
Why should strong firewall rules be used? Implement strong firewall rules to control which traffic is allowed to enter or exit the server. Use specific IP address ranges and port numbers to restrict access to authorized users and devices.
10.3. Monitor Port Usage
Why should port usage be monitored? Regularly monitor port usage to identify any unusual activity or potential security threats. Use network monitoring tools to track which ports are being used and by whom.
10.4. Keep Software Updated
Why should software be kept updated? Keep all software and applications updated to the latest versions. Software updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities in port handling.
11. The Role of Ports in Cloud Computing
What role do ports play in cloud computing? In cloud computing environments, ports play a critical role in enabling communication between virtual machines, containers, and other cloud services. Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud use ports to manage network traffic and ensure that services can communicate securely and efficiently.
11.1. Security Groups
What are security groups? Cloud providers use security groups to control access to virtual machines and other cloud resources. Security groups act as virtual firewalls, allowing you to specify which ports are open and which IP addresses are allowed to access them.
11.2. Load Balancers
What are load balancers? Load balancers distribute network traffic across multiple virtual machines or containers. They use port numbers to direct traffic to the correct service, ensuring that requests are handled efficiently and that no single server is overloaded.
11.3. Containerization
What is containerization? Containerization technologies like Docker use ports to map services running inside containers to ports on the host system. This allows you to run multiple containers on a single host without port conflicts.
12. Server Ports and Network Security Best Practices
What are the network security best practices related to server ports? Securing server ports is paramount to maintaining a robust and resilient network infrastructure. Below are several best practices to fortify your server’s defenses:
12.1. Regularly Audit Open Ports
Why regularly audit open ports? Regularly auditing open ports is essential to identify any unnecessary or vulnerable ports that could be exploited by attackers. Use port scanning tools to assess your server’s exposure and promptly close any ports that are not required. This proactive approach minimizes the attack surface and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
12.2. Implement Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Why implement IDS and IPS? Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are crucial for monitoring network traffic and detecting malicious activities targeting specific ports. These systems analyze traffic patterns, identify anomalies, and automatically block or alert administrators to potential threats. According to a study by Cisco, organizations that implement IDS/IPS solutions experience a significant reduction in successful cyberattacks.
12.3. Educate Employees on Port Security Risks
Why educate employees on port security risks? Human error remains a significant factor in many security breaches. Educating employees about the risks associated with open ports, phishing attacks, and malware can significantly reduce the likelihood of security incidents. Training should cover topics such as recognizing suspicious emails, avoiding untrusted websites, and adhering to secure password practices.
13. The Future of Server Ports: Emerging Trends
What are the emerging trends related to server ports? As technology evolves, so do the ways in which server ports are used and managed. Here are some emerging trends to watch:
13.1. Dynamic Port Allocation
What is dynamic port allocation? Dynamic port allocation is becoming more common as applications increasingly rely on cloud-based services and containerization. This approach allows ports to be assigned dynamically as needed, improving resource utilization and scalability.
13.2. Portless Services
What are portless services? Portless services are emerging as a way to simplify network configuration and reduce the attack surface. These services use alternative methods of communication, such as service meshes, to eliminate the need for traditional port-based connections.
13.3. AI-Powered Port Management
What is AI-powered port management? Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to automate port management tasks, such as identifying and closing unused ports, detecting anomalies, and predicting potential security threats. AI-powered port management can help organizations improve their security posture and reduce the operational overhead of managing server ports.
