Virtualized Server solutions offer a powerful way to optimize IT infrastructure. At rental-server.net, we provide comprehensive information and solutions to help you navigate the world of server virtualization. By understanding virtualized servers, you can unlock increased efficiency, flexibility, and cost savings for your business, alongside enhanced data protection and streamlined resource allocation.
1. Understanding Virtualized Servers: A Comprehensive Overview
What exactly is a virtualized server, and how does it differ from a traditional physical server?
A virtualized server is a software-defined representation of a physical server, enabling multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine. This abstraction of hardware resources allows for efficient utilization, greater flexibility, and reduced infrastructure costs, making it a cornerstone of modern IT environments. Let’s delve deeper into the mechanics and benefits of virtualized servers.
In a traditional setup, each server typically runs a single operating system and application, leading to underutilization of resources. According to a report by the Uptime Institute, servers in traditional data centers often operate at only 15% to 20% of their capacity. This inefficiency results in wasted processing power, memory, and storage, as well as increased energy consumption and physical space requirements.
Virtualized servers address these issues by introducing a layer of software called a hypervisor. The hypervisor abstracts the underlying hardware from the operating systems and applications, allowing multiple VMs to run concurrently on the same physical server. Each VM operates as an independent entity with its own operating system, applications, and resources.
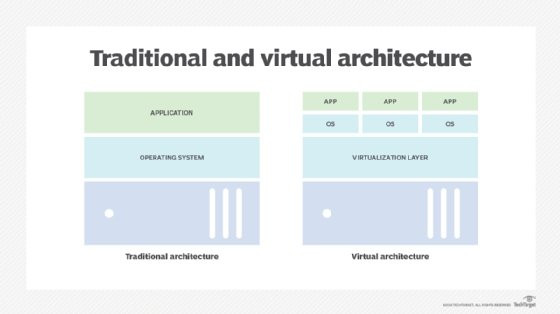 Virtualized Server Architecture
Virtualized Server Architecture
Virtualized servers use software to simulate hardware functionality, enabling multiple operating systems and applications on a single server.
1.1 How Virtualized Servers Work
The core component of server virtualization is the hypervisor, which manages the allocation of physical resources to the VMs. There are two main types of hypervisors:
- Type 1 (Bare-Metal) Hypervisors: These hypervisors run directly on the hardware without an underlying operating system. Examples include VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.
- Type 2 (Hosted) Hypervisors: These hypervisors run on top of an existing operating system. Examples include VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox.
The hypervisor creates a virtual environment in which each VM can operate independently. It virtualizes the CPU, memory, storage, and network resources, providing each VM with its own dedicated allocation. This isolation ensures that one VM’s activities do not interfere with the performance or stability of other VMs on the same physical server.
1.2 Benefits of Virtualized Servers
Virtualized servers offer numerous advantages, including:
- Improved Resource Utilization: By running multiple VMs on a single physical server, organizations can significantly increase resource utilization, reducing waste and maximizing the return on investment.
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Server virtualization leads to lower hardware costs, as fewer physical servers are needed. It also reduces energy consumption, cooling requirements, and physical space, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Increased Flexibility and Scalability: Virtualized servers enable organizations to quickly provision and deploy new VMs as needed, providing greater flexibility and scalability. This agility allows businesses to respond rapidly to changing demands and opportunities.
- Simplified Management: Virtualization platforms offer centralized management tools that simplify the administration of VMs. These tools provide features such as live migration, automated resource allocation, and performance monitoring, making it easier to manage and maintain the virtualized environment.
- Enhanced Availability and Disaster Recovery: Virtualized servers facilitate high availability and disaster recovery solutions. VMs can be easily backed up, replicated, and moved to different physical servers, ensuring business continuity in the event of hardware failures or other disruptions.
1.3 Key Components of a Virtualized Server Environment
Understanding the various components that make up a virtualized server environment is crucial for effective management and optimization:
- Hypervisor: The core software layer that creates and manages virtual machines, allocating hardware resources and ensuring isolation between VMs.
