Are you looking to create your own Minecraft Bedrock server on your PC? With How To Host A Bedrock Server On Pc, you can easily set up a personalized gaming experience for you and your friends. At rental-server.net, we provide you with the resources and knowledge needed to get your server up and running smoothly. Discover the best dedicated server solutions and Minecraft server hosting options to enhance your multiplayer experience.
1. Understanding the Basics of Hosting a Bedrock Server
What does it take to host a Bedrock server on your PC? Let’s dive into the fundamentals to ensure a seamless setup.
Hosting a Minecraft Bedrock server involves several key steps and considerations. Understanding these basics will help you create a stable and enjoyable multiplayer experience. Here’s what you need to know:
1.1 What is a Minecraft Bedrock Server?
A Minecraft Bedrock server allows multiple players to connect and play together in a shared world. Unlike single-player mode, a server provides a persistent and collaborative environment. The Bedrock edition of Minecraft is designed for cross-platform play, meaning players on Windows 10, Xbox, PlayStation, Nintendo Switch, and mobile devices can all join the same server.
1.2 Why Host Your Own Server?
Hosting your own server offers several advantages:
- Customization: Tailor the game rules, world settings, and player permissions to your liking.
- Control: Manage who can join your server and ensure a safe and friendly environment.
- Performance: Optimize server performance to reduce lag and ensure smooth gameplay.
- Community: Build a dedicated community of players who enjoy playing together.
According to a survey by Statista, approximately 45% of Minecraft players prefer joining private servers to play with friends, highlighting the importance of custom and controlled environments.
1.3 Essential Requirements
Before you begin, ensure your PC meets the following minimum requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 10 (version 1703 or later) or Ubuntu 18 or later.
- Processor: 64-bit Intel or AMD processor with 2 cores.
- RAM: 1 GB RAM (more is recommended for larger player counts).
- Network: A stable internet connection.
1.4 Key Steps to Host a Bedrock Server
Here’s a brief overview of the steps involved in setting up your Bedrock server:
- Download the Server Software: Obtain the Bedrock server software from the official Minecraft website.
- Configure Server Properties: Customize settings such as game mode, difficulty, and maximum player count.
- Port Forwarding: Configure your router to allow external connections to your server.
- Start the Server: Run the server software and ensure it’s accessible to players.
- Invite Friends: Share your server’s IP address with friends so they can join.
By understanding these basics, you’ll be well-prepared to host your own Minecraft Bedrock server and create a unique gaming experience for you and your community.
2. Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up Your Bedrock Server on PC
Ready to get your Minecraft Bedrock server up and running? Follow these detailed steps to set up your server on your PC:
Setting up a Minecraft Bedrock server can seem daunting, but with a step-by-step guide, you can easily create a server for you and your friends. Here’s how to do it:
2.1 Downloading the Bedrock Server Software
-
Visit the Official Minecraft Website: Go to the official Minecraft server download page.
-
Download the Software: Find the download link for the Bedrock server software suitable for your operating system (Windows or Ubuntu).
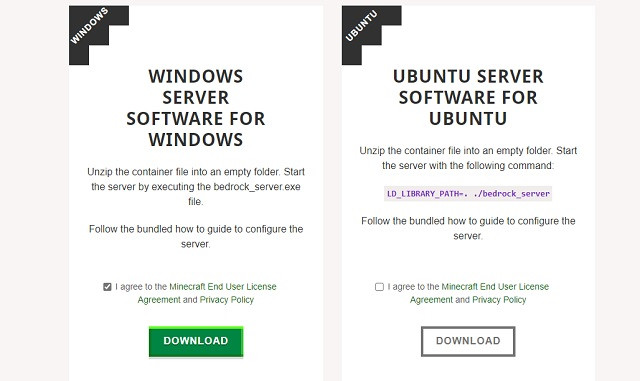 Minecraft Bedrock server download
Minecraft Bedrock server download -
Extract the Files: Once the download is complete, extract the contents of the ZIP file to a folder on your computer. For example, you can create a folder named
MinecraftBedrockServeron your desktop.
