What Is My Email Server? Your email server is the backbone of your email communication, handling the sending, receiving, and storage of your electronic messages. Rental-server.net provides you with the resources and insights needed to choose the best server solutions, ensuring seamless and secure email operations. Dive in to discover how to identify and manage your email server effectively, enhancing your business and personal communication strategies with robust email hosting and email infrastructure.
1. Understanding What Your Email Server Is
What is my email server, and why is it so crucial? An email server is a computer system that sends and receives email. It’s the central hub for all your email communications, ensuring messages reach their intended recipients.
1.1. Defining the Email Server
At its core, an email server functions like a post office for digital correspondence. According to a study by Radicati Group, over 333 billion emails are sent and received daily worldwide. These servers use specific protocols to manage email traffic.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Handles the sending of email.
- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Allows you to access your email from multiple devices.
- POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3): Downloads email to a single device and often deletes it from the server.
1.2. The Significance of Knowing Your Email Server
Why should you care about what your email server is? Knowing your email server details is essential for:
- Setting up email clients: Whether on your computer or smartphone, you need the correct server information to configure your email.
- Troubleshooting issues: When email isn’t working, server details help diagnose the problem.
- Ensuring security: Understanding your server allows you to implement the right security measures.
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements for data handling and email archiving.
1.3. Different Types of Email Servers
There are several types of email servers, each with its own benefits.
| Type of Server | Description | Benefits |
| — | — | — |
| Shared Server | Multiple users share the same server resources. | Cost-effective for small businesses and personal use. |
| Dedicated Server | You have exclusive use of a server. | Enhanced performance, security, and customization options. |
| VPS (Virtual Private Server) | A virtualized server environment with dedicated resources. | Balances cost and performance, suitable for growing businesses. |
| Cloud Server | Email services hosted on a cloud infrastructure. | Scalability, reliability, and flexible pricing. |
Choosing the right type depends on your specific needs. According to Gartner, the cloud email market is projected to grow by 15% annually, reflecting its increasing adoption.
2. Identifying Your Email Server Information
How do you find out what your email server is? There are several methods to identify your email server information, depending on your email client and operating system.
2.1. Finding Email Server Details on Desktop Clients
Desktop email clients like Outlook and Apple Mail store your server information for easy access.
2.1.1. Outlook for PC
- Open Outlook: Launch the Outlook application on your computer.
- Go to File: Click on the “File” tab in the top left corner.
- Account Settings: Navigate to “Account Settings” and then “Account Settings” again.
- Select Your Account: On the “Email” tab, double-click the account you want to check.
- Server Information: Under “Server Information,” you’ll find your incoming mail server (IMAP) and outgoing mail server (SMTP) names.
- More Settings: For port information, click “More Settings…” and then the “Advanced” tab.
2.1.2. Outlook for Mac
- Open Outlook: Launch Outlook on your Mac.
- Preferences: Click “Outlook” in the toolbar, then select “Preferences.”
- Accounts: Click “Accounts.”
- Select Your Account: In the left sidebar, click the account you want to examine.
- Server Details: Find the “Incoming server” and “Outgoing server” fields. The longer text box contains the server name, and the box to the right displays the port number.
2.1.3. Apple Mail (Mac Desktop)
- Open Mail: Launch the Apple Mail application.
- Preferences: Click “Mail” in the toolbar and select “Preferences.”
- Accounts: In the left sidebar, select the account you’re interested in.
- Account Information: Select “Account Information.”
- Find Server Names: The “Incoming Mail Server” field shows your IMAP server name, and the “Outgoing Mail Server” field shows your SMTP server name.
- Edit SMTP Server List: You may need to use the dropdown menu to select “Edit SMTP server list” to view the SMTP server name and port.
2.2. Finding Email Server Details on Mobile Devices
Mobile devices also store your email server information, though accessing it can be slightly different.
2.2.1. iPhone (Apple Mail)
![]() iPhone Settings Icon
iPhone Settings Icon
- Open Settings: Go to your iPhone’s “Settings.”
- Mail: Scroll down and select “Mail.”
 iPhone Settings Mail
iPhone Settings Mail
- Accounts: Tap “Accounts.”
- Select Account: Choose the email account you want to investigate.
- Account Details: Under “IMAP,” select “Account.”
- Server Information: This screen displays your incoming (IMAP) and outgoing (SMTP) mail server details.
2.2.2. Android (Native Android Email Client)
 Android Settings Apps
Android Settings Apps
- Open Settings: Go to your Android’s “Settings.”
- Apps: Click on “Apps.”
 Android Settings Apps Email
Android Settings Apps Email
- Email: Select “Email.”
- Select Email Address: Choose your email address.
- Server Settings: Under “Advanced Settings,” click “Server Settings.”
