Getting a “DNS Server Not Responding” error can be a frustrating experience. But don’t worry! This guide from rental-server.net will explain what this error means and offer proven solutions to get you back online, ensuring seamless access to your favorite websites and online services with optimal server performance and reliability. Explore various server options and find the perfect match for your hosting needs, including dedicated servers and VPS solutions.
1. What Does “DNS Server Not Responding” Actually Mean?
The “DNS Server Not Responding” error signifies that your device can’t establish a connection with a DNS server, preventing you from accessing websites; however, restarting your router, clearing your DNS cache, modifying DNS server settings, checking for firewall issues, and updating network drivers are standard fixes.
Let’s break it down. DNS, or Domain Name System, is like the internet’s phonebook. It translates easy-to-remember domain names (like rental-server.net) into numerical IP addresses (like 192.168.1.1) that computers use to locate websites. When you encounter this error, your computer can’t find the correct IP address for the website you’re trying to visit. It’s like trying to call someone with the wrong phone number.
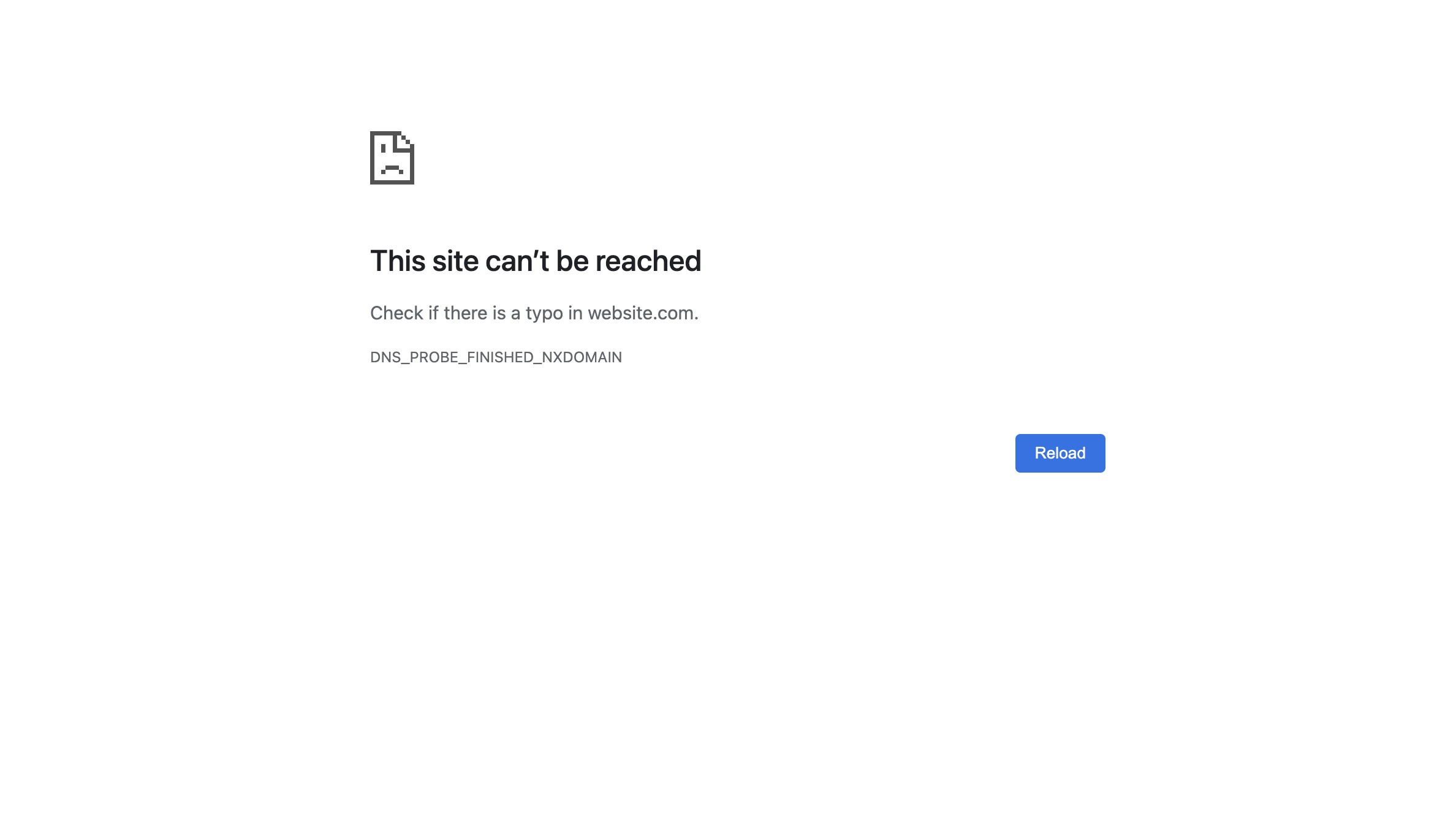 DNS Server Not Responding Error
DNS Server Not Responding Error
The DNS system stores information about domains and their corresponding IP addresses in a decentralized network of DNS servers. Computers connect to these DNS servers to fetch the IP addresses of domain names to connect to websites and other internet services.
There are various forms of this error message, such as “The DNS server is not responding” or “Device or resource (DNS server) is not responding.” You might also see browser-specific messages like “This Site Can’t Be Reached” with error codes like DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN.
2. What Causes the “DNS Server Not Responding” Error?
The “DNS Server Not Responding” error can stem from a number of root issues. Identifying the reason is the first step in successfully resolving the problem. Here’s a rundown of common causes:
- DNS Server Outage: The DNS server itself might be temporarily down due to high traffic or an outage.
- Network Connectivity Issues: A weak Wi-Fi signal, a faulty Ethernet cable, or incorrect network settings can disrupt communication with the DNS server.
- Corrupted DNS Cache: Your computer stores a DNS cache to speed up website loading. If this cache becomes corrupted, it can lead to the error.
- Incorrect DNS Settings: Using incorrect or outdated DNS server addresses in your network configuration will prevent your device from connecting to a functional DNS server.
- Firewall or Antivirus Interference: Overly strict settings in your firewall or antivirus software can block communication with the DNS server.
- Misconfigured Network Adapters: Incorrect settings or corrupted drivers for your network adapter can cause DNS resolution failures.
3. How to Troubleshoot Network Problems Effectively?
Before diving into more technical solutions, running network diagnostics can often pinpoint the problem. Most operating systems have built-in tools for this.
- On macOS: Hold the Option key and click the Wi-Fi status icon in the menu bar. Select “Open Wireless Diagnostics” and follow the on-screen instructions. The tool provides detailed information about any detected network issues.
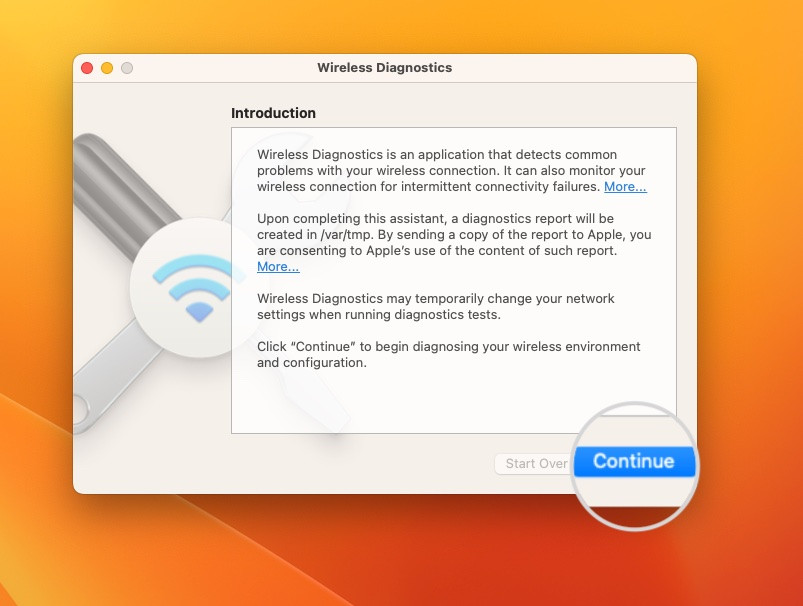 Network Diagnostics Wizard on Mac
Network Diagnostics Wizard on Mac
- On Windows 10: Open the Windows menu, type “control panel,” and select “Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.” Choose “Troubleshoot problems” and then “Additional troubleshooters > Internet Connections > Run the troubleshooter.” The results will list any detected issues and offer steps for repair.
 Open Network and Internet options on Windows to troubleshoot the network
Open Network and Internet options on Windows to troubleshoot the network
4. How Can Using a Different Web Browser Help?
A simple yet effective troubleshooting step is to try accessing the website using a different web browser. If the error disappears in another browser, it suggests that the issue might be specific to your primary browser, potentially due to expired cached files or a corrupted installation. For instance, if you typically use Google Chrome, try accessing the site with Microsoft Edge or Mozilla Firefox.
5. Why Should I Test With Another Device?
Problems within your device can sometimes interfere with DNS resolution. To determine if the issue is localized to your primary device, attempt to access the website on another device, such as your smartphone using mobile data. If the website loads without error on the secondary device, it indicates a malfunction within your primary device.
6. How Does Restarting Your Computer in Safe Mode Help?
Operating system (OS) issues or third-party software can often trigger the DNS server error. Restarting your computer in Safe Mode can help identify if add-on applications conflict with your OS. Safe Mode loads only the core functionalities of your operating system, excluding third-party applications.
- Safe Mode on Windows 10: Hold SHIFT while clicking Restart in the Windows menu. Then select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. Finally, choose the appropriate Safe Mode option.
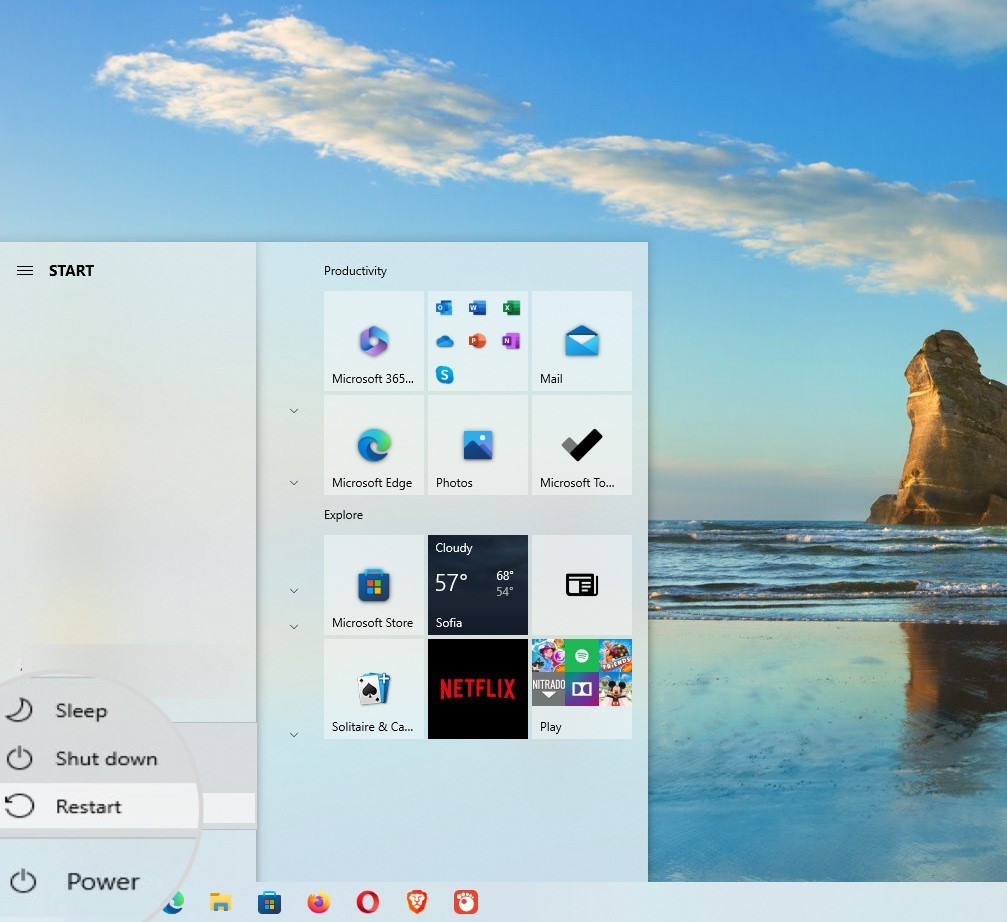 How to restart Windows in Safe Mode
How to restart Windows in Safe Mode
- Safe Mode on Mac: Restart your Mac and hold SHIFT during startup. Release SHIFT when you see the login screen.