2.2 Configuring Server Properties
-
Open the
server.propertiesFile: In the extracted folder, locate theserver.propertiesfile and open it with a text editor like Notepad or Visual Studio Code. -
Customize Server Settings: Modify the settings to your liking. Here are some key settings to consider:
server-name: Set the name of your server (e.g.,My Awesome Server).gamemode: Choose the game mode (survival,creative, oradventure).difficulty: Set the difficulty level (peaceful,easy,normal, orhard).max-players: Define the maximum number of players allowed on the server.server-port: The port your server will run on (default is19132).allow-cheats: Enable or disable cheats (set totrueorfalse).online-mode: Setting totruerequires players to authenticate with Minecraft servers. Setting tofalseis only recommended for local network play.
-
Save the File: After making your changes, save the
server.propertiesfile.
Here is an example of what your server.properties file might look like:
server-name=My Awesome Server
gamemode=survival
difficulty=normal
max-players=20
server-port=19132
allow-cheats=false
online-mode=true2.3 Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is crucial for allowing players outside your local network to connect to your server.
-
Find Your Router’s IP Address: Open Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Ubuntu) and type
ipconfig(Windows) orip addr(Ubuntu). Look for the “Default Gateway” address. -
Access Your Router’s Settings: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar. Log in using your router’s username and password (usually found on the router itself or in its manual).
-
Navigate to Port Forwarding Settings: Look for a section called “Port Forwarding,” “NAT Forwarding,” or similar. The exact name and location will vary depending on your router model.
-
Create a New Port Forwarding Rule:
- Service Name: Enter a name for the rule (e.g.,
Minecraft Bedrock). - Port Range: Enter
19132for both the start and end port. - Protocol: Select
TCP/UDPorBoth. - Internal IP Address: Enter the local IP address of your PC (found using
ipconfigorip addr).
- Service Name: Enter a name for the rule (e.g.,
-
Save the Rule: Save the new port forwarding rule.
2.4 Starting the Server
- Run the
bedrock_server.exeFile: In the folder where you extracted the server files, double-click thebedrock_server.exefile (Windows) or run thebedrock_serverexecutable (Ubuntu). - Allow Access Through Firewall: If prompted by the Windows Firewall, make sure to allow access for both private and public networks.
- Server Console: A console window will appear, displaying server information and logs. The server is now running.
2.5 Connecting to the Server
-
Find Your Public IP Address: Search “what is my IP” on Google to find your public IP address.
-
Open Minecraft Bedrock: Launch Minecraft Bedrock on your device.
-
Navigate to the Servers Tab: Click “Play,” then go to the “Servers” tab.
-
Add Server: Click “Add Server.”
-
Enter Server Details:
- Server Name: Enter a name for your server.
- Server Address: Enter your public IP address.
- Port: Enter
19132(or the port you specified inserver.properties).
-
Join Server: Click “Play” to join your server.
By following these detailed steps, you can successfully set up your Minecraft Bedrock server on your PC and start playing with your friends.
3. Customizing Your Bedrock Server for the Best Experience
How can you customize your Bedrock server to provide the best possible experience for your players? Let’s explore the various options available.
Customizing your Minecraft Bedrock server can significantly enhance the gaming experience for you and your players. Here are several ways to customize your server to create a unique and engaging environment:
3.1 Modifying Server Properties
The server.properties file is your primary tool for customizing basic server settings.
-
Access the
server.propertiesFile: Open theserver.propertiesfile in your server directory using a text editor. -
Adjust Key Settings:
level-name: Change the name of the world that will be loaded.level-seed: Specify a seed for generating a new world. Use this to create unique and interesting landscapes.force-gamemode: Force players to use the specified game mode upon joining.pvp: Enable or disable player-versus-player combat.spawn-animalsandspawn-monsters: Control whether animals and monsters spawn in the world.tick-distance: Determines the distance at which the server processes game ticks around players.
-
Save and Restart: Save the
server.propertiesfile and restart the server for the changes to take effect.
3.2 Installing Resource Packs and Custom Worlds
Resource packs and custom worlds can dramatically change the look and feel of your server.
- Download Resource Packs: Find and download resource packs from reputable sources like CurseForge or the Minecraft Marketplace.
- Add Resource Packs to the Server: Place the downloaded
.mcpackfiles in theresource_packsfolder within your server directory. - Apply Resource Packs: In the
server.propertiesfile, specify the resource packs to be used by adding their filenames to thetexturepack-requiredandbehaviorpack-requiredsettings. - Custom Worlds: Download custom world templates or create your own using Minecraft: Bedrock Edition.
- Add Worlds to the Server: Place the world folder in the
worldsdirectory. - Specify the World: In the
server.propertiesfile, set thelevel-nameto the name of your custom world folder. - Restart the Server: Save the changes and restart the server.