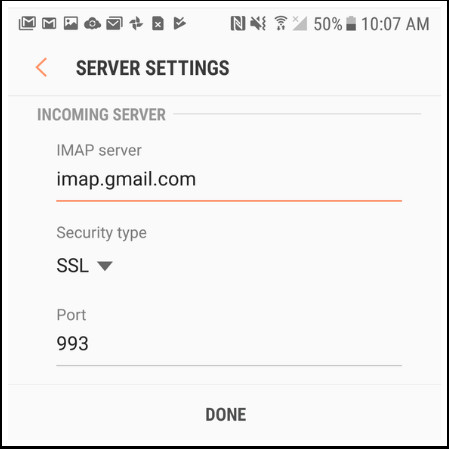 Android Email Server Settings
Android Email Server Settings
- Access Server Information: You’ll be directed to the “Server Settings” screen, where you can find your server details.
2.3. Using Webmail Interfaces
Webmail interfaces can also provide server information, though it may require a bit more digging.
2.3.1. Gmail
- Log into Gmail: Sign in to your Gmail account.
- Settings: Click the gear icon in the top right corner and select “Settings.”
- Accounts and Import: Click on the “Accounts and Import” tab.
- Check Mail from Other Accounts: Find the “Check mail from other accounts” section.
- Edit Info: If you’ve added another account, click “edit info” to see the server settings.
2.3.2. Yahoo Mail
- Log into Yahoo Mail: Sign in to your Yahoo Mail account.
- Settings: Click the gear icon and select “More Settings.”
- Security: Go to “Security.”
- App Passwords: Generate an app password if necessary.
- Server Settings: Use the app password to access server settings in your email client.
2.4. Contacting Your Email Provider
If you can’t find your server information through the methods above, contacting your email provider is a reliable option. Providers like Gmail, Yahoo, and smaller hosting companies can offer direct support. According to a survey by Statista, customer satisfaction with email provider support averages around 75%, highlighting the usefulness of this approach.
3. Why Knowing Your Email Server Matters
Understanding your email server is more than just a technical detail; it directly impacts your ability to manage your email effectively.
3.1. Setting Up Email Clients Correctly
When setting up email clients, accurate server information is crucial. Incorrect settings can lead to:
- Connection errors: Unable to send or receive emails.
- Synchronization issues: Emails not syncing across devices.
- Security vulnerabilities: Opening your account to potential threats.
3.2. Troubleshooting Email Issues
Knowing your server details is invaluable when troubleshooting email problems. Common issues include:
- Email sending failures: Often due to incorrect SMTP settings.
- Email receiving failures: Usually related to IMAP or POP3 configurations.
- Authentication errors: Problems with your username or password.
Having the correct server information allows you to quickly identify and resolve these issues.
3.3. Enhancing Email Security
Understanding your email server enables you to implement better security measures. This includes:
- Using SSL/TLS encryption: Securing the connection between your device and the server.
- Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: Verifying the authenticity of your emails to prevent spoofing and phishing.
- Regularly updating your email client: Ensuring you have the latest security patches.
3.4. Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
For businesses, knowing your email server is essential for complying with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. These regulations require you to protect sensitive data, including email communications. Proper server management helps you:
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) measures: Preventing sensitive information from leaving your organization.
- Maintain email archives: Storing emails for compliance and legal purposes.
- Ensure data residency: Keeping data within specific geographic regions to comply with local laws.
4. Common Email Server Settings and What They Mean
To effectively manage your email, it’s important to understand common email server settings.
4.1. Incoming Mail Server (IMAP/POP3)
The incoming mail server is responsible for receiving emails. IMAP and POP3 are the two main protocols used.
- IMAP: Allows you to access your email from multiple devices, keeping messages on the server.
- Port: 143 (non-SSL), 993 (SSL)
- POP3: Downloads email to a single device and typically deletes it from the server.
- Port: 110 (non-SSL), 995 (SSL)
4.2. Outgoing Mail Server (SMTP)
The outgoing mail server is used to send emails. SMTP settings are crucial for ensuring your emails reach their destinations.
- Port: 25 (non-SSL, often blocked), 587 (STARTTLS), 465 (SSL)
4.3. Encryption (SSL/TLS)
Encryption protocols like SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) secure the connection between your email client and the server.
- SSL: An older encryption protocol.
- TLS: The successor to SSL, providing stronger security.
Enabling SSL/TLS ensures that your email communications are protected from eavesdropping.
4.4. Authentication
Authentication settings verify your identity when sending or receiving emails. Common authentication methods include:
- Username and Password: The most common method, requiring a valid username and password.
- OAuth: A more secure method that allows third-party apps to access your email without revealing your password.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method.