- Virtual Machines (VMs): Independent software containers that run their own operating systems and applications, utilizing virtualized hardware resources provided by the hypervisor.
- Virtual Hardware: The virtualized representations of physical hardware components, such as CPUs, memory, storage, and network interfaces, which are presented to the VMs.
- Management Tools: Software applications that provide centralized management and monitoring of the virtualized environment, including VM provisioning, resource allocation, and performance monitoring.
- Storage Solutions: Storage systems that provide the underlying storage infrastructure for the virtualized environment, supporting various storage protocols and configurations to meet different performance and capacity requirements.
- Networking Components: Virtual switches, routers, and firewalls that enable network connectivity between VMs and the external network, providing secure and efficient communication within the virtualized environment.
By understanding these components and their interactions, IT professionals can effectively design, deploy, and manage virtualized server environments to meet their organization’s specific needs and goals. Rental-server.net provides detailed resources and expert guidance to help you navigate the complexities of server virtualization and optimize your IT infrastructure for maximum performance and efficiency.
2. Identifying Your Search Intent: What Are You Really Looking For?
What are the primary reasons people search for information about virtualized servers?
Understanding the search intent behind the keyword “virtualized server” is crucial for delivering relevant and valuable content. Users typically search for information on virtualized servers for a variety of reasons, ranging from understanding the basic concept to finding specific solutions for their business needs. Here are five key search intents:
- Definition and Explanation: Users want to understand what a virtualized server is, how it works, and its key components. They are looking for clear and concise explanations of the technology.
- Benefits and Advantages: Users are interested in the benefits of using virtualized servers, such as cost savings, improved resource utilization, and increased flexibility. They want to know how virtualized servers can improve their IT infrastructure.
- Types and Options: Users want to learn about the different types of server virtualization, such as bare-metal hypervisors, hosted hypervisors, and containers. They also want to know about the various vendors and products available in the market.
- Use Cases and Applications: Users are looking for real-world examples of how virtualized servers are used in different industries and scenarios. They want to see how virtualized servers can solve specific problems and improve business outcomes.
- Implementation and Management: Users need practical guidance on how to implement and manage virtualized servers, including best practices for deployment, migration, and troubleshooting. They are looking for step-by-step instructions and expert advice.
2.1 Understanding the ‘Why’ Behind the Search
To cater to these diverse search intents, content creators need to provide comprehensive and informative resources that address the specific needs of each type of user. This includes:
- Beginner-Friendly Guides: Clear and concise explanations of the basic concepts and terminology related to virtualized servers.
- In-Depth Analysis: Detailed discussions of the benefits, advantages, and disadvantages of using virtualized servers.
- Comparative Reviews: Objective comparisons of different virtualization technologies, vendors, and products.
- Case Studies: Real-world examples of how organizations have successfully implemented and managed virtualized servers.
- Practical Tutorials: Step-by-step instructions and best practices for deploying, migrating, and troubleshooting virtualized servers.
By understanding the search intent behind the keyword “virtualized server,” content creators can deliver targeted and valuable information that meets the needs of their audience. Rental-server.net is committed to providing comprehensive and informative resources that address the diverse search intents of users interested in server virtualization.
3. Crafting the Perfect Headline: Attract and Engage Your Audience
How do you create a compelling headline that captures the essence of virtualized servers?
A well-crafted headline is crucial for attracting readers and conveying the value of your content. For the topic of virtualized servers, a strong headline should incorporate the primary keyword, address a specific user intent, and create a sense of curiosity or urgency. Here are several headline options:
- What Are The Benefits Of Using A Virtualized Server?
- How Does A Virtualized Server Improve Business Efficiency?
- Virtualized Server: Is It The Right Choice For Your Business?
- What Are The Different Types Of Virtualized Servers Available?
- Virtualized Servers: How To Choose The Best Solution For Your Needs?