3.3 Using Server Commands
Server commands allow you to manage and modify the server environment in real-time.
-
Access the Server Console: Open the server console window.
-
Execute Commands: Type commands directly into the console and press Enter. Some useful commands include:
/gamemode <player> <mode>: Change a player’s game mode./give <player> <item> <amount>: Give a player an item./tp <player> <x> <y> <z>: Teleport a player to specified coordinates./kick <player> [reason]: Kick a player from the server./ban <player> [reason]: Ban a player from the server./whitelist add <player>: Add a player to the whitelist.
-
Op Permissions: To use commands, players must be granted operator (op) permissions. Use the
/op <player>command in the console to grant these permissions.
3.4 Implementing Behavior Packs
Behavior packs can modify the game’s mechanics, add new entities, and alter existing behaviors.
- Download Behavior Packs: Find and download behavior packs from reliable sources.
- Add Behavior Packs to the Server: Place the downloaded
.mcpackfiles in thebehavior_packsfolder within your server directory. - Apply Behavior Packs: In the
server.propertiesfile, add the behavior pack’s filename to thebehaviorpack-requiredsetting. - Restart the Server: Save the changes and restart the server.
By implementing these customization options, you can create a truly unique and engaging Minecraft Bedrock server that caters to your community’s preferences.
4. Essential Server Commands for Bedrock Edition
What are the essential server commands you should know for managing your Bedrock server? Let’s explore some of the most useful ones.
Understanding and utilizing server commands is crucial for managing your Minecraft Bedrock server effectively. These commands allow you to control various aspects of the game, moderate player behavior, and customize the server environment. Here are some essential server commands you should know:
4.1 Basic Administrative Commands
These commands are fundamental for server administration and player management.
/op <player>: Grants operator (admin) privileges to a player. Operators can use all server commands.- Example:
/op JohnDoe
- Example:
/deop <player>: Revokes operator privileges from a player.- Example:
/deop JohnDoe
- Example:
/kick <player> [reason]: Removes a player from the server. Adding a reason helps inform the player why they were kicked.- Example:
/kick JohnDoe Griefing
- Example:
/ban <player> [reason]: Permanently bans a player from the server.- Example:
/ban JohnDoe Hacking
- Example:
/pardon <player>: Unbans a previously banned player.- Example:
/pardon JohnDoe
- Example:
/whitelist add <player>: Adds a player to the server’s whitelist, allowing them to join even when the whitelist is enabled.- Example:
/whitelist add JohnDoe
- Example:
/whitelist remove <player>: Removes a player from the whitelist.- Example:
/whitelist remove JohnDoe
- Example:
/whitelist on: Enables the server’s whitelist, preventing non-whitelisted players from joining./whitelist off: Disables the server’s whitelist./whitelist list: Lists all players currently on the whitelist.
4.2 Game Management Commands
These commands allow you to control the game environment and player experiences.
/gamemode <mode> [player]: Changes the game mode for a player or yourself. Modes include survival, creative, adventure, and spectator.- Example:
/gamemode creative JohnDoe
- Example:
/difficulty <difficulty>: Sets the difficulty level of the server. Options include peaceful, easy, normal, and hard.- Example:
/difficulty hard
- Example:
/time set <value>: Sets the current game time. Values can be a specific time (e.g., 0 for sunrise, 6000 for midday) or a relative time (e.g., day, night).- Example:
/time set day
- Example:
/weather <type> [duration]: Sets the current weather. Types include clear, rain, and thunder. The duration is optional and specifies how long the weather should last in seconds.- Example:
/weather rain 300
- Example:
/tp <target> <destination>: Teleports a player to another player or to specific coordinates.- Example:
/tp JohnDoe JaneDoe(teleports JohnDoe to JaneDoe) - Example:
/tp JohnDoe 100 64 50(teleports JohnDoe to coordinates 100, 64, 50)
- Example:
/give <player> <item> [amount]: Gives a player a specified item.- Example:
/give JohnDoe diamond 64
- Example:
4.3 World Management Commands
These commands allow you to manage the server’s world settings.