If the error disappears in Safe Mode, it confirms that a third-party application is interfering with the DNS server connection. The culprit could be your firewall, antivirus software, or another application.
7. Should I Restart My Router or Modem?
Routers can also experience problems that lead to the DNS Server Not Responding error. Like computers, routers store cached data that can become invalid over time. Restarting your router can often resolve these issues. Simply turn it off, wait a few minutes, and then turn it back on.
8. Can Disabling Antivirus and Firewall Software Help?
While antivirus and firewall software are crucial for online security, they can sometimes inadvertently block legitimate internet traffic, leading to the “DNS Server Not Responding” error. Temporarily disabling these programs can help determine if they are the cause.
- Disabling the Firewall on macOS: Go to System Settings > Network > Firewall and turn the switch off.
 How to disable the firewall on Mac
How to disable the firewall on Mac
- Disabling the Firewall on Windows: Go to Windows menu > Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Firewall & network protection. Select the active network and turn the firewall off.
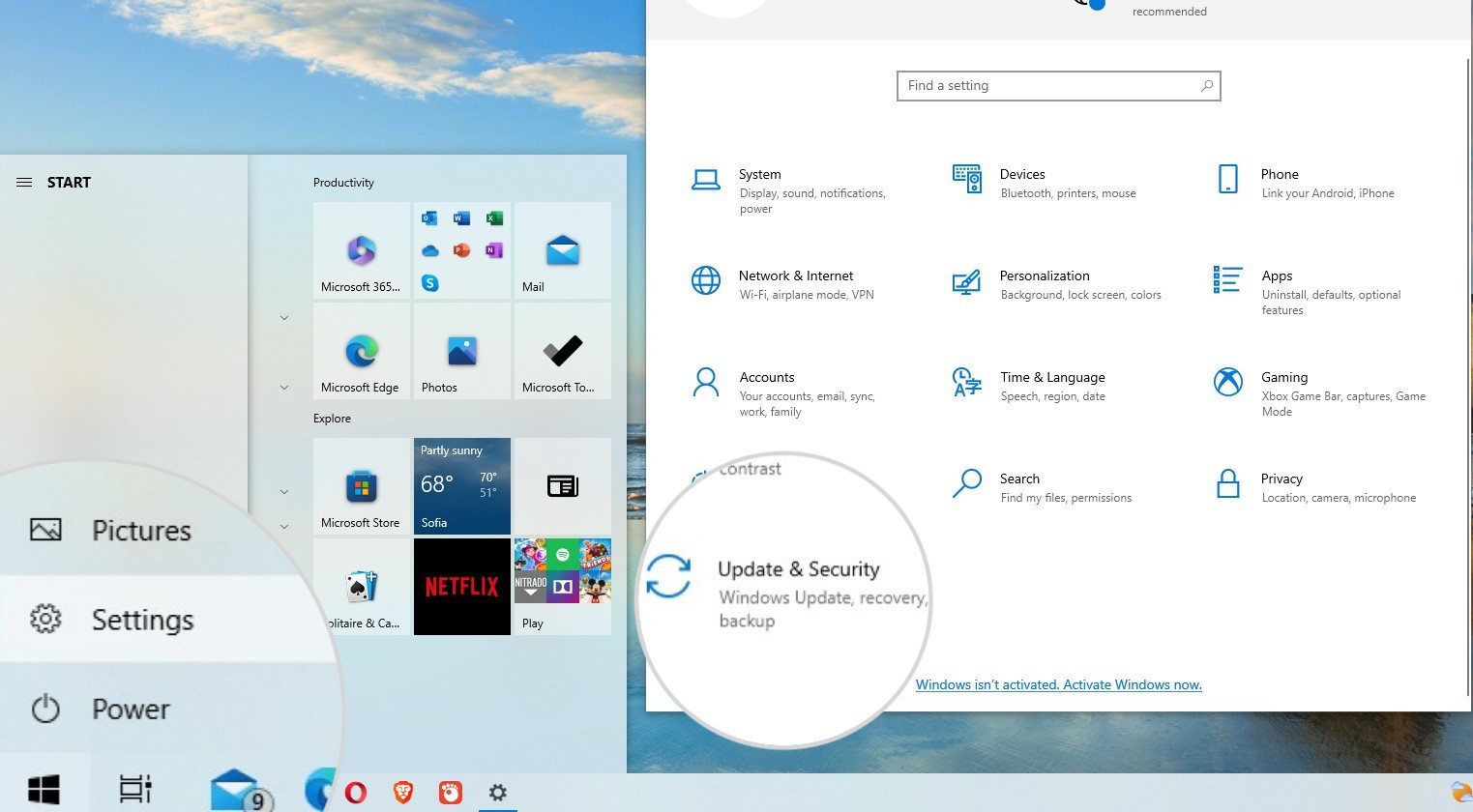 Open Updates and Security settings on Windows to disable the firewall
Open Updates and Security settings on Windows to disable the firewall
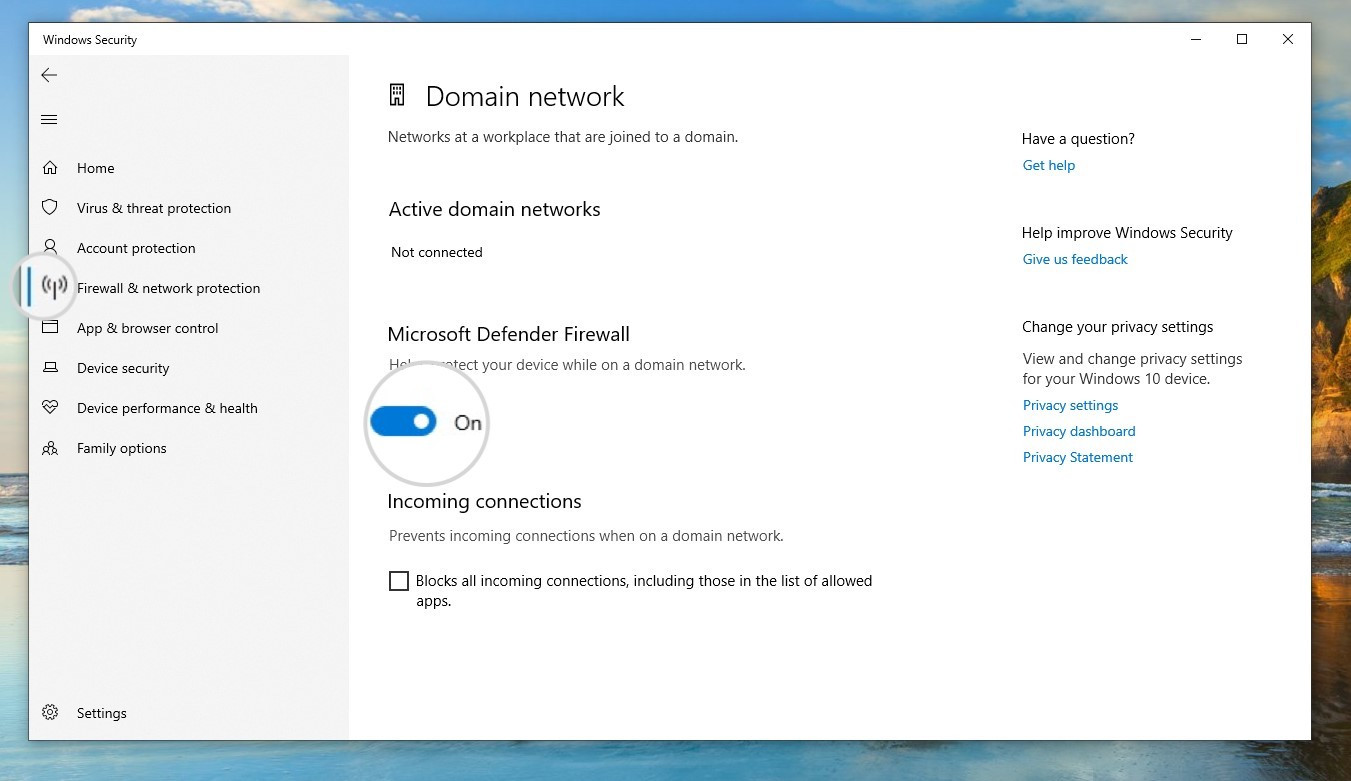 How to disable the firewall on Windows
How to disable the firewall on Windows
If the website loads correctly after disabling your security software, you may need to adjust its settings to allow communication with DNS servers.
9. How Does Disabling Other Connections Help?
When your device is registered on multiple network connections, conflicts can arise, disrupting your DNS configuration. To resolve this, keep only your primary network connection active and disable any secondary connections.
- On macOS: Go to System Settings > Network, select the network to remove, click the three dots menu, and select “Forget This Network.”