- Virtualized Server: Reduce IT Costs And Enhance Performance?
- What Is A Virtualized Server: A Comprehensive Guide For Beginners?
These headlines aim to capture the user’s attention by addressing common questions and concerns related to virtualized servers. They also incorporate the primary keyword and use action-oriented language to encourage clicks.
3.1 Key Elements of an Effective Headline
When crafting a headline for your virtualized server content, consider the following elements:
- Clarity: The headline should clearly communicate the topic of the content and the value it provides to the reader.
- Relevance: The headline should be relevant to the user’s search intent and address their specific needs and interests.
- Keywords: The headline should incorporate the primary keyword and related terms to improve search engine visibility.
- Emotional Appeal: The headline should evoke curiosity, excitement, or urgency to encourage clicks and engagement.
- Brevity: The headline should be concise and easy to read, typically between 7 and 12 words.
By following these guidelines, you can create headlines that capture the attention of your target audience and drive traffic to your virtualized server content. Rental-server.net provides expert advice and resources to help you craft compelling headlines that attract and engage your audience.
4. The AIDA Model: Capturing and Retaining Your Audience’s Attention
How can you use the AIDA model to structure your virtualized server content for maximum impact?
The AIDA model (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action) is a marketing framework that outlines the stages a potential customer goes through before making a purchase or taking a desired action. By structuring your virtualized server content according to the AIDA model, you can effectively capture and retain your audience’s attention, generate interest in your solutions, create a desire for your products or services, and ultimately drive conversions.
4.1 Applying the AIDA Model to Virtualized Server Content
Here’s how to apply the AIDA model to your virtualized server content:
- Attention: Capture the reader’s attention with a compelling headline, an engaging introduction, and visually appealing elements. Use striking images, videos, and infographics to draw the reader in and make them want to learn more.
- Interest: Generate interest by highlighting the key benefits of virtualized servers, such as cost savings, improved resource utilization, and increased flexibility. Provide valuable information, insights, and expert advice that addresses the reader’s specific needs and interests.
- Desire: Create a desire for your virtualized server solutions by showcasing real-world examples, case studies, and testimonials that demonstrate the positive impact of your products or services. Emphasize the unique features, capabilities, and advantages of your offerings.
- Action: Encourage the reader to take action by providing clear and compelling calls to action (CTAs), such as “Contact Us,” “Request a Demo,” or “Get a Free Quote.” Make it easy for the reader to contact you, learn more about your solutions, and make a purchase.
By following the AIDA model, you can create virtualized server content that effectively engages your audience, generates interest in your solutions, creates a desire for your products or services, and ultimately drives conversions. Rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you apply the AIDA model to your content and achieve your marketing goals.
5. Why Virtualized Servers Matter: Understanding the Core Benefits
Why are virtualized servers considered essential for modern IT infrastructure?
Virtualized servers have become a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure due to their ability to optimize resource utilization, reduce costs, and increase flexibility. By abstracting the underlying hardware from the operating systems and applications, virtualized servers enable organizations to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. This leads to significant benefits, including:
- Improved Resource Utilization: Virtualized servers allow organizations to maximize the use of their hardware resources. In traditional environments, servers often sit idle or underutilized, wasting valuable processing power, memory, and storage. With virtualization, multiple VMs can share the same physical resources, ensuring that they are used efficiently.
- Reduced Costs: Virtualization reduces the need for physical servers, leading to lower hardware costs. It also reduces energy consumption, cooling requirements, and physical space, resulting in significant cost savings. These savings can be reinvested in other areas of the business, such as research and development or marketing.
- Increased Flexibility: Virtualized servers provide greater flexibility and agility. New VMs can be quickly provisioned and deployed as needed, allowing organizations to respond rapidly to changing business demands. This agility enables businesses to seize new opportunities and stay ahead of the competition.