/seed: Displays the seed of the current world./gamerule <rule> <value>: Modifies various game rules that affect the world and gameplay. Some useful rules include:doDaylightCycle: Prevents the day-night cycle.keepInventory: Keeps players’ inventory after death.mobSpawning: Controls whether mobs spawn.commandBlockEnabled: Enables or disables command blocks.- Example:
/gamerule doDaylightCycle false
/locate <structure>: Locates the nearest specified structure, such as a village or temple.- Example:
/locate village
- Example:
4.4 Miscellaneous Commands
These commands provide additional functionality for server management.
/say <message>: Sends a message to all players on the server.- Example:
/say Welcome to the server
- Example:
/tell <player> <message>: Sends a private message to a specific player.- Example:
/tell JohnDoe Hello
- Example:
/clear <player> [item]: Clears a player’s inventory, optionally specifying an item to clear.- Example:
/clear JohnDoe diamond
- Example:
/effect <player> <effect> [duration] [amplifier]: Applies a status effect to a player.- Example:
/effect JohnDoe regeneration 30 5(gives JohnDoe regeneration V for 30 seconds)
- Example:
By mastering these essential server commands, you’ll be well-equipped to manage your Minecraft Bedrock server, maintain a positive player experience, and customize the game to your liking.
5. Optimizing Your Bedrock Server for Performance
How can you optimize your Bedrock server to ensure smooth and lag-free gameplay? Let’s discuss key optimization techniques.
Optimizing your Minecraft Bedrock server is essential to ensure smooth and enjoyable gameplay, especially when hosting multiple players. Here are several techniques to improve your server’s performance:
5.1 Hardware Considerations
The hardware your server runs on plays a crucial role in its performance.
- Processor: A fast multi-core processor is essential. Aim for at least an Intel Core i5 or AMD Ryzen 5 processor.
- RAM: Allocate sufficient RAM to the server. 2GB to 4GB is generally sufficient for a small server, but larger servers with more players may require 8GB or more.
- Storage: Use an SSD (Solid State Drive) for the server’s storage. SSDs offer much faster read and write speeds compared to traditional HDDs, which can significantly improve loading times and overall performance.
- Network: A stable and high-bandwidth internet connection is crucial. Ensure your network can handle the traffic generated by multiple players.
5.2 Software Configuration
Proper software configuration can also improve server performance.
-
Optimize
server.properties: Adjust settings in theserver.propertiesfile to optimize performance.tick-distance: Reduce the tick distance to decrease the area the server simulates around each player. A lower value can improve performance but may reduce the level of detail in distant areas.max-players: Set a reasonable maximum player count based on your hardware capabilities.simulation-distance: Similar totick-distance, this setting controls the render distance for the server. Lowering this value can improve performance.
-
Regular Restarts: Restart the server periodically to clear memory and prevent performance degradation. Schedule restarts during off-peak hours to minimize disruption.
5.3 Network Optimization
Optimizing your network settings can reduce lag and improve connectivity.
- Wired Connection: Use a wired Ethernet connection instead of Wi-Fi for the server to ensure a more stable and reliable connection.
- Port Forwarding: Ensure port forwarding is correctly configured on your router to allow players to connect to the server.
- Firewall Configuration: Configure your firewall to allow traffic on the server port (default is 19132).
- Quality of Service (QoS): If your router supports QoS, prioritize network traffic for the Minecraft server to ensure it receives sufficient bandwidth.
5.4 Monitoring and Maintenance
Regularly monitor and maintain your server to identify and address performance issues.
- Resource Monitoring: Use system monitoring tools to track CPU usage, RAM usage, and network traffic. Identify any bottlenecks and address them accordingly.
- Log Analysis: Review server logs for errors or warnings that may indicate performance issues.
- Regular Updates: Keep the server software and operating system up to date with the latest patches and updates to ensure optimal performance and security.
5.5 Additional Tips
- Limit Redstone Activity: Excessive redstone contraptions can cause significant lag. Encourage players to use redstone efficiently.
- Optimize World Generation: Pre-generate the world to reduce lag when players explore new areas. Use tools like Minecraft region fixer to optimize the existing world files.
- Disable Unnecessary Features: Disable any unnecessary features or plugins that may be consuming server resources.
By implementing these optimization techniques, you can significantly improve the performance of your Minecraft Bedrock server and provide a smoother, more enjoyable gaming experience for your players. According to a study by the Uptime Institute, optimized server configurations can reduce downtime by up to 25%.
6. Troubleshooting Common Bedrock Server Issues
Facing problems with your Bedrock server? Let’s troubleshoot some common issues and how to resolve them.
