In today’s fast-paced digital world, data is the lifeblood of every business. Ensuring the integrity and accessibility of this data is paramount. Server Backup has transitioned from a mere option to an indispensable necessity for maintaining business continuity and robust data protection. Whether you are a small business owner, manage IT infrastructure for a large enterprise, or provide managed services, a deep understanding of effective server backup strategies is crucial. It can be the shield that protects you from potentially devastating downtime and irretrievable data loss.
This comprehensive guide delves into five actionable tips for server backup, designed to empower you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. You’ll learn how to establish and manage backup processes that are precisely tailored to your unique requirements, industry-specific regulations, and broader organizational goals.
 Server-Backup-Resources
Server-Backup-Resources
1) Step-by-Step Guide: How to Back up Your Server Effectively
Creating a robust server backup strategy is a two-pronged approach. It requires automation to ensure consistency and minimize human error, and regular review to adapt to evolving data landscapes and business needs. This proactive strategy significantly enhances your chances of swift data and system recovery in the face of data loss incidents, such as accidental deletions, hardware failures, or sophisticated ransomware attacks.
Here’s a structured, step-by-step approach to effective server backup:
-
Identify and Prioritize Critical Data Assets: Not all data is created equal when it comes to backups. Begin by pinpointing the data that is most vital to your business operations. This typically includes essential files, core databases, critical system configurations, and application data. Remember, data prioritization is not a one-time task. Regularly re-evaluate your critical data assets to incorporate new applications, evolving file structures, and expanding datasets. This dynamic approach ensures your backup strategy remains aligned with your current business priorities.
-
Select Optimal Backup Destinations: Choosing the right backup destination is a critical decision. Your options broadly fall into two categories: local storage (such as external hard drives or network-attached storage (NAS)) and cloud-based storage. Many organizations today are adopting a hybrid approach, strategically blending both local and cloud destinations. In fact, numerous governmental and industry compliance standards mandate that businesses maintain both on-site and off-site backups to ensure comprehensive data redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities. The hybrid model offers the advantage of faster local restores for day-to-day recovery needs, combined with the security and accessibility of offsite cloud backups for disaster scenarios.
-
Establish a Consistent Backup Schedule: A well-defined backup schedule is the backbone of any reliable server backup strategy. The frequency of your backups should be carefully determined based on your business’s Recovery Point Objective (RPO) – the maximum acceptable data loss in the event of an incident. For business-critical data, consider daily, or even hourly, backups to both local and offsite storage locations. Less critical data might be adequately protected with weekly backups. Crucially, automate your backup scheduling to eliminate the risk of human error and ensure backups are executed consistently and reliably at predetermined times. Automation minimizes the chance of backups being accidentally skipped or forgotten, providing continuous data protection.
-
Rigorous Testing of the Backup and Restore Process: Having backups is only half the battle. You must verify that these backups are functional and that you can reliably restore your data when needed. Regularly conduct test restores to confirm the integrity of your backups and the efficiency of your recovery procedures. This step is often overlooked but is absolutely vital. Testing not only validates that your backups are working correctly but also familiarizes your IT team with the recovery process, ensuring a smoother and faster recovery in a real data loss scenario. This proactive testing significantly reduces downtime and data loss impact.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Log Review: Proactive monitoring of your server backup processes is essential for identifying and resolving potential issues before they escalate. Consistently monitor backup logs to ensure all backup jobs are running smoothly and successfully. Regular log reviews can reveal errors, failures, or storage capacity issues that might otherwise go unnoticed. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly prevents data protection gaps. Imagine discovering weeks into a data loss event that your backup storage had been malfunctioning – regular monitoring prevents such scenarios.
A thoughtfully planned, technologically sound, and diligently managed server backup strategy is the cornerstone of business resilience. With such a strategy in place, the recovery time following a data loss incident becomes the primary factor separating organizations from swiftly resuming normal business operations.
To delve deeper into constructing a comprehensive backup and recovery strategy tailored to your specific business requirements, explore our detailed whitepaper: “How to Build a Better Backup Strategy.”