- Simplified Management: Virtualization platforms offer centralized management tools that simplify the administration of VMs. These tools provide features such as live migration, automated resource allocation, and performance monitoring, making it easier to manage and maintain the virtualized environment.
- Enhanced Availability: Virtualized servers facilitate high availability and disaster recovery solutions. VMs can be easily backed up, replicated, and moved to different physical servers, ensuring business continuity in the event of hardware failures or other disruptions.
5.1 Addressing the Challenges of Traditional Servers
Before the advent of server virtualization, organizations faced several challenges related to traditional server environments, including:
- Underutilization: Servers often sat idle or underutilized, wasting valuable resources and increasing costs.
- Complexity: Managing a large number of physical servers was complex and time-consuming.
- Inflexibility: Provisioning new servers was a lengthy and cumbersome process.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling up IT infrastructure required significant investments in new hardware.
- High Costs: Hardware, energy, and space costs were high due to the need for multiple physical servers.
Virtualized servers address these challenges by providing a more efficient, flexible, and cost-effective solution for managing IT infrastructure.
5.2 Virtualization as a Cornerstone of Cloud Computing
Server virtualization is also a cornerstone of cloud computing. Cloud providers use virtualization technologies to create and manage virtualized resources that can be accessed on demand. This enables them to offer a wide range of services, such as infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).
By leveraging server virtualization, cloud providers can offer scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions to businesses of all sizes. This has led to the widespread adoption of cloud computing and the transformation of the IT landscape. Rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you understand the benefits of virtualized servers and leverage them to optimize your IT infrastructure.
6. Demystifying Server Virtualization: How Does It All Work?
What is the technical process behind server virtualization, and how does it enable multiple virtual machines?
Server virtualization works by abstracting the underlying hardware from the operating systems and applications, allowing multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server. This abstraction is achieved through a software layer called a hypervisor, which manages the allocation of physical resources to the VMs.
6.1 The Role of the Hypervisor
The hypervisor is the core component of server virtualization. It sits between the physical hardware and the VMs, providing a virtualized environment in which each VM can operate independently. There are two main types of hypervisors:
- Type 1 (Bare-Metal) Hypervisors: These hypervisors run directly on the hardware without an underlying operating system. Examples include VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.
- Type 2 (Hosted) Hypervisors: These hypervisors run on top of an existing operating system. Examples include VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox.
The hypervisor creates a virtualized environment by emulating the hardware resources that each VM requires. This includes the CPU, memory, storage, and network interfaces. The hypervisor then allocates these virtualized resources to each VM, ensuring that they have the necessary resources to run their operating systems and applications.
6.2 Resource Allocation and Management
The hypervisor is responsible for managing the allocation of physical resources to the VMs. It uses a variety of techniques to optimize resource utilization, such as:
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: The hypervisor can dynamically allocate resources to VMs based on their current needs. This ensures that VMs have the resources they need when they need them, without wasting resources on idle VMs.
- Resource Prioritization: The hypervisor can prioritize resources for critical VMs, ensuring that they receive the resources they need even when the physical server is under heavy load.
- Resource Pooling: The hypervisor can pool resources from multiple physical servers, creating a virtualized resource pool that can be used to support a large number of VMs.
By optimizing resource allocation and management, the hypervisor enables organizations to maximize the use of their hardware resources and improve the performance of their applications.
6.3 Isolation and Security
The hypervisor also provides isolation and security for the VMs. Each VM operates in its own isolated environment, preventing it from interfering with other VMs on the same physical server. This isolation ensures that one VM’s activities do not affect the performance or stability of other VMs.
The hypervisor also provides security features to protect the VMs from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. This includes access control, encryption, and intrusion detection. Rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you understand how server virtualization works and how to implement it in your organization.
7. Navigating the Disadvantages: Addressing the Potential Drawbacks
What are the potential disadvantages of using virtualized servers, and how can they be mitigated?
