Encountering the dreaded blue screen with the error code 0xc000000e on your Windows Server 2008 R2 system can be a frustrating experience. This error, often accompanied by the message “The selected entry could not be loaded because the application is missing or corrupt,” indicates a problem preventing Windows from booting correctly. Specifically, it points to issues with winload.exe, a critical boot file. This article will guide you through the common causes of this Server 2008 R2 Status 0xc000000e error and provide detailed, step-by-step solutions to get your server back online.
Understanding the Windows Server 2008 R2 Status 0xc000000e Error
The error message itself clearly states that the boot process is failing because a necessary application, in this case winload.exe, is either missing or corrupted. Winload.exe is the Windows Boot Loader application, responsible for loading the operating system kernel. When this file is inaccessible or damaged, the boot process grinds to a halt, resulting in the status 0xc000000e error.
Common Causes of the 0xc000000e Error
Several factors can lead to the server 2008 r2 status 0xc000000e error. Understanding these causes is the first step towards effective troubleshooting:
- Missing or Corrupt Boot Files: Essential boot files, including
winload.exeitself, might be accidentally deleted, corrupted by disk errors, or damaged during system operations. - Boot Configuration Data (BCD) Issues: The BCD stores boot configuration parameters. Corruption or misconfiguration within the BCD can prevent Windows from locating and loading the necessary boot files.
- Master Boot Record (MBR) or Boot Sector Corruption: Damage to the MBR or boot sector of the hard drive can disrupt the initial stages of the boot process, leading to the 0xc000000e error.
- Recent Hardware Changes: Newly installed or changed hardware components can sometimes cause boot issues if the operating system doesn’t recognize or properly configure them.
- Read-Only Disk Volume: If the system volume becomes inadvertently set to read-only, Windows cannot write necessary boot information, hindering the boot process.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Resolve Error 0xc000000e
The following solutions are presented in increasing order of complexity, starting with the most common and straightforward fixes.
1. Startup Repair via Command Prompt
Windows Server 2008 R2’s Startup Repair tool can automatically diagnose and fix many boot problems, including those related to registry corruption and file-based errors. Here’s how to access it through the command prompt:
-
Boot from Windows Server 2008 or R2 Installation Media: Insert your Windows Server 2008 R2 DVD or USB and boot your server from it.
-
Navigate to Repair Options: On the initial setup screen, select your language and keyboard settings, then click “Next”. In the subsequent screen, click “Repair your computer” located in the bottom-left corner.
-
Access Command Prompt: In the “System Recovery Options” window, choose your Windows installation and click “Next”. Then, select “Command Prompt” from the available tools.
-
Run Startup Repair: In the command prompt, type the following command and press Enter:
cd X:sourcesrecovery startrep.exe(Note:
X:represents the drive letter of your installation media. It might be different depending on your system configuration.)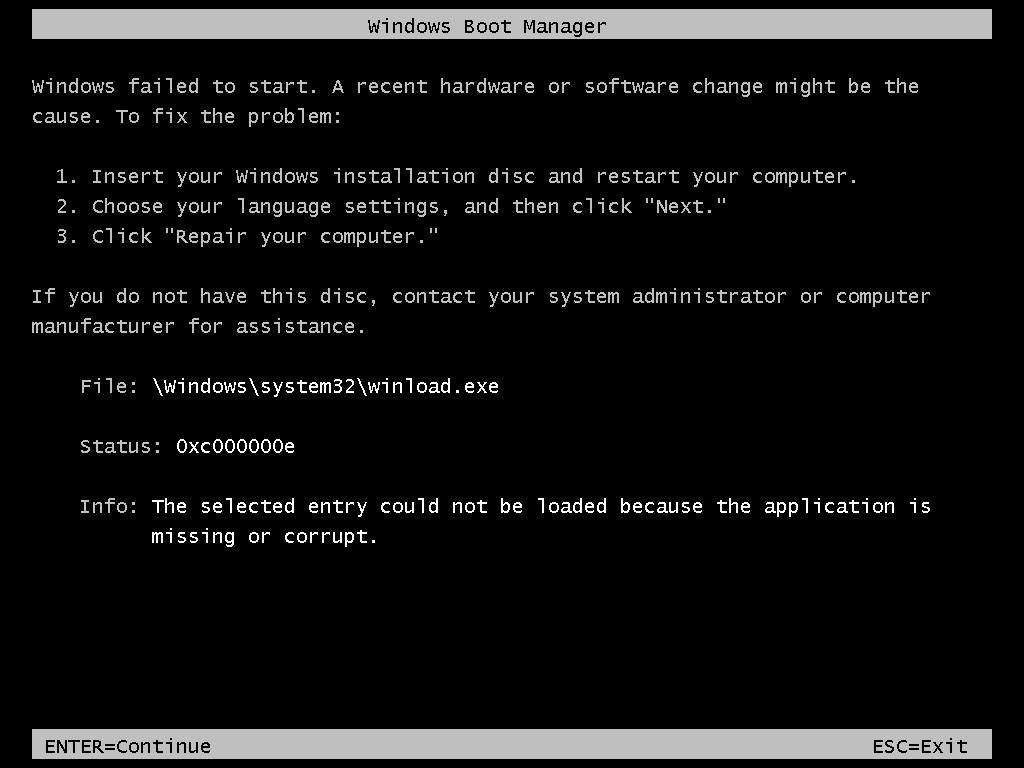 Windows Server 2008 R2 boot error screen displaying status code 0xc000000e and the message 'The selected entry could not be loaded because the application is missing or corrupt.'