2) Understanding File vs. System Server Backup Approaches
Choosing the right type of server backup is crucial, and understanding the difference between file-level and system-level (image-based) backups is fundamental to making informed decisions.
File Backup Explained
File backup focuses on selecting and backing up specific files and folders that you designate. It meticulously copies these chosen items and tracks any changes made to them since the last backup. File backup is renowned for its simplicity and ease of use, especially when it comes to restoring individual files or folders. If you need to recover a specific document or a directory of files, file backup allows for granular recovery without needing to restore the entire system.
Typically, file backups are stored in a compressed, proprietary format. This means that the same software used to create the backup is required to restore the data. The backup process usually begins with an initial full backup of all selected data, followed by incremental or differential backups that capture only the changes made since the last full or incremental backup.
For example, NovaBACKUP utilizes an efficient “incremental forever” backup scheme. In this approach, the first backup creates a full copy of all selected files. Subsequent backups then only transfer the changes at the file or block level, significantly reducing backup time and storage space. This method allows you to maintain multiple recovery points, enabling you to restore files from different points in time, even weeks or months in the past, depending on your retention settings. This versioning capability is invaluable for recovering from accidental file modifications or deletions.
Image Backup: A System-Wide Approach
Image-based backup, also known as system image backup, disk image backup, or disaster recovery backup, takes a holistic approach. It creates a complete snapshot of your entire server system, including the operating system, installed applications, system settings, and all data. Think of it as a mirror image of your server at a specific point in time. Image backups are often performed periodically in addition to regular file backups to provide a comprehensive disaster recovery solution.
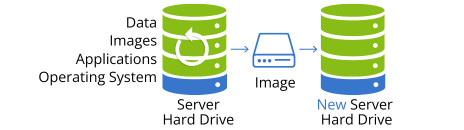 Image-Backup
Image-Backup
The primary advantage of image backup is rapid system recovery. In a disaster scenario where your entire server fails or becomes corrupted, you can quickly restore the entire system to a new server (even one with different hardware) exactly as it was at the time of the backup. This significantly minimizes downtime and gets your systems back online quickly. Some advanced backup solutions offer the capability to store image backups as virtual hard disks (VHD/VHDX). These virtual disks can be directly mounted as virtual machines using hypervisors like Hyper-V, further accelerating access to critical system information and data during a recovery process. This feature is particularly beneficial for disaster recovery drills and minimizing recovery time objectives (RTOs).
 Server-stack-1
Server-stack-1
3) Local Server Backup Storage Options: Choosing the Right Media
Selecting the appropriate storage device for your local server backups is a critical decision with significant implications for backup performance, reliability, and cost. It’s important to understand that a robust backup strategy typically involves more than just setting up a single storage device like a Network Attached Storage (NAS) unit. A truly secure and dependable backup solution often utilizes multiple backup destinations and storage types, incorporating the principles of the 3-2-1 rule (discussed later).
When evaluating local server backup storage options, choose devices that align with your specific environment, budget, and scalability needs. For instance, backing up a single physical server might be efficiently handled by a direct-attached hard drive or solid-state drive, whereas a larger, more complex infrastructure might benefit from a high-performance NAS. Regardless of the chosen media, scalability is a key consideration. Your storage solution should be able to expand seamlessly as your data volumes grow over time.
Here’s a concise overview of common local backup storage options, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages:
External Hard Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SSDs), and USB Drives
Advantages: External HDDs, SSDs, and USB drives are known for their ease of use and plug-and-play convenience. They offer fast data transfer rates and high storage capacities at a relatively low cost per gigabyte. They are particularly suitable for small businesses or individual servers with moderate data volumes.
Disadvantages: These devices are physically vulnerable. Hard disk drives (HDDs) are especially susceptible to damage from drops or impacts. They also pose a security risk as they are easily portable and can be stolen, leading to potential data breaches if not properly secured and encrypted.