While virtualized servers offer numerous advantages, they also have some potential disadvantages that organizations should consider. These include:
- Performance Overhead: Virtualization introduces a layer of abstraction that can result in some performance overhead. The hypervisor requires resources to manage the VMs, which can reduce the overall performance of the physical server.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing a virtualized environment can be complex, requiring specialized skills and knowledge. Organizations need to invest in training and resources to ensure that their IT staff can effectively manage the virtualized environment.
- Security Risks: Virtualization can introduce new security risks if not properly implemented and managed. VMs can be vulnerable to attacks if they are not properly secured, and the hypervisor itself can be a target for malicious actors.
- Licensing Costs: Virtualization software and operating systems require licenses, which can add to the overall cost of the virtualized environment.
- Single Point of Failure: If the physical server hosting the VMs fails, all of the VMs running on that server will be affected. This can result in significant downtime and data loss.
7.1 Mitigating the Disadvantages
Fortunately, there are several steps that organizations can take to mitigate the potential disadvantages of using virtualized servers:
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Proper resource allocation can minimize the performance overhead associated with virtualization. Organizations should carefully monitor the resource usage of their VMs and adjust the allocation as needed.
- Invest in Training: Organizations should invest in training and resources to ensure that their IT staff has the skills and knowledge to effectively manage the virtualized environment.
- Implement Security Best Practices: Organizations should implement security best practices to protect their VMs from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. This includes using strong passwords, enabling encryption, and implementing intrusion detection systems.
- Consider Licensing Costs: Organizations should carefully consider the licensing costs associated with virtualization software and operating systems when planning their virtualized environment.
- Implement Redundancy: Organizations should implement redundancy to protect against the risk of a single point of failure. This can include using multiple physical servers, implementing failover clustering, and using data replication technologies.
By taking these steps, organizations can mitigate the potential disadvantages of using virtualized servers and realize the full benefits of this technology. Rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you navigate the challenges of server virtualization and implement best practices for your organization.
8. Exploring the Variety: What Types of Server Virtualization Exist?
What are the different approaches to server virtualization, and how do they differ in implementation and performance?
Server virtualization can be implemented using several different approaches, each with its own characteristics and trade-offs. The main types of server virtualization include:
- Full Virtualization: This approach uses a hypervisor to completely abstract the underlying hardware from the VMs. Each VM runs its own operating system and applications in an isolated environment. Full virtualization provides the greatest level of isolation and compatibility but can introduce some performance overhead.
- Paravirtualization: This approach requires the operating systems of the VMs to be modified to work with the hypervisor. This allows the VMs to communicate directly with the hypervisor, reducing the performance overhead associated with full virtualization. However, paravirtualization requires more effort to implement and is not compatible with all operating systems.
- Operating System-Level Virtualization: This approach uses the operating system to create multiple isolated environments, called containers, on a single physical server. Containers share the same operating system kernel but have their own file system, processes, and network interfaces. Operating system-level virtualization provides the highest level of performance and density but offers less isolation than full virtualization.
8.1 Comparing Virtualization Approaches
| Approach | Isolation | Performance | Compatibility | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Virtualization | High | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Paravirtualization | High | High | Low | High |
| Operating System-Level Virtualization | Low | High | Moderate | Low |
The choice of virtualization approach depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. Full virtualization is a good choice for organizations that need a high level of isolation and compatibility. Paravirtualization is a good choice for organizations that need high performance but are willing to modify their operating systems. Operating system-level virtualization is a good choice for organizations that need high density and performance but do not require a high level of isolation.
8.2 Virtualized Containers
Virtualized containers, such as Docker, have gained popularity in recent years. The basic concept of containers is identical to hosted virtualization where a hypervisor is installed atop a host OS, and virtual instances all share the same OS. But the hypervisor layer — for example, Docker and Apache Mesos — is tailored specifically for high volumes of small, efficient VMs intended to share common components or dependencies such as binaries and libraries.
Containers offer a lightweight and portable way to package and deploy applications. They are often used in microservices architectures, where applications are composed of small, independent services that can be deployed and scaled independently. Rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you understand the different types of server virtualization and choose the best approach for your organization.