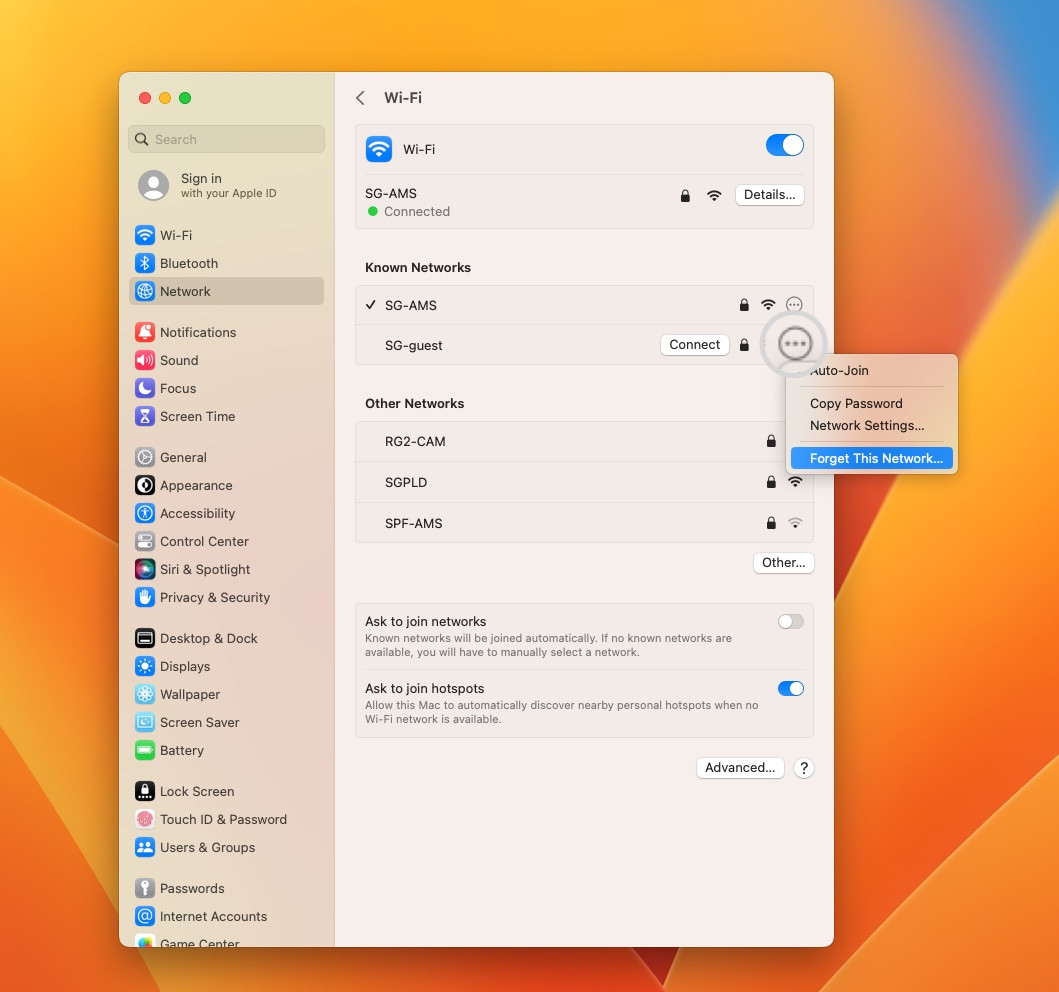 How to disable a network on Mac
How to disable a network on Mac
- On Windows: Go to Windows menu > Settings > Network & Internet and select “Change adapter options.” Right-click on a secondary network and choose “Disable.”
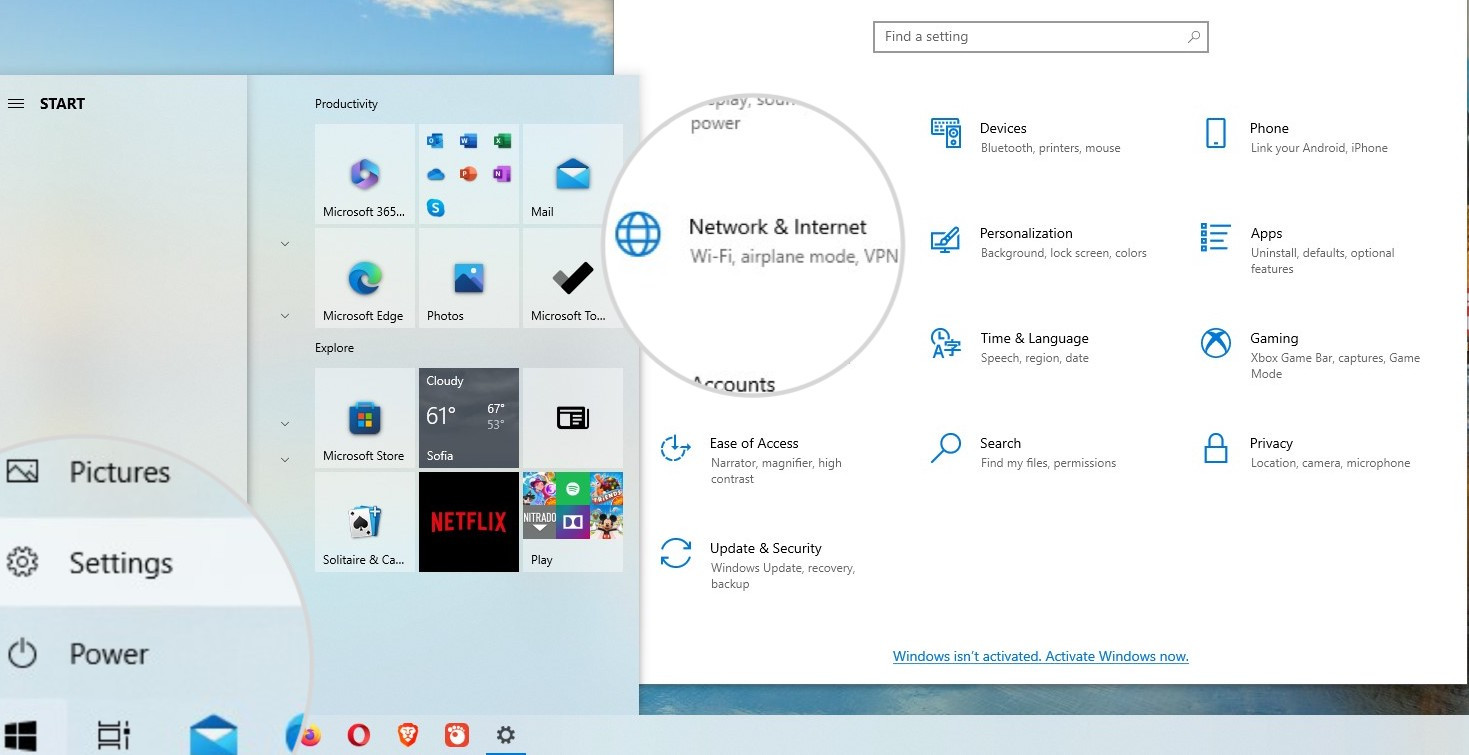 Open Network and Internet Settings on Windows to disable a network
Open Network and Internet Settings on Windows to disable a network
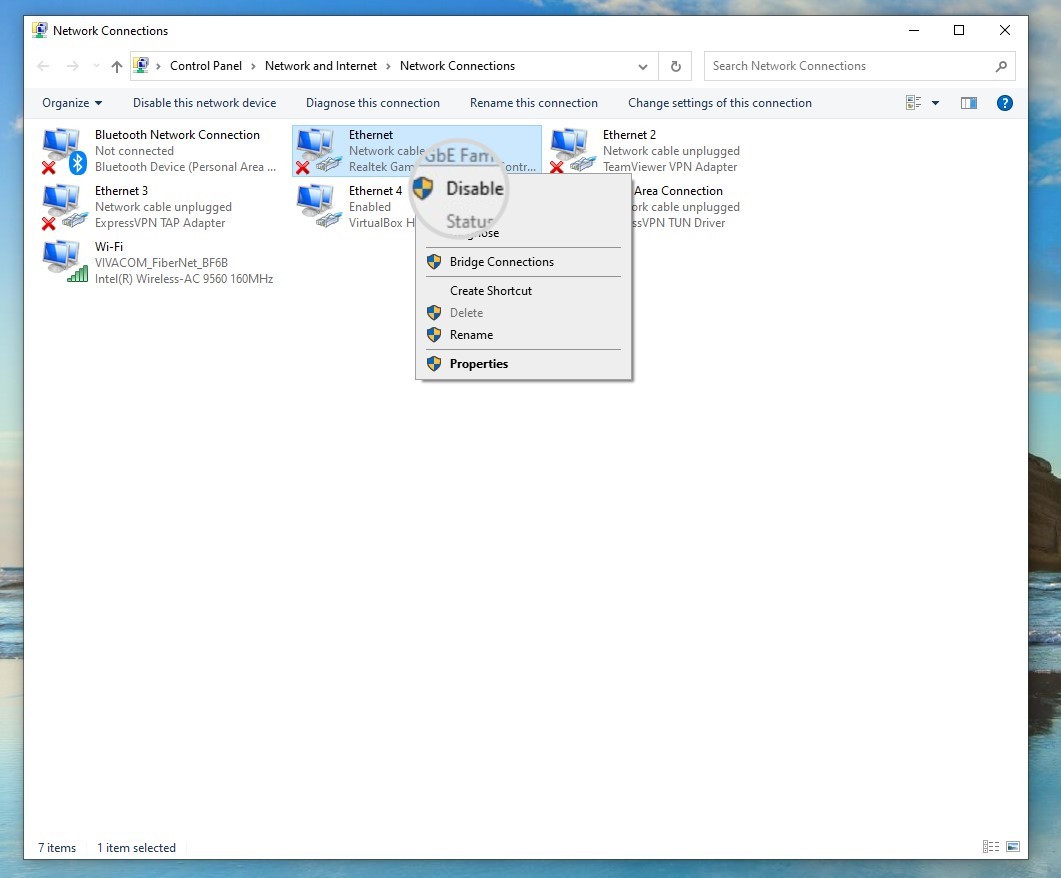 How to disable a network on Windows
How to disable a network on Windows
10. Should I Change the DNS Server Address?
Your operating system relies on functional DNS servers to correctly translate domain names into IP addresses. If the default DNS server is experiencing issues, switching to an alternative DNS server can resolve the “DNS Server Not Responding” error. Popular options include Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) and Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
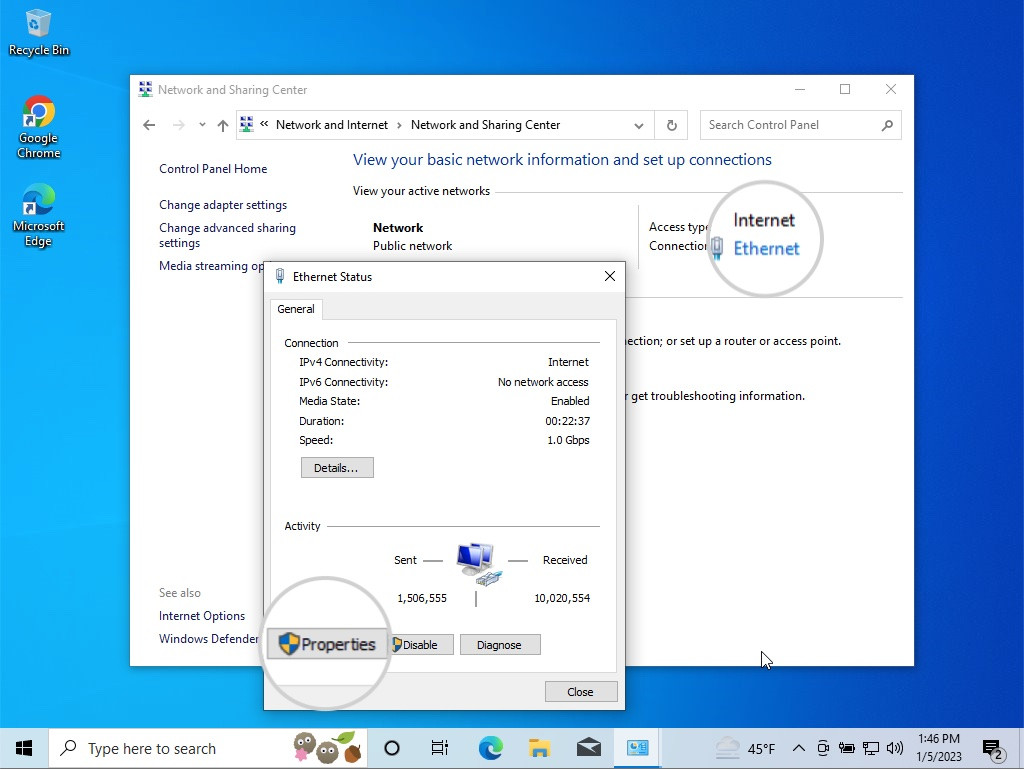
- Changing DNS Servers on Windows: Go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center. Click on your active network, select Properties, highlight Internet Protocol Version 4, and click Properties again. Choose “Use the following DNS server addresses” and enter the preferred and alternate DNS server addresses.