5. Choosing the Right Email Server for Your Needs
Selecting the right email server is a critical decision that depends on your specific requirements.
5.1. Factors to Consider
When choosing an email server, consider the following factors:
- Storage: How much email storage do you need?
- Security: What level of security do you require?
- Reliability: How important is uptime for your email service?
- Scalability: Can the server handle future growth?
- Cost: What is your budget for email services?
5.2. Options for Email Servers
There are several options for email servers, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
| Server Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shared Hosting | Email hosting included with web hosting plans. | Cost-effective, easy to set up. | Limited resources, potential security risks. |
| VPS Hosting | Virtual private server with dedicated resources. | More control, better performance. | Requires technical knowledge. |
| Dedicated Hosting | Entire server dedicated to your email needs. | Maximum control, high performance. | Expensive, requires significant technical expertise. |
| Cloud Email Services | Email services like Gmail, Outlook 365, and Zoho Mail. | Scalable, reliable, easy to use. | Less control over server settings. |
5.3. On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based Email Servers
A key decision is whether to host your email server on-premise or use a cloud-based service.
5.3.1. On-Premise Email Servers
On-premise email servers involve hosting the server within your own infrastructure.
- Pros:
- Full control over server settings and data.
- Compliance with strict data residency requirements.
- Cons:
- High upfront and ongoing costs.
- Requires significant IT expertise.
- Responsibility for security and maintenance.
5.3.2. Cloud-Based Email Servers
Cloud-based email servers are hosted by a third-party provider.
- Pros:
- Scalable and flexible.
- Lower upfront costs.
- Managed security and maintenance.
- Cons:
- Less control over server settings.
- Reliance on the provider’s security measures.
- Potential data residency concerns.
5.4. Popular Email Server Providers
Several providers offer excellent email server solutions.
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite): Offers Gmail for business with additional features.
- Microsoft 365: Includes Outlook and Exchange Online for business email.
- Zoho Mail: A cost-effective email solution for small businesses.
- Amazon SES (Simple Email Service): A scalable email sending service for developers.
- SendGrid: A cloud-based email delivery platform.
6. Managing and Maintaining Your Email Server
Once you have an email server, proper management and maintenance are essential.
6.1. Monitoring Server Performance
Regularly monitor your server’s performance to identify and resolve issues before they impact your email service. Key metrics to monitor include:
- Uptime: The percentage of time the server is operational.
- Latency: The time it takes for emails to be sent and received.
- Resource usage: CPU, memory, and disk usage.
- Email delivery rates: The percentage of emails that successfully reach their recipients.
6.2. Implementing Security Measures
Security should be a top priority when managing your email server. Implement the following measures:
- Firewall: Protect your server from unauthorized access.
- Antivirus software: Scan for and remove malware.
- Intrusion detection system (IDS): Monitor for suspicious activity.
- Regular security audits: Identify and address vulnerabilities.
6.3. Backing Up Your Email Data
Regularly back up your email data to prevent data loss in the event of a server failure or security breach. Best practices for backups include:
- Automated backups: Schedule backups to run automatically.
- Offsite storage: Store backups in a separate location from the server.
- Regular testing: Verify that backups can be restored successfully.
6.4. Keeping Software Up to Date
Keep your email server software and operating system up to date with the latest security patches and bug fixes. This helps protect your server from known vulnerabilities.
6.5. Optimizing Server Configuration
Optimize your server configuration to improve performance and security. This includes:
- Tuning SMTP settings: Optimizing email delivery rates.
- Configuring DNS records: Ensuring proper email authentication.
- Implementing email filtering: Blocking spam and malicious emails.
7. Troubleshooting Common Email Server Issues
Even with proper management, you may encounter email server issues. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them.
7.1. Email Sending Issues
If you’re unable to send emails, check the following:
- SMTP settings: Verify that your SMTP server, port, and authentication settings are correct.
- Firewall: Ensure that your firewall is not blocking outgoing SMTP traffic.
- Blacklisting: Check if your server’s IP address is blacklisted.
- Authentication: Make sure your email client is properly authenticated with the SMTP server.
7.2. Email Receiving Issues
If you’re unable to receive emails, check the following:
- IMAP/POP3 settings: Verify that your IMAP or POP3 server, port, and authentication settings are correct.
- Firewall: Ensure that your firewall is not blocking incoming IMAP or POP3 traffic.
- DNS records: Check that your MX records are properly configured.
- Spam filtering: Ensure that your emails are not being filtered as spam.
7.3. Authentication Errors
Authentication errors can occur when your username or password is incorrect. To resolve these errors:
- Verify credentials: Double-check your username and password.
- Reset password: Reset your password if you’ve forgotten it.
- Check for lockout: Ensure your account hasn’t been locked out due to too many failed login attempts.