9. Real-World Examples: Exploring Use Cases for Virtualized Servers
How are virtualized servers used in different industries and scenarios to solve specific business problems?
Virtualized servers are used in a wide range of industries and scenarios to solve specific business problems. Some common use cases include:
- Server Consolidation: Organizations use virtualized servers to consolidate their physical servers, reducing hardware costs, energy consumption, and physical space requirements.
- Test and Development: Virtualized servers provide an ideal environment for testing and developing new applications. Developers can quickly provision and deploy VMs to test their code without affecting the production environment.
- Disaster Recovery: Virtualized servers facilitate disaster recovery solutions by allowing organizations to quickly recover their critical applications and data in the event of a disaster.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud providers use virtualized servers to offer a wide range of services, such as infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).
- Desktop Virtualization: Organizations use virtualized servers to host virtual desktops, allowing users to access their desktops and applications from any device, anywhere.
9.1 Industry-Specific Use Cases
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations use virtualized servers to store and manage patient data, run electronic health record (EHR) systems, and support telemedicine applications.
- Finance: Financial institutions use virtualized servers to process transactions, manage risk, and support online banking applications.
- Education: Educational institutions use virtualized servers to provide students with access to virtual labs, online learning resources, and virtual desktops.
- Retail: Retail organizations use virtualized servers to manage inventory, process orders, and support e-commerce applications.
These are just a few examples of how virtualized servers are used in different industries and scenarios. The specific use cases will vary depending on the needs and requirements of the organization.
9.2 Benefits Across Industries
Regardless of the industry, virtualized servers offer several key benefits:
- Cost Savings: Reduced hardware, energy, and space costs.
- Increased Flexibility: Ability to quickly provision and deploy new VMs.
- Improved Availability: Enhanced disaster recovery and business continuity.
- Simplified Management: Centralized management tools for VMs.
- Enhanced Security: Isolated environments for VMs.
Rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you understand how virtualized servers can be used in your industry and scenario to solve specific business problems.
10. Virtualized Server Management: Best Practices for Optimization
What are the best practices for managing virtualized servers to ensure optimal performance and security?
Managing virtualized servers requires a combination of practical experience, clear policies, conscientious planning, and capable tools. By following these best practices, organizations can ensure optimal performance, security, and reliability of their virtualized environment:
- Plan Your Virtualization Strategy: Before implementing virtualization, develop a clear strategy that outlines your goals, objectives, and requirements. This strategy should include a detailed assessment of your existing infrastructure, applications, and workloads.
- Choose the Right Hypervisor: Select a hypervisor that meets your specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as performance, scalability, compatibility, and licensing costs.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Properly allocate resources to VMs based on their current needs. Monitor resource usage and adjust the allocation as needed to ensure optimal performance.
- Implement Security Best Practices: Implement security best practices to protect your VMs from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. This includes using strong passwords, enabling encryption, and implementing intrusion detection systems.
- Automate VM Management: Automate VM management tasks, such as provisioning, patching, and monitoring, to reduce manual effort and improve efficiency.
- Monitor Performance and Availability: Continuously monitor the performance and availability of your VMs to identify and resolve issues before they impact your business.
- Implement Backup and Disaster Recovery: Implement backup and disaster recovery solutions to protect your VMs from data loss and ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster.
- Regularly Review and Update Your Virtualization Environment: Regularly review and update your virtualization environment to ensure that it is aligned with your business needs and that you are taking advantage of the latest features and technologies.
10.1 Essential Tools for Virtualized Server Management
Several tools can help organizations manage their virtualized servers effectively:
- Hypervisor Management Tools: VMware vCenter Server, Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager, Citrix XenCenter.
- Performance Monitoring Tools: SolarWinds Virtualization Manager, ManageEngine Applications Manager, Veeam One.