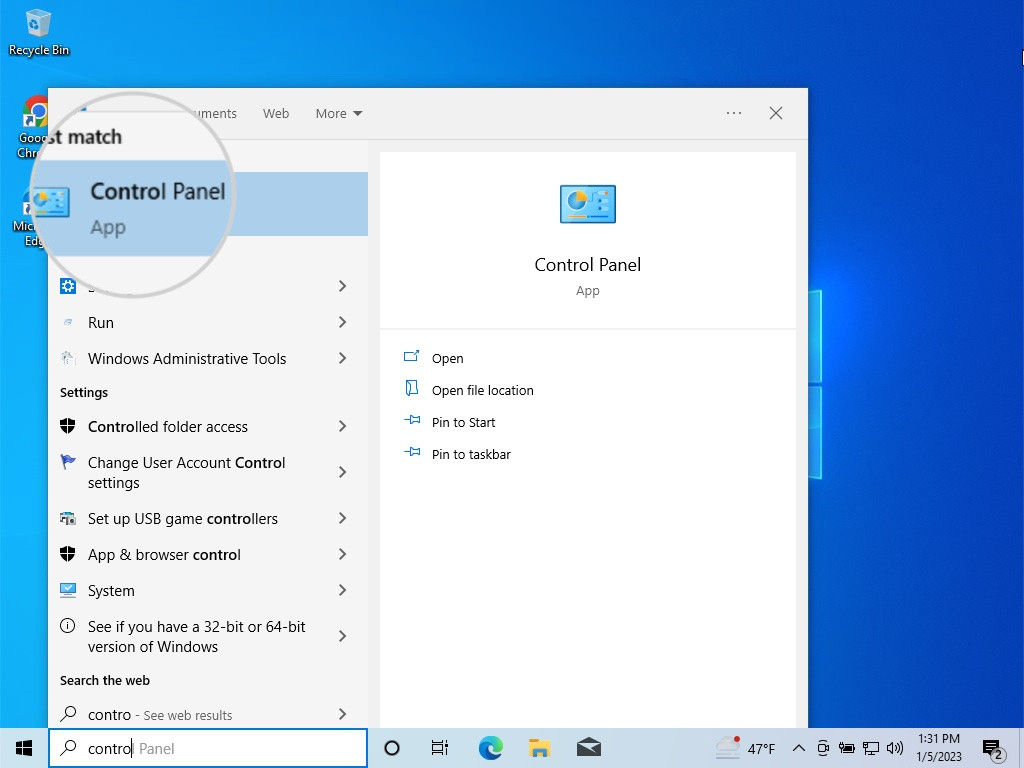 Open Control Panel on Windows to change the DNS servers
Open Control Panel on Windows to change the DNS servers
 Open the network
Open the network
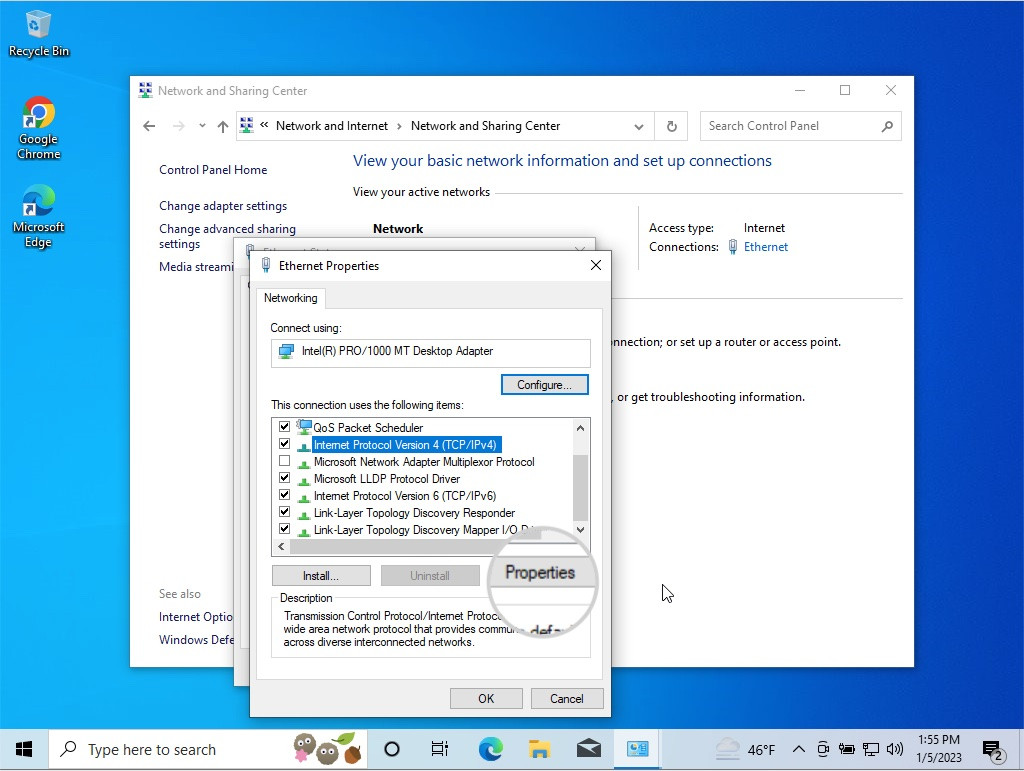 Open the Internet Protocol 4 properties to change the DNS servers
Open the Internet Protocol 4 properties to change the DNS servers
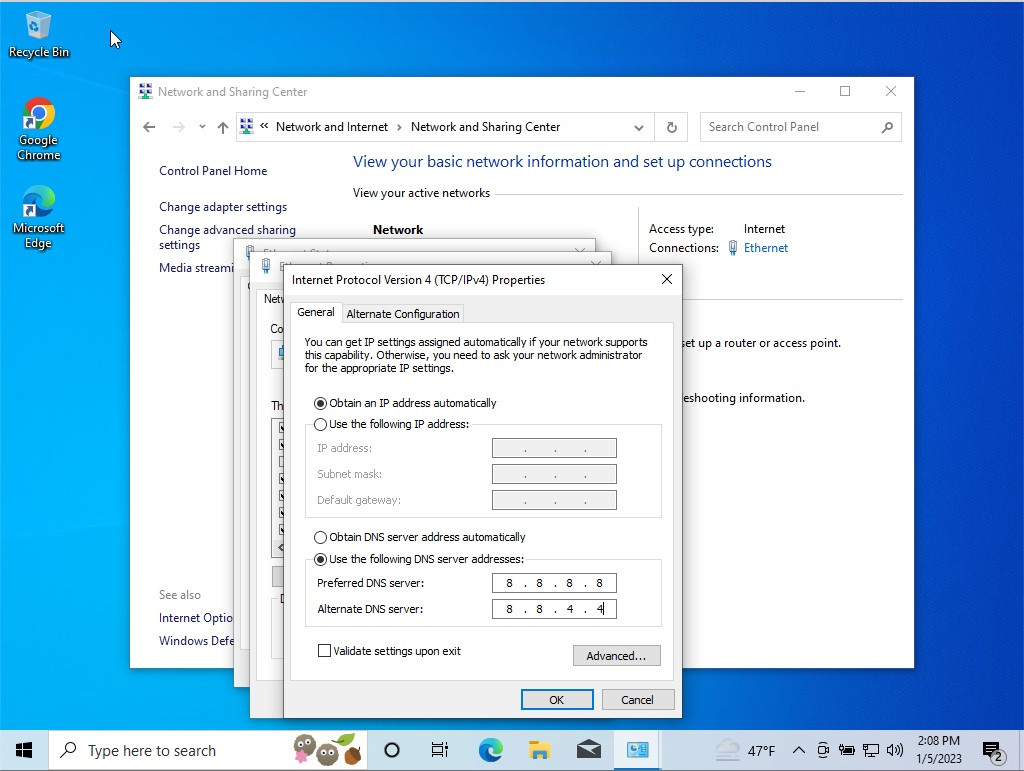 Change the DNS servers on Windows to fix
Change the DNS servers on Windows to fix
- Changing DNS Servers on macOS: Go to System Settings > Network, select your active network, and click Details. Open the DNS tab and add your preferred DNS servers using the “+” sign.