- OAuth configuration: If using OAuth, ensure it’s properly configured.
7.4. Server Downtime
If your email server is experiencing downtime, take the following steps:
- Check server status: Contact your hosting provider or check their status page.
- Investigate the cause: Determine the cause of the downtime.
- Implement failover: If possible, switch to a backup server.
- Communicate with users: Keep your users informed about the downtime and estimated time to resolution.
8. Future Trends in Email Server Technology
The email server landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging.
8.1. AI-Powered Email Security
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to enhance email security by:
- Detecting phishing attacks: Identifying and blocking sophisticated phishing attempts.
- Preventing malware: Scanning emails for malicious attachments and links.
- Analyzing user behavior: Detecting anomalies that may indicate a compromised account.
8.2. Enhanced Encryption Standards
New encryption standards are being developed to provide stronger protection for email communications. This includes:
- End-to-end encryption: Encrypting emails so that only the sender and recipient can read them.
- Quantum-resistant encryption: Protecting against attacks from quantum computers.
8.3. Serverless Email Architectures
Serverless architectures are becoming more popular for email services. These architectures allow you to:
- Scale resources on demand: Automatically adjust resources based on traffic.
- Reduce costs: Only pay for the resources you use.
- Simplify management: Eliminate the need to manage servers.
8.4. Integration with Collaboration Tools
Email servers are increasingly being integrated with collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams. This allows you to:
- Share emails directly in collaboration channels.
- Receive email notifications within your collaboration platform.
- Centralize communication and improve productivity.
9. How Rental-Server.net Can Help You
Navigating the complexities of email servers can be daunting. That’s where rental-server.net comes in. We provide comprehensive resources to help you understand, choose, and manage the right server solutions for your needs.
9.1. Expert Guidance on Server Selection
Choosing the right server is crucial. Rental-server.net offers expert guidance to help you evaluate your options based on your specific requirements. Whether you need a dedicated server, VPS, or cloud-based solution, we provide detailed comparisons and recommendations.
9.2. Access to Top-Rated Hosting Providers
We partner with top-rated hosting providers to offer you a wide range of server solutions. Our partners provide reliable, secure, and scalable services, ensuring your email communications are always available.
9.3. Comprehensive Resources and Tutorials
Rental-server.net offers a wealth of resources, including tutorials, articles, and guides, to help you manage your email server effectively. From setting up your server to troubleshooting common issues, we have you covered.
9.4. Cost-Effective Solutions
We understand the importance of cost-effectiveness. Rental-server.net helps you find the best deals on server solutions, ensuring you get the most value for your money.
10. FAQs About Email Servers
10.1. What is an email server port?
An email server port is a specific endpoint used for communication between your email client and the email server. Common ports include 25 (SMTP), 587 (SMTP with TLS), 465 (SMTPS), 143 (IMAP), 993 (IMAPS), 110 (POP3), and 995 (POP3S).
10.2. How do I find my outgoing mail server?
You can find your outgoing mail server (SMTP) settings in your email client’s account settings or by contacting your email provider.
10.3. What is the difference between IMAP and POP3?
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) allows you to access your email from multiple devices, keeping messages on the server. POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) downloads email to a single device and often deletes it from the server.
10.4. How do I secure my email server?
To secure your email server, use SSL/TLS encryption, implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, regularly update your software, and use a firewall and antivirus software.
10.5. What is an MX record?
An MX (Mail Exchange) record is a DNS record that specifies the mail servers responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a domain.
10.6. Can I host my own email server?
Yes, you can host your own email server, but it requires technical expertise and ongoing maintenance. Alternatively, you can use a cloud-based email service.
10.7. What is email spoofing?
Email spoofing is the creation of email messages with a forged sender address. It is often used in phishing attacks and spam campaigns.
10.8. How do I prevent email spoofing?
You can prevent email spoofing by implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for your domain.
10.9. What is a dedicated email server?
A dedicated email server is a server that is exclusively used for email services. It provides enhanced performance, security, and control compared to shared hosting.
10.10. How much does it cost to host an email server?
The cost of hosting an email server varies depending on the type of server (shared, VPS, dedicated, cloud) and the provider. Shared hosting can cost as little as a few dollars per month, while dedicated servers can cost hundreds of dollars per month.
Understanding what your email server is, is the first step toward ensuring reliable and secure email communications. With the right knowledge and tools, you can effectively manage your email and leverage it to enhance your business and personal interactions. Visit rental-server.net today to explore our comprehensive server solutions and take control of your email infrastructure.
Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States
Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000
Website: rental-server.net
Take the next step towards optimal email management. Contact rental-server.net now and discover the perfect hosting solution tailored to your needs.