- Automation Tools: Microsoft PowerShell, Ansible, Puppet.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery Tools: Veeam Backup & Replication, Acronis Backup, Veritas Backup Exec.
By using these tools and following the best practices outlined above, organizations can ensure that their virtualized environment is well-managed and that they are realizing the full benefits of server virtualization.
10.2 Seeking Professional Guidance
For organizations new to virtualization or those seeking to optimize their existing environment, seeking professional guidance can be invaluable. Rental-server.net offers expert consulting services to help you develop a virtualization strategy, choose the right hypervisor, implement best practices for management, and optimize your virtualized environment for peak performance and security. Our team of experienced virtualization experts can provide tailored solutions to meet your specific needs and help you achieve your business goals. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you succeed with virtualized servers. Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States. Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000. Website: rental-server.net.
11. Migration Strategies: How to Move to Virtualized Servers Smoothly
What are the key steps and considerations for migrating from physical servers to a virtualized environment?
Migrating from physical servers to a virtualized environment can be a complex and challenging process, but it can also deliver significant benefits in terms of cost savings, flexibility, and scalability. To ensure a smooth and successful migration, organizations should follow these key steps:
-
Assess Your Environment: Conduct a thorough assessment of your existing physical servers, applications, and workloads. Identify the servers that are good candidates for virtualization and those that are not.
-
Plan Your Migration: Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines the steps you will take to migrate your servers to the virtualized environment. This plan should include a timeline, resource allocation, and testing procedures.
-
Choose a Migration Method: Select a migration method that is appropriate for your environment and your applications. Common migration methods include:
- Physical-to-Virtual (P2V): Converting a physical server directly into a virtual machine.
- Replication: Replicating data from a physical server to a virtual machine.
- Reinstallation: Reinstalling the operating system and applications on a new virtual machine.
-
Prepare Your Virtualization Infrastructure: Ensure that your virtualization infrastructure is properly configured and ready to support the migrated servers. This includes installing and configuring the hypervisor, setting up storage and networking, and configuring security settings.
-
Migrate Your Servers: Migrate your servers to the virtualized environment using the chosen migration method. Monitor the migration process closely and troubleshoot any issues that arise.
-
Test Your Migrated Servers: Thoroughly test your migrated servers to ensure that they are functioning properly and that all applications are working as expected.
-
Optimize Your Virtualized Environment: Optimize your virtualized environment to ensure optimal performance and resource utilization. This includes adjusting resource allocation, configuring security settings, and implementing monitoring tools.
11.1 Key Considerations for Migration
- Application Compatibility: Ensure that your applications are compatible with the virtualized environment.
- Data Integrity: Protect the integrity of your data during the migration process.
- Downtime: Minimize downtime during the migration process.
- Security: Maintain security during and after the migration process.
- Testing: Thoroughly test your migrated servers to ensure that they are functioning properly.
11.2 Tools for Seamless Migration
Several tools can help organizations migrate from physical servers to a virtualized environment:
- VMware vCenter Converter: Converts physical servers and virtual machines to VMware virtual machines.
- Microsoft Virtual Machine Converter: Converts physical servers and virtual machines to Hyper-V virtual machines.
- PlateSpin Migrate: Migrates physical servers and virtual machines to various virtualization platforms.
Rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you plan and execute a smooth and successful migration to virtualized servers.
12. Vendors and Products: Exploring Virtualized Server Options
Which vendors offer virtualized server solutions, and what are the key features of their products?
Several vendors offer virtualized server solutions, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the leading vendors include:
- VMware: VMware is the leading vendor of virtualization software, offering a wide range of products for server virtualization, desktop virtualization, and cloud computing. VMware’s flagship product, vSphere, is a comprehensive virtualization platform that provides advanced features for resource management, security, and availability.
- Microsoft: Microsoft offers Hyper-V, a virtualization platform that is integrated into Windows Server. Hyper-V is a popular choice for organizations that are already standardized on Microsoft Windows Server platforms.