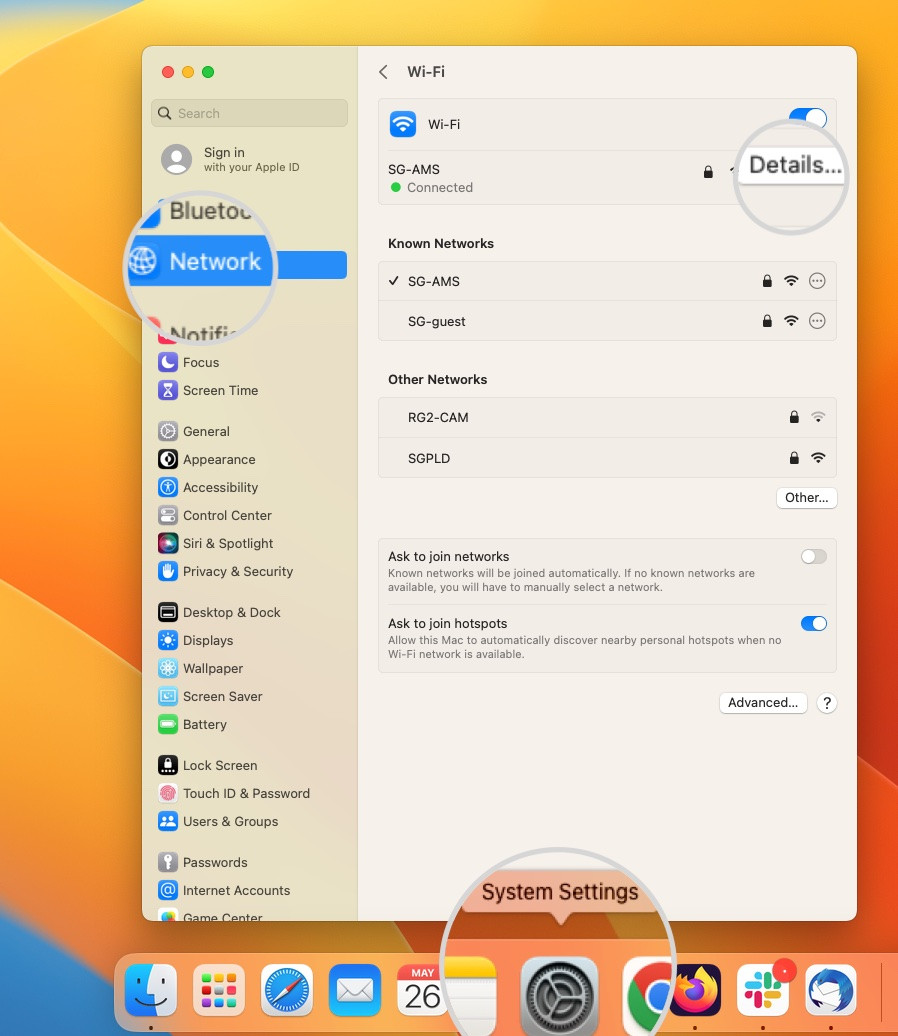 Open Network settings on Mac to change DNS servers
Open Network settings on Mac to change DNS servers
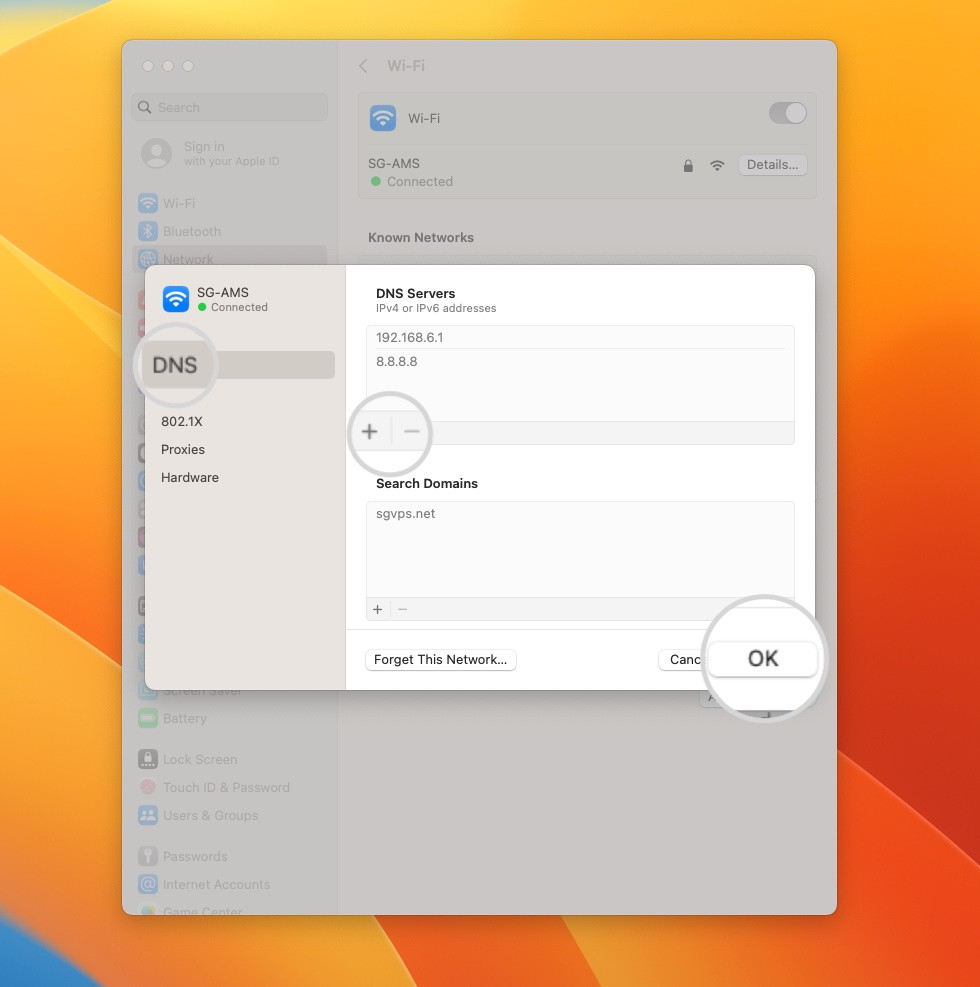 Change the DNS servers on Mac to fix
Change the DNS servers on Mac to fix
11. How Do I Flush the DNS Cache?
The DNS cache on your operating system can sometimes become outdated or corrupted, leading to the “DNS Server Not Responding” error. Clearing the DNS cache forces your computer to retrieve the most up-to-date DNS information.
- Flushing DNS Cache on Windows: Open Command Prompt as administrator and run the command
ipconfig /flushdns. - Flushing DNS Cache on macOS: Open Terminal and run the command
$ sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder(for macOS Monterey and later). - Flushing DNS Cache on Linux: The command varies depending on your Linux distribution. Common commands include
$ sudo resolvectl flush-cachesor$ sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches.
Consult rental-server.net for detailed guides on flushing the DNS cache on different operating systems.
12. Why Should I Update My Network Adapter Driver?
An outdated or corrupted network adapter driver can cause DNS-related issues. Updating the driver ensures that your network adapter is functioning correctly and communicating effectively with your network.
The easiest way to update your network adapter driver on Windows is to let Windows find the right drivers and update your adapter automatically.
- Open the Windows menu.
- Use the search bar and type “device manager.“
- Open Device Manager.
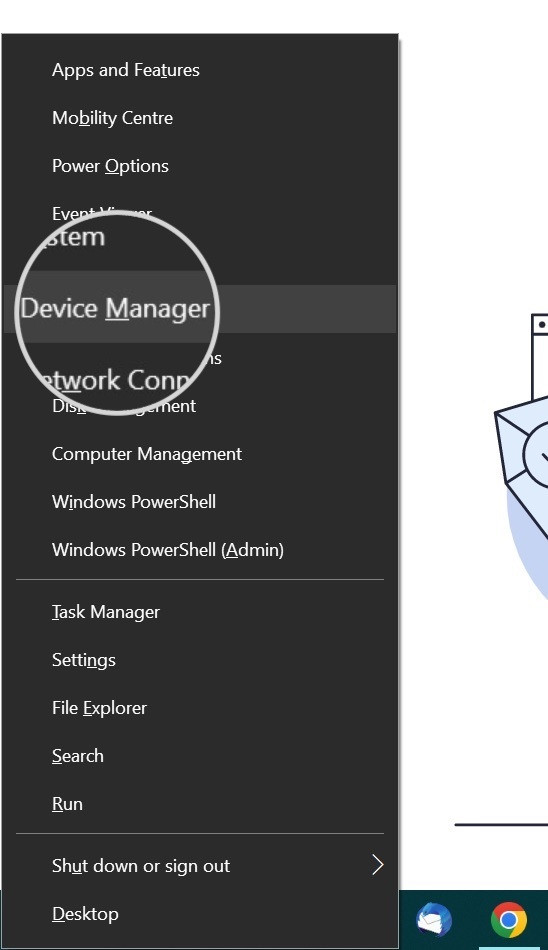 Open Device Manager in Windows to update network drivers