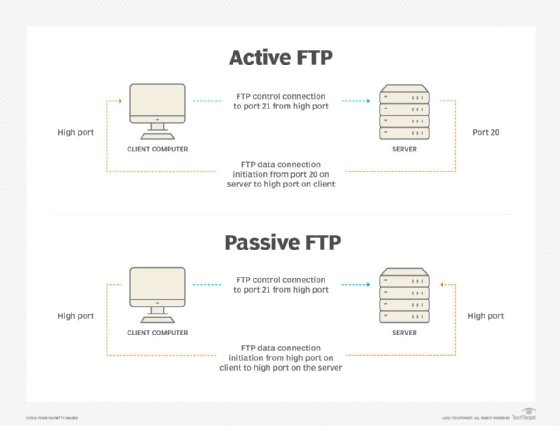 Active FTP and passive FTP diagram
Active FTP and passive FTP diagram
14. Choosing the Right Server Rental with Optimal Port Configuration
How to choose the right server rental with optimal port configuration? Selecting the right server rental involves careful consideration of port configuration to ensure optimal performance, security, and scalability. At rental-server.net, we understand these needs and offer a range of server solutions tailored to meet your specific requirements.
14.1. Understanding Your Requirements
What should be considered when understanding requirements? Before choosing a server rental, assess your application’s port requirements. Determine the number of ports needed, the types of traffic (TCP or UDP), and any specific security requirements.
14.2. Evaluating Server Providers
What should be considered when evaluating server providers? Evaluate server providers based on their port management capabilities. Look for providers that offer robust firewall options, customizable security groups, and tools for monitoring port usage.
14.3. Considering Scalability
Why should scalability be considered? Consider the scalability of the server rental. Ensure that the provider can accommodate your future port needs as your application grows.
At rental-server.net, we offer a variety of server rental options with flexible port configurations to meet your evolving needs. Our expert team can help you choose the right server solution and configure it for optimal performance and security. Contact us today to learn more about our services. Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States. Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000. Website: rental-server.net.
15. Server Port FAQs
15.1. What is the port number for localhost?
What is the port number for localhost? Localhost typically uses the IP address 127.0.0.1. Port 80 is the standard port for HTTP.
15.2. What is port number 8080 used for?
What is port number 8080 used for? Port 8080 is often used for web servers and can be added to the end of the domain name to drive traffic to the web server.
15.3. What is port number 3360 used for?
What is port number 3360 used for? Port 3360 is used by TCP/IP networks, which require handshaking to establish end-to-end communication.
15.4. How do I find my IP address and port number?
How do I find my IP address and port number? To find your public IP address, search “what is my IP?” on a search engine like Google. Identifying a port number depends on your operating system and running programs.
15.5. What is a proxy server address and port number?
What is a proxy server address and port number? A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a client device and the remote server, using its own IP address. The port number 8080 is commonly used for web servers, proxy, and caching.
15.6. What is the port number for Gmail?
What is the port number for Gmail? Gmail uses both Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) and SMTP. The IMAP port is 993, and the SMTP port is 25.
15.7. What is the difference between a port and a socket?
What is the difference between a port and a socket? A port is a virtual point for network connections, while a socket is an endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs running on the network.
15.8. Why are some ports considered “well-known”?
Why are some ports considered “well-known”? Well-known ports are reserved for essential services like HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443), ensuring standardized communication.
15.9. Can I change the default port for a service?
Can I change the default port for a service? Yes, you can change the default port for a service, but it requires careful configuration and may affect compatibility with other systems.
15.10. How does port forwarding work?
How does port forwarding work? Port forwarding redirects network traffic from one port to another, allowing external devices to access services on a private network.
By understanding these FAQs, you can better manage your server ports and ensure optimal performance and security.
Conclusion: Mastering Server Ports for Optimal Performance
Understanding what is a port in a server is crucial for anyone managing or utilizing server technology. From enabling efficient communication between applications to securing your network against potential threats, ports play a vital role in server functionality. At rental-server.net, we provide the resources and expertise you need to navigate the complexities of server management.
Whether you’re a system administrator, a web developer, or a business owner, understanding server ports will empower you to make informed decisions and optimize your server infrastructure. Explore our website, rental-server.net, to discover a wide range of server rental options and expert guidance.
Ready to take your server management to the next level? Visit rental-server.net today to explore our services and find the perfect server solution for your needs. Let us help you optimize your server performance and security. Contact us today to learn more about our services. Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States. Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000. Website: rental-server.net.