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
Advantages: NAS devices provide centralized network-accessible storage, making them ideal for backing up multiple servers or workstations. Many NAS units offer built-in redundancy features like RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), which protects against data loss due to drive failures. They also provide centralized management and access control.
Disadvantages: NAS devices typically have a higher initial purchase cost compared to external drives. Setting up and managing a NAS often requires some level of technical expertise, particularly for configuring network settings, user permissions, and advanced features.
For a deeper dive into the benefits of NAS for your backup strategy, explore our “Essential Guide to NAS as Backup Storage for SMBs.”
A Crucial Note on Backup Appliances: If you are considering a dedicated backup appliance that bundles hardware and backup software, ensure that the appliance offers flexibility in terms of storage destinations. Critically, it should seamlessly integrate with other storage options, including cloud storage, to enable a well-rounded and resilient backup strategy that adheres to best practices like the 3-2-1 rule.
 Cloud-Storage-Options
Cloud-Storage-Options
4) Offsite and Cloud Server Backup: Embracing the 3-2-1 Rule
The 3-2-1 backup rule is a cornerstone of modern data protection strategies and is frequently cited as a best practice for ensuring backup reliability and recoverability.
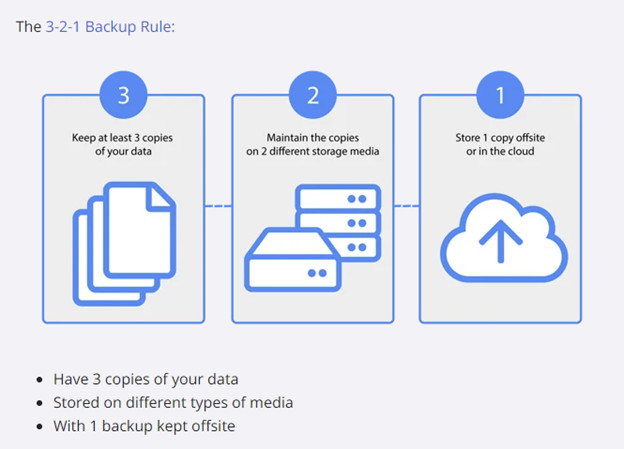 3-2-1-rule
3-2-1-rule
The 3-2-1 rule elegantly states: maintain 3 copies of your data, on 2 different types of storage media, with 1 copy stored offsite. This rule addresses various data loss scenarios, from hardware failures to site-wide disasters. The “offsite” component is particularly crucial for safeguarding against localized disasters that could affect your primary location.
Cloud-based storage has revolutionized offsite backup, making it significantly more convenient and cost-effective for businesses of all sizes. Cloud backups provide robust protection against a wide range of threats, including floods, fires, earthquakes, and other natural disasters, as well as cyberattacks that could compromise on-premises infrastructure.
When evaluating cloud backup for your servers, consider these key factors:
-
Scalability: Cloud storage offers unparalleled scalability. You can easily scale your storage capacity up or down based on your fluctuating data volumes. You eliminate the need for upfront hardware investments and the ongoing management of physical storage infrastructure. This pay-as-you-go model is particularly advantageous for businesses experiencing rapid data growth or seasonal data fluctuations.
-
Disaster Recovery: Cloud backups are inherently offsite, providing a critical layer of protection against localized disasters that could cripple your primary site. In the event of a fire, flood, or other catastrophic event at your office, your cloud backups remain safe and accessible. You can restore your servers and data from virtually anywhere with an internet connection, enabling business continuity even in the face of significant disruptions.
-
Cost Considerations: Cloud backup typically operates on a subscription-based model, offering predictable and manageable operating expenses (OpEx). This eliminates large capital expenditures (CapEx) associated with purchasing and maintaining on-premises backup infrastructure. However, carefully review cloud backup pricing models and be mindful of potential data transfer fees, egress charges (fees for retrieving data), and hidden costs related to bandwidth usage. Optimize your backup strategy to minimize these costs while maintaining adequate data protection.