Open Device Manager in Windows to update network drivers
4. Double-click on Network adapters to expand the menu.
5. Right-click on your current adapter, and select Update driver.
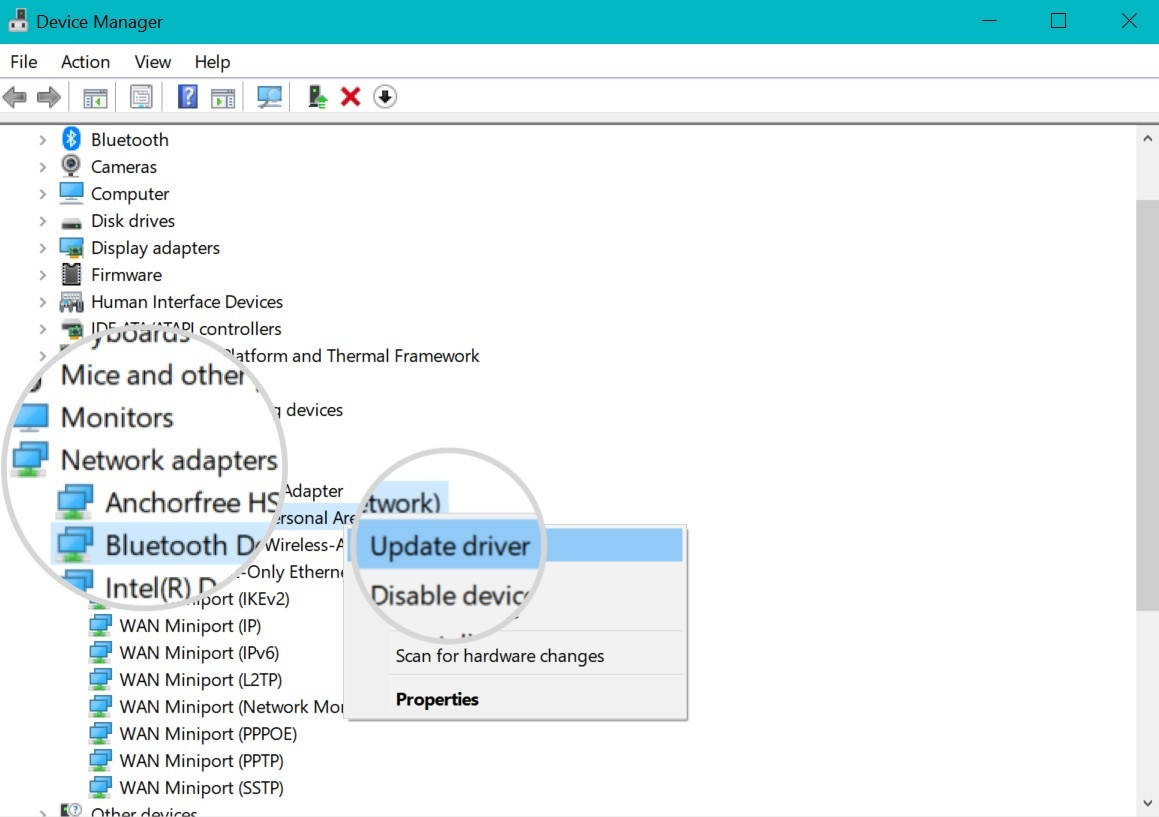 Update the network adapter
Update the network adapter
6. In the following window, choose Search automatically for drivers.
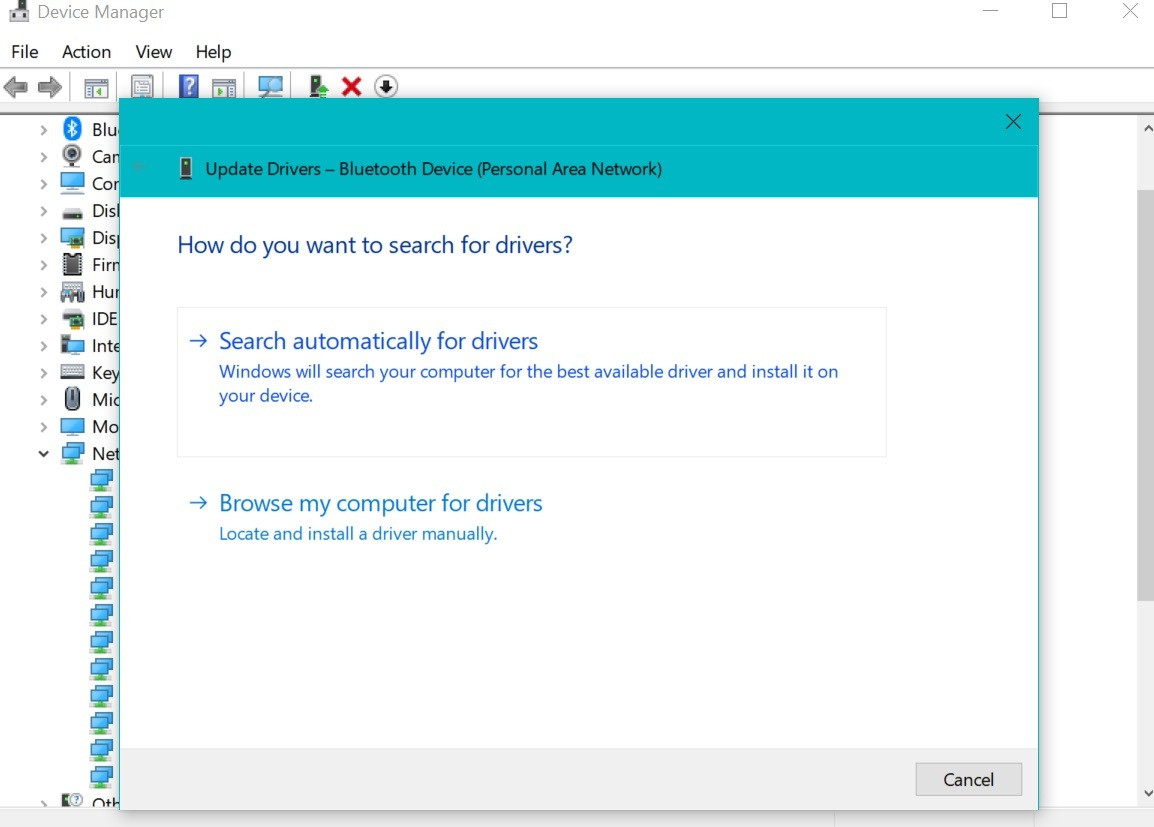 Update automatically the network adapter
Update automatically the network adapter
13. Should I Disable Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)?
IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol, but it’s not yet universally adopted. Compatibility issues can sometimes lead to network connectivity problems, including DNS issues. Disabling IPv6 can resolve the “DNS Server Not Responding” error in some cases.
- Disabling IPv6 on Windows: Go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center. Click on your current network connection and select Properties. Uncheck the box for Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) and click OK.
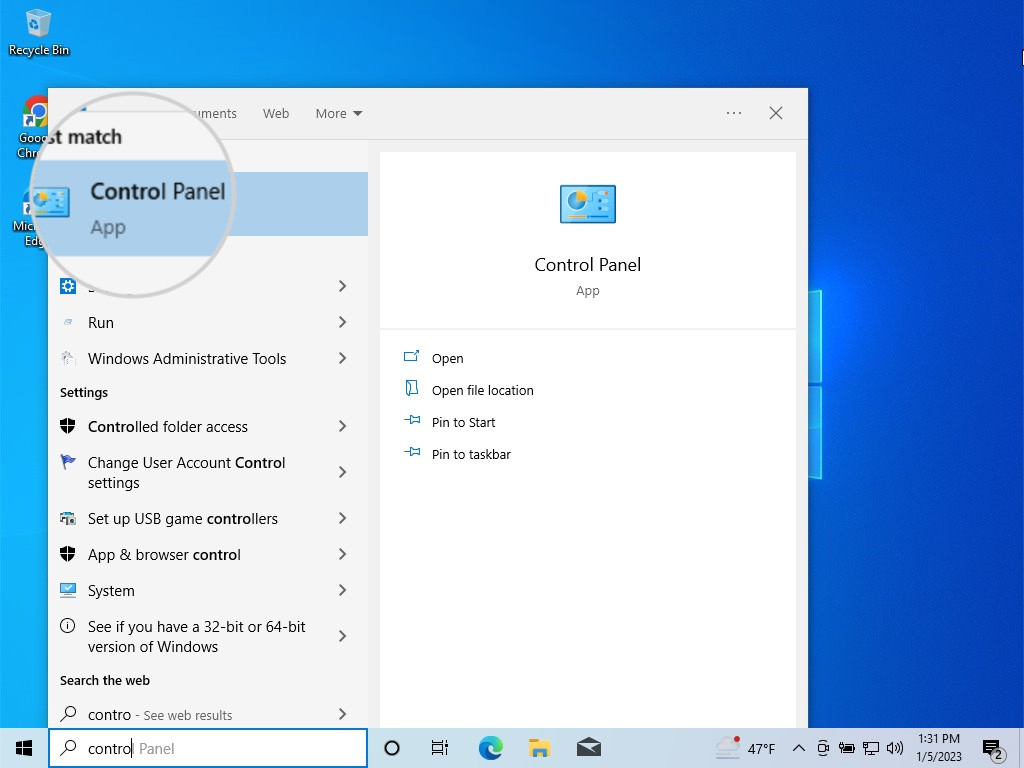 Open Control Panel in Windows to disable IPv6
Open Control Panel in Windows to disable IPv6
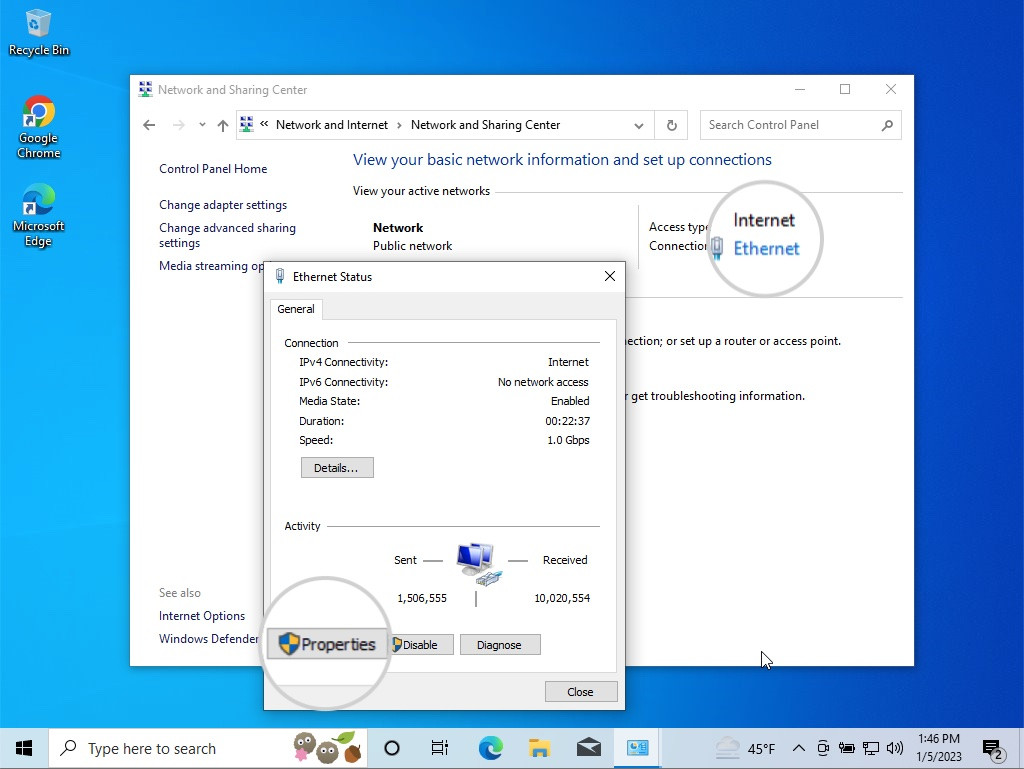 Open the network properties to disable IPv6
Open the network properties to disable IPv6
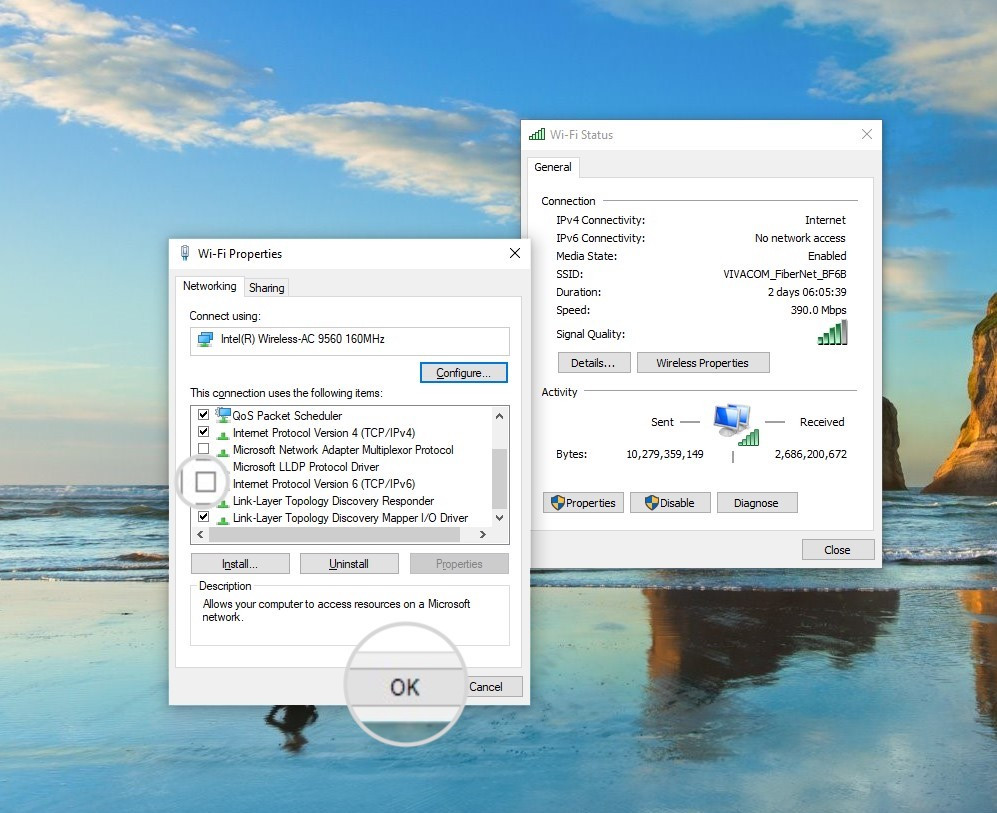 Disable IPv6 to fix the
Disable IPv6 to fix the
- Disabling IPv6 on macOS: Go to System Settings > Network, select your primary network connection, and click Details. Open the TCP/IP tab and set Configure IPv6 to “Off.” If this option is unavailable, you can disable IPv6 using Terminal with the command
$ networksetup -setv6off Ethernet && networksetup -setv6off Wi-Fi.