Running a Minecraft Bedrock server can sometimes present challenges. Here are some common issues you might encounter and how to troubleshoot them effectively:
6.1 Connection Issues
Players may experience difficulty connecting to the server due to various reasons.
-
Incorrect IP Address: Ensure players are using the correct public IP address of the server. They can find this by searching “what is my IP” on Google from the server’s host machine.
-
Port Forwarding Problems:
- Check Configuration: Verify that port forwarding is correctly configured on the router. Ensure the correct port (default is 19132) is forwarded to the server’s local IP address.
- Firewall: Ensure the firewall is not blocking connections on port 19132. Create exceptions for both TCP and UDP protocols.
-
Server Not Running: Ensure the server is running and the console window is open. If the server has crashed, restart it.
-
Online Mode Issues: If the
online-modesetting inserver.propertiesis set totrue, ensure all players have a valid Minecraft account and are logged in. If set tofalse, this bypasses authentication but is only recommended for local network play. -
DNS Issues: Sometimes, DNS issues can prevent players from connecting. Try having players use a different DNS server, such as Google’s public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).
6.2 Performance Issues
Lag and performance drops can ruin the gaming experience.
-
High CPU or RAM Usage:
- Monitor Resources: Use system monitoring tools to check CPU and RAM usage. If either is consistently high, consider upgrading your hardware or reducing the number of players.
- Restart Regularly: Restart the server periodically to free up memory and reduce resource consumption.
-
Network Latency:
- Check Connection: Ensure the server has a stable and high-bandwidth internet connection.
- Reduce Tick Distance: Lower the
tick-distancesetting inserver.propertiesto reduce the area the server simulates around each player.
-
Redstone Lag: Excessive redstone contraptions can cause significant lag. Encourage players to use redstone efficiently and limit complex designs.
-
World Generation: Pre-generate the world to reduce lag when players explore new areas. Use tools like Minecraft region fixer to optimize the existing world files.
6.3 Server Crashing
Server crashes can be frustrating, but identifying the cause can help prevent future issues.
- Review Logs: Check the server logs for error messages or exceptions that may indicate the cause of the crash.
- Memory Issues: Insufficient RAM can lead to crashes. Ensure the server has enough allocated memory.
- Plugin Conflicts: If using plugins, disable them one by one to identify any conflicting plugins.
- Corrupted World Files: Corrupted world files can cause crashes. Restore the world from a backup if available.
- Outdated Software: Ensure the server software and operating system are up to date with the latest patches and updates.
6.4 Command Issues
Commands may not work as expected due to permission or syntax errors.
- Operator Permissions: Ensure the player using the command has operator (op) permissions. Use the
/op <player>command in the console to grant these permissions. - Syntax Errors: Double-check the syntax of the command. Refer to the Minecraft Bedrock command list for correct usage.
- Command Blocks: Ensure command blocks are enabled in the server settings (
commandBlockEnabledgamerule).
6.5 General Tips
- Backups: Regularly back up the server’s world files to prevent data loss in case of crashes or corruption.
- Community Support: Consult the Minecraft community forums or support channels for assistance with troubleshooting.
- Resource Monitoring: Continuously monitor server resources to identify and address potential issues before they cause problems.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively address common issues and maintain a stable and enjoyable Minecraft Bedrock server.
7. Exploring Alternative Hosting Solutions
Is hosting on your PC not ideal? Discover alternative hosting solutions for your Bedrock server.
Hosting a Minecraft Bedrock server on your PC can be a great way to get started, but it may not be ideal in the long run. Resource limitations, internet bandwidth constraints, and the need for constant uptime can make it challenging to provide a seamless gaming experience. Fortunately, several alternative hosting solutions are available:
7.1 Minecraft Server Hosting Providers
Minecraft server hosting providers offer pre-configured servers optimized for running Minecraft. These providers handle the technical aspects of server management, allowing you to focus on building your community and enjoying the game.
-
Advantages:
- Reliability: Hosting providers offer high uptime guarantees and redundant infrastructure.
- Performance: Servers are optimized for Minecraft and typically offer better performance than hosting on a personal PC.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down as needed to accommodate changing player counts.
- Support: Hosting providers offer technical support to help with any issues that may arise.
- Ease of Use: Most providers offer user-friendly control panels for managing server settings, installing mods, and more.
-
Popular Providers:
- Apex Hosting