Windows Server 2008 R2 boot error screen displaying status code 0xc000000e and the message 'The selected entry could not be loaded because the application is missing or corrupt.'Startup Repair will scan your system for issues and attempt to fix them automatically. This process may take some time.
2. System File Checker (SFC) Scan
The System File Checker (SFC) is a powerful utility that can scan for and restore corrupted system files, including winload.exe and other critical boot components.
-
Boot to Command Prompt (as described in Startup Repair steps 1-3).
-
Run SFC Scan: In the command prompt, execute the following command:
SFC.EXE /scannow /offbootdir=c: /offwindir=c:windows(Note:
c:is assumed to be your system drive letter. Adjust it if your system drive is assigned a different letter.)This command instructs SFC to scan all protected system files and replace corrupted files with cached copies. The
/offbootdirand/offwindirparameters are essential when running SFC from the recovery environment, as they specify the location of the offline boot directory and Windows directory, respectively. -
Exit and Reboot: Once the SFC scan is complete, type
exitand press Enter to close the command prompt. Then, restart your server to see if Windows boots normally.
3. Diskpart and Bootrec Commands for Disk and Boot Record Issues
If the previous steps fail, the issue might stem from disk-related problems, such as a read-only volume or corruption in the MBR or boot sector. Diskpart and Bootrec are command-line tools to address these scenarios.
-
Boot to Command Prompt (as described in Startup Repair steps 1-3).
-
Use Diskpart to Check and Correct Read-Only Volume:
- Type
diskpartand press Enter to start the Diskpart utility. - Type
list volumeand press Enter to display a list of volumes on your system. - Identify your system volume (usually the largest one and likely labeled with a drive letter). Note the volume number.
- Type
select volume #(replace#with the volume number of your system volume) and press Enter. - Type
attribute volumeand press Enter to view the volume’s attributes. Check if “Read-only” is set to “Yes”. - If “Read-only” is “Yes”, clear the read-only attribute by typing
att vol clear readonlyand pressing Enter. - You can also clear other attributes like hidden, no default drive letter, and shadow copy using commands like
att vol clear hidden,att vol clear nodefaultdriveletter, andatt vol clear shadowcopy. - Assign a drive letter if needed:
assign letter=c:(or your desired letter). - Type
exitand press Enter to exit Diskpart.
- Type
-
Use Bootrec to Repair MBR and BCD:
- In the command prompt (after exiting Diskpart), use the Bootrec tool to repair the MBR, boot sector, and rebuild the BCD. Execute the following commands one by one, pressing Enter after each:
bootrec /fixmbr bootrec /fixboot bootrec /rebuildbcd bootrec /fixmbrwrites a new MBR to the system partition.bootrec /fixbootwrites a new boot sector to the system partition.bootrec /rebuildbcdscans all disks for Windows installations and allows you to add them to the BCD.
- In the command prompt (after exiting Diskpart), use the Bootrec tool to repair the MBR, boot sector, and rebuild the BCD. Execute the following commands one by one, pressing Enter after each:
-
Reboot the Server: After running Bootrec commands, type
exitand press Enter to close the command prompt. Restart your server and check if the boot error is resolved.
4. BCD Editing via Bcdedit
In some cases, directly editing the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) might be necessary, especially if the boot device or OS device settings are incorrect.
-
Boot to Command Prompt (as described in Startup Repair steps 1-3).
-
Use Bcdedit to Set Boot Devices: In the command prompt, use the
bcdedittool to ensure the boot device and OS device are correctly pointing to your system partition. Execute the following commands:bcdedit /set {default} device partition=c: bcdedit /set {default} osdevice partition=c: bcdedit /set {bootmgr} device partition=c:(Again, replace
c:with your system drive letter if it’s different.) -
Re-run Startup Repair (Optional): After editing BCD entries, you can try running Startup Repair again (
cd X:sourcesrecovery, thenstartrep.exe) as it might now be more effective with the corrected BCD settings. -
Reboot the Server: Type
exitand press Enter, then restart your server.
Conclusion
The server 2008 r2 status 0xc000000e error can be a significant hurdle, but by systematically following these troubleshooting steps, you can often resolve the issue without resorting to drastic measures like system restoration or rebuilding the server. Remember to proceed methodically through each solution, testing after each step to determine if the error has been resolved. By understanding the potential causes and applying the appropriate fixes, you can effectively recover your Windows Server 2008 R2 system and minimize downtime.