- Citrix: Citrix offers XenServer, an open-source virtualization platform that is commercially supported by Citrix. XenServer is a popular choice for organizations that need a flexible and cost-effective virtualization solution.
- Red Hat: Red Hat offers Red Hat Virtualization, an open-source virtualization platform that is based on the Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) hypervisor. Red Hat Virtualization is a popular choice for organizations that are standardized on Linux environments.
12.1 Comparing Key Features
| Feature | VMware vSphere | Microsoft Hyper-V | Citrix XenServer | Red Hat Virtualization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypervisor Type | Bare-metal | Bare-metal | Bare-metal | Bare-metal |
| Operating System Support | Wide | Windows | Wide | Linux |
| Resource Management | Advanced | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Security Features | Advanced | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Availability Features | Advanced | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Management Tools | Advanced | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Licensing Costs | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
The choice of virtualization vendor depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. VMware vSphere is a good choice for organizations that need a comprehensive virtualization platform with advanced features. Microsoft Hyper-V is a good choice for organizations that are already standardized on Microsoft Windows Server platforms. Citrix XenServer is a good choice for organizations that need a flexible and cost-effective virtualization solution. Red Hat Virtualization is a good choice for organizations that are standardized on Linux environments.
12.2 Making the Right Choice
Rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you evaluate the different virtualization vendors and products and choose the best solution for your organization.
13. The Future of Virtualization: Trends and Innovations to Watch
What are the emerging trends and innovations in server virtualization, and how will they shape the future of IT infrastructure?
Server virtualization has come a long way in the last two decades, and it continues to evolve at a rapid pace. Some of the emerging trends and innovations in server virtualization include:
- Cloud Integration: Server virtualization is becoming increasingly integrated with cloud computing, enabling organizations to seamlessly move workloads between on-premises data centers and the cloud.
- Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI): HCI combines compute, storage, and networking resources into a single, integrated system, simplifying management and reducing costs.
- Containers: Containers provide a lightweight and portable way to package and deploy applications, enabling organizations to improve application velocity and efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to automate and optimize virtualization management tasks, such as resource allocation, performance monitoring, and security.
- Edge Computing: Server virtualization is being extended to the edge of the network, enabling organizations to process data closer to the source and improve application performance.
13.1 The Impact of These Trends
These trends and innovations are shaping the future of IT infrastructure by:
- Increasing Flexibility: Organizations can quickly provision and deploy new resources as needed.
- Improving Efficiency: Resources are utilized more efficiently, reducing costs and improving performance.
- Simplifying Management: Management tasks are automated and streamlined, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
- Enhancing Security: Security is improved through the use of AI-powered security tools and techniques.
- Enabling New Use Cases: Server virtualization is being extended to new environments, such as the edge of the network, enabling organizations to support new use cases.
13.2 Staying Ahead of the Curve
To stay ahead of the curve, organizations should:
- Embrace Cloud Integration: Integrate their on-premises virtualization environment with the cloud.
- Explore HCI: Consider adopting HCI to simplify management and reduce costs.
- Adopt Containers: Use containers to improve application velocity and efficiency.
- Leverage AI: Leverage AI to automate and optimize virtualization management tasks.
- Extend Virtualization to the Edge: Extend virtualization to the edge of the network to support new use cases.
rental-server.net provides expert guidance and resources to help you understand the emerging trends and innovations in server virtualization and prepare for the future of IT infrastructure.
14. FAQ: Answering Your Burning Questions About Virtualized Servers
What are the most frequently asked questions about virtualized servers?
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about virtualized servers:
- What is a virtualized server?
A virtualized server is a software-defined representation of a physical server, enabling multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine. - How does server virtualization work?
Server virtualization works by abstracting the underlying hardware from the operating systems and applications, allowing multiple VMs to run on a single physical server. - What are the benefits of using virtualized servers?
The benefits of using virtualized servers include improved resource utilization, reduced costs, increased flexibility, simplified