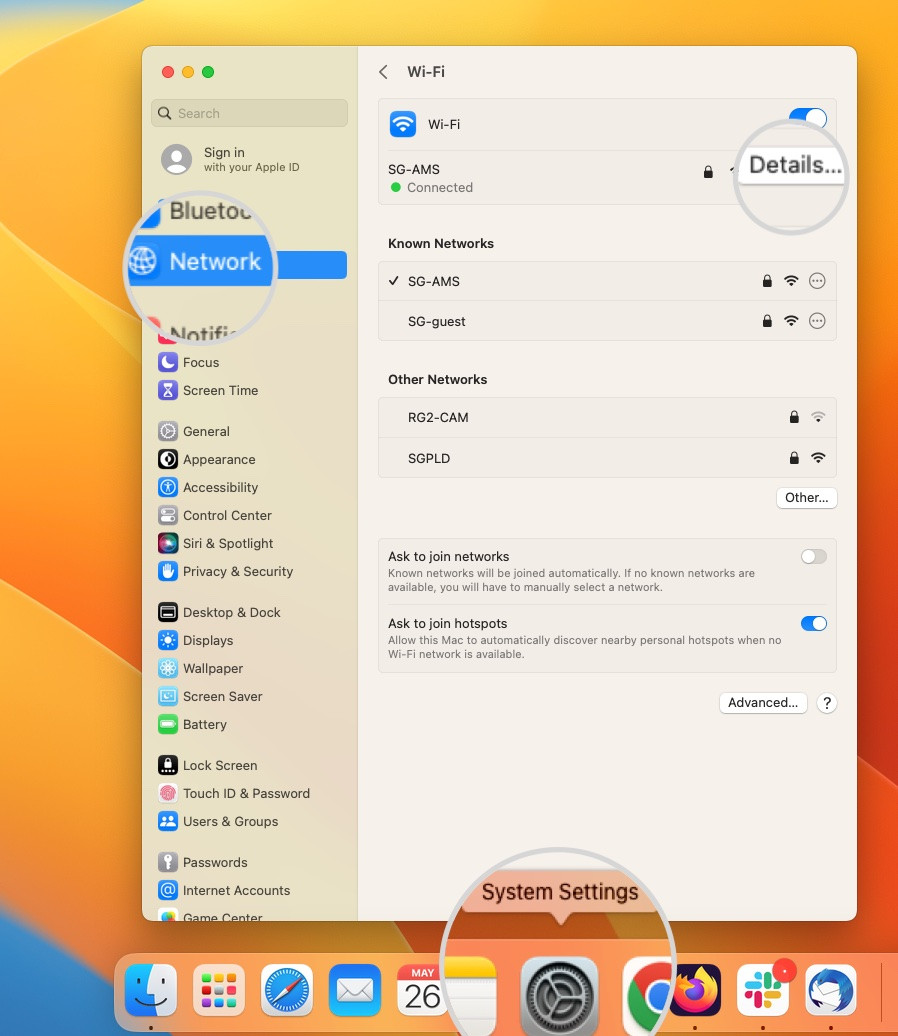 Open the network details on Mac to disable IPv6
Open the network details on Mac to disable IPv6
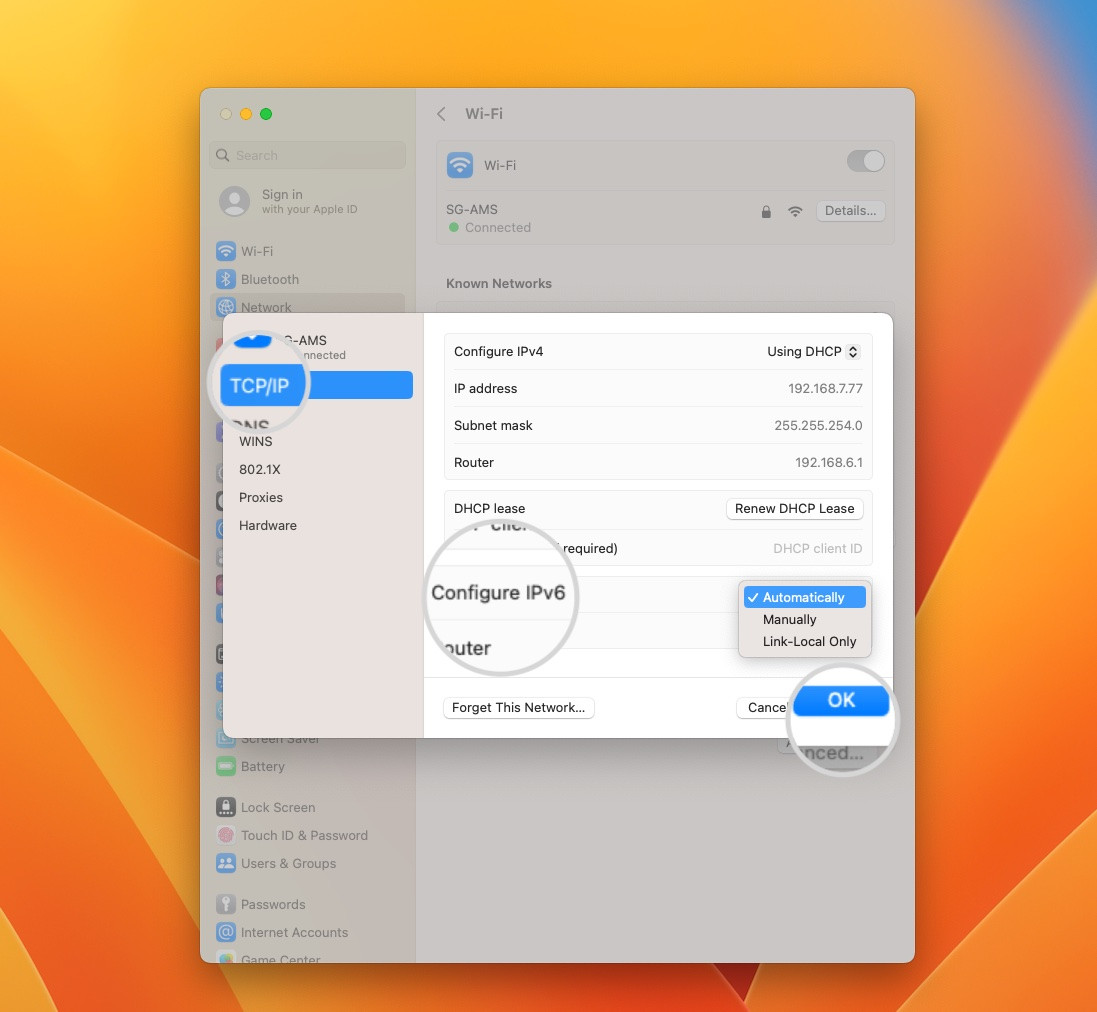 How to disable IPv6 on Mac
How to disable IPv6 on Mac
Find the Perfect Server Solution for Your Needs
If you’re looking for reliable and high-performance server solutions, explore the options available at rental-server.net. We offer a range of dedicated servers, VPS hosting, and cloud servers to meet your specific requirements. Our servers are located in state-of-the-art data centers across the USA, including Virginia, ensuring optimal performance and low latency for your applications and websites.
Ready to take your online presence to the next level?
- Explore our dedicated server options: rental-server.net
- Discover the flexibility of VPS hosting: rental-server.net
- Scale your resources with our cloud server solutions: rental-server.net
Our expert team is available to help you choose the perfect server solution for your business. Contact us today to learn more!
Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States
Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000
Website: rental-server.net
Conclusion
The “DNS Server Not Responding” error can be a frustrating experience, but with a systematic approach, you can identify and resolve the underlying cause. This guide has provided you with a comprehensive set of troubleshooting steps to get you back online quickly and efficiently.
Remember, if you’re looking for reliable and high-performance server solutions in the USA, rental-server.net is your trusted partner. We offer a wide range of dedicated servers, VPS hosting, and cloud servers to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discover the perfect server solution for your business!
DNS Server Not Responding FAQ
1. How Do I Find My DNS Server?
You can find your DNS server settings in your operating system’s network settings.
- On macOS: Go to System Settings > Network > select your active network > Details > DNS. The DNS server addresses are listed under “DNS Servers.” You can also use Terminal and run the command
$ scutil --dns | grep 'nameserver[[0-9]*]'.