-
Speed of Recovery: Restoring data from local backups is generally faster than restoring from the cloud, especially for large datasets. Cloud restore speeds are heavily dependent on your internet bandwidth. A hybrid backup solution, strategically combining local and cloud backups, offers an optimal balance. Keep the most recent, frequently accessed backups locally for rapid restores, and leverage cloud backups for long-term retention, disaster recovery, and offsite protection. This hybrid approach provides the speed of local restores for day-to-day needs and the resilience of cloud backups for disaster scenarios.
In conclusion, the optimal approach is rarely “local backup or cloud backup,” but rather “local backup and cloud backup.” By consistently backing up to both local and cloud storage, you harness the speed and convenience of local access with the redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities of an offsite cloud copy.
Advanced backup solutions, such as NovaBACKUP, empower you to seamlessly integrate local and cloud backups within a single “hybrid backup” job. This unified approach streamlines backup management, saves time, and enhances overall efficiency.
To further explore the advantages of cloud backup and its role in maximizing data protection, consult our whitepaper: “Leverage Cloud Backup for Maximum Data Protection.”
5) Enhancing Security for Your Server Backups: Fortifying Against Threats
Beyond implementing redundant backup locations, securing your server backups against unauthorized access and cyber threats is paramount, especially in the face of escalating ransomware attacks.
While a backup solution alone cannot prevent a ransomware attack, it serves as your last line of defense, enabling rapid data recovery without succumbing to ransom demands. To bolster the security of your backups and ensure their integrity even after a cyber incident, consider implementing these vital security measures:
- Encryption: Securing Data at Rest and in Transit: Encryption is a fundamental security practice for protecting your backup data. Encrypting backups both in transit (during transfer to storage) and at rest (while stored) renders the data unreadable to unauthorized individuals. While sophisticated ransomware may still encrypt the already encrypted backup files, encryption prevents attackers from accessing and exfiltrating your sensitive backup data in a readable format.
In a sobering statistic, 30% of ransomware attacks that involved data encryption also resulted in data theft. Source: Sophos 2023 Ransomware Report This underscores the critical importance of encryption to protect data confidentiality and prevent data breaches alongside data recovery.
- Regular Software Updates: Maintaining a Secure Environment: Maintaining up-to-date software is crucial for minimizing security vulnerabilities. Regularly apply software updates to your backup software, operating systems, and all applications running on your servers. These updates often include critical security patches that address known vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats. Ensure your backup software vendor provides ongoing updates for bug fixes, compatibility with the latest operating systems and applications, and performance enhancements. A proactive approach to software updates is essential for maintaining a secure and resilient backup environment.
 Backup-files
Backup-files
Extra Tip: Key Considerations When Selecting a Server Backup Solution
Choosing the right server backup solution is a critical decision that directly impacts your data protection posture. With a plethora of options available in the market, selecting the solution that best aligns with your specific needs can be challenging.
In addition to the server backup strategies discussed above, consider these key factors when evaluating backup software for your servers:
-
Real-time Reporting and Alerting: Proactive monitoring and timely alerts are essential for ensuring backup success and identifying potential issues promptly. Your backup solution should provide real-time reporting on backup job status and offer flexible alert configurations, including email notifications. Ideally, you should be able to set up granular alerts for individual backup jobs, as well as receive daily, weekly, or monthly summary reports providing a consolidated overview of your backup environment.
-
Competent Local Support: When you encounter technical issues or require assistance with your backup solution, access to responsive and knowledgeable technical support is invaluable. Prioritize backup vendors that offer local support teams staffed by trained professionals who understand your environment and can provide effective and timely assistance. Avoid solutions that rely solely on generic, overseas call centers with limited technical expertise. Local support ensures you receive the personalized and expert help you need, when you need it most.
This list is not exhaustive, and your specific business requirements may necessitate considering additional factors when selecting a server backup solution.
At NovaBACKUP, we specialize in providing robust and reliable backup and restore software tailored to meet the diverse needs of businesses. We are dedicated to helping you find the optimal server backup solution for your organization. Please don’t hesitate to contact us for a no-obligation consultation.