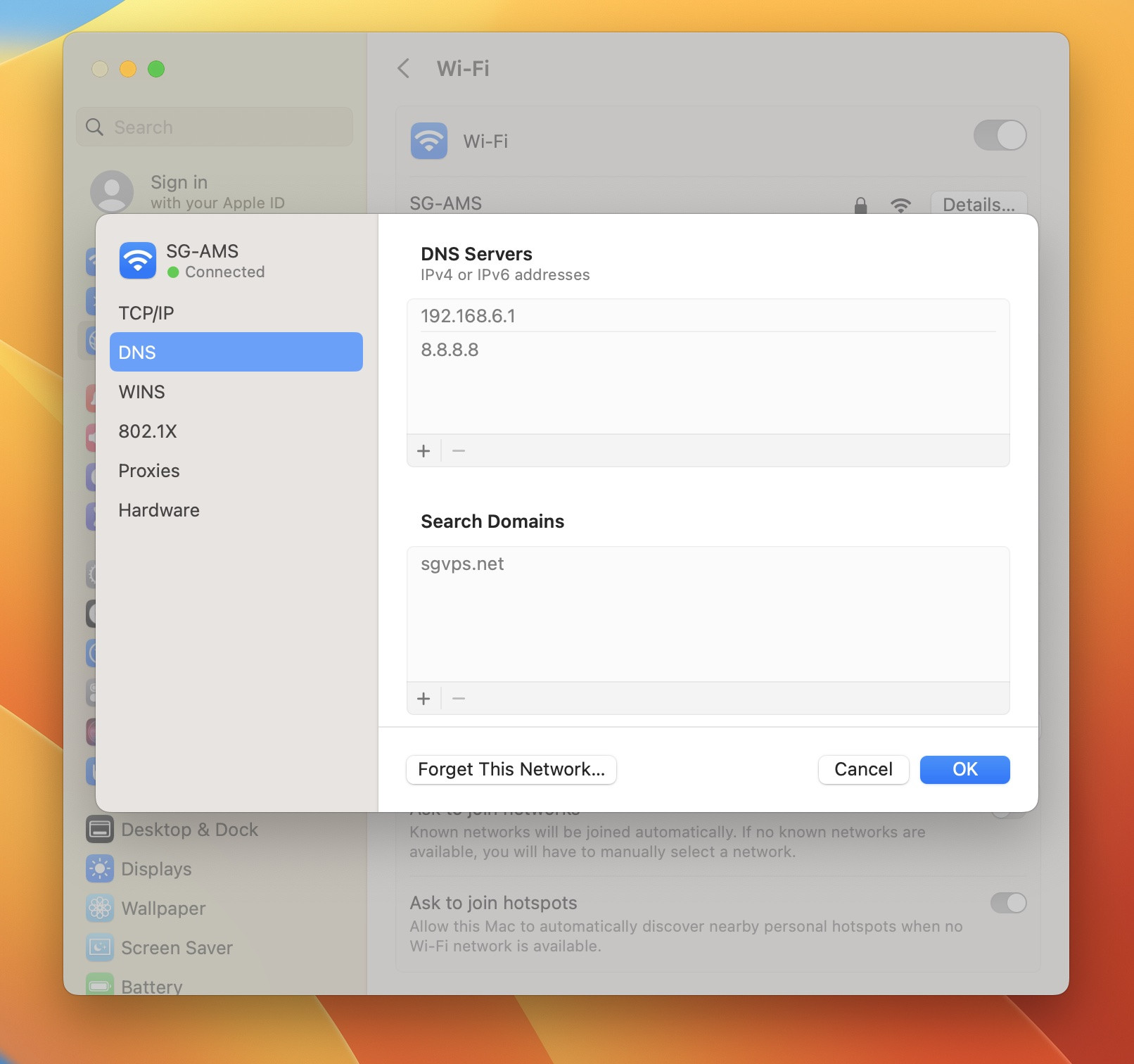 How to find your DNS servers on Mac
How to find your DNS servers on Mac
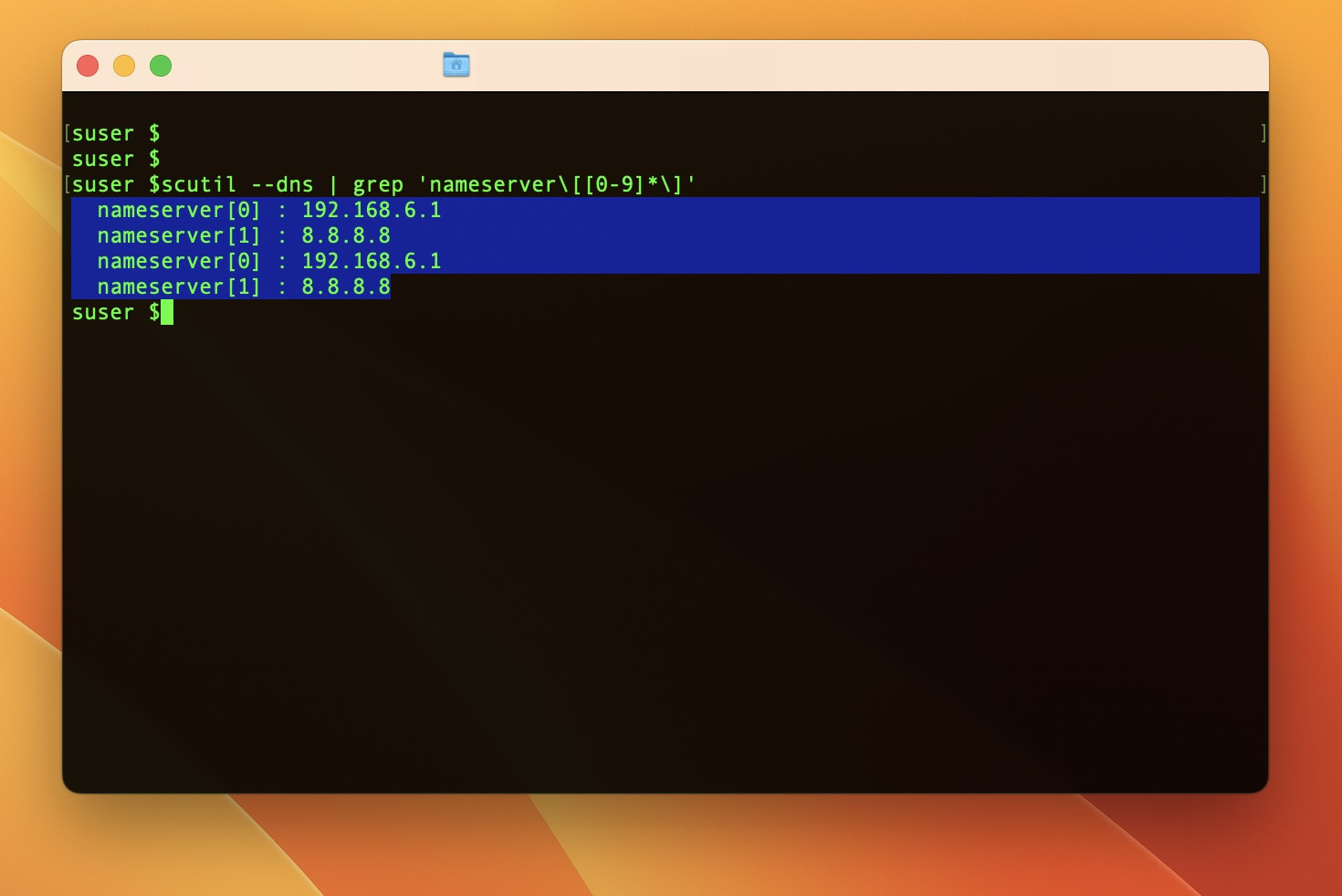 How to find your DNS servers in Terminal on Mac
How to find your DNS servers in Terminal on Mac
- On Windows: Go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > click on your active network > Details. You can also use Command Prompt and run the command
ipconfig /all.
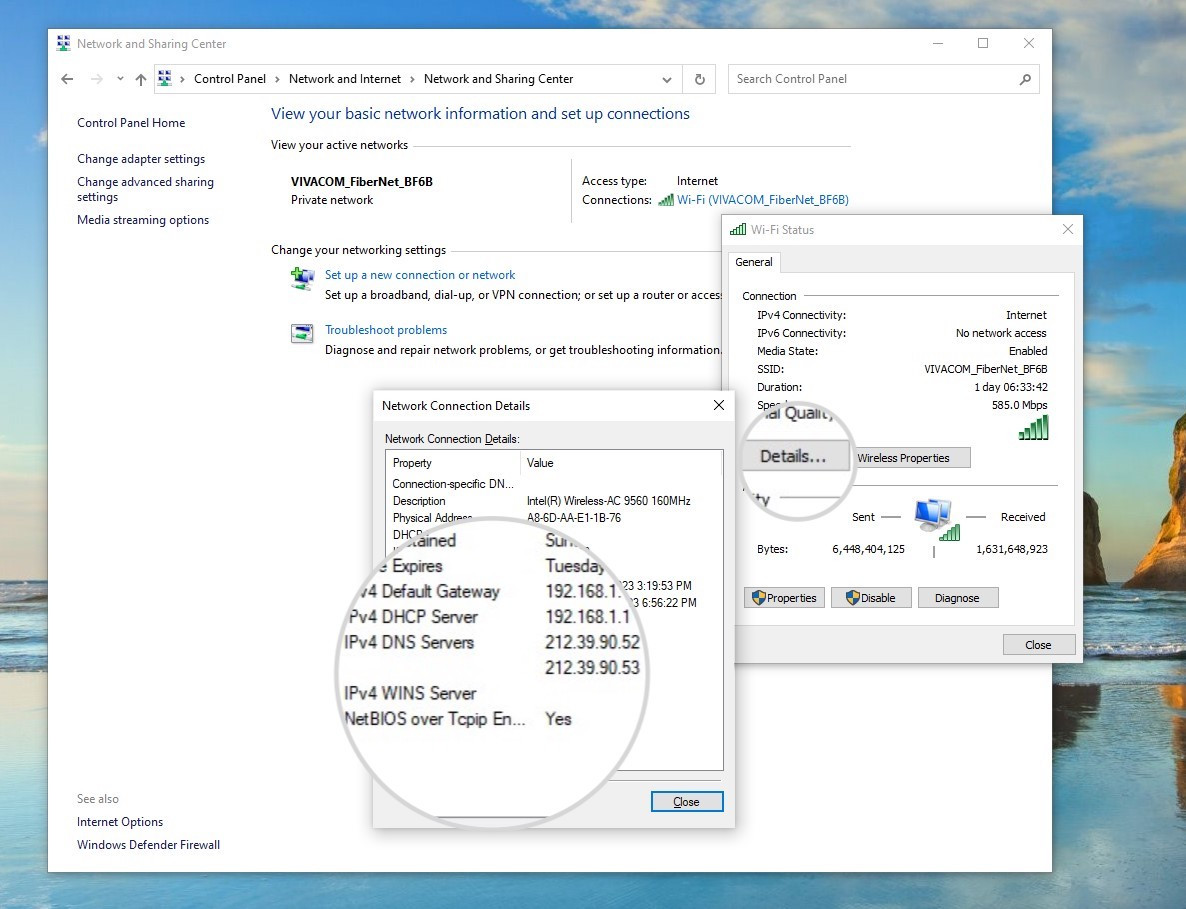 How to find your DNS servers on Windows
How to find your DNS servers on Windows
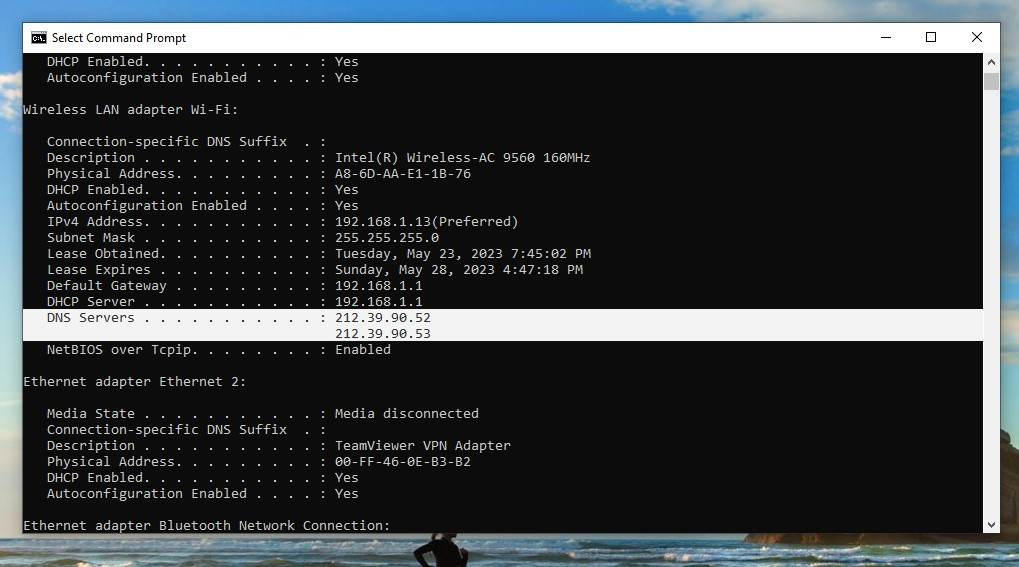 Find your DNS server in Command Prompt on Windows
Find your DNS server in Command Prompt on Windows
2. How Do I Know If I Have DNS Problems?
If the DNS server is down, your computer won’t be able to resolve website addresses. Your browser will display an error message like “This Site Can’t Be Reached” or “Hmm. We’re having trouble finding that site,” often accompanied by an error code like DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN. You can also ping the DNS server addresses to test their responsiveness using Terminal (macOS) or Command Prompt (Windows).
 Ping the DNS server address to check if it is responsive
Ping the DNS server address to check if it is responsive
3. Is It Safe to Reset DNS?
Yes, it is safe to reset your DNS. Flushing your DNS cache periodically is recommended to update the information in your DNS resolver, fix DNS-related errors, and prevent DNS spoofing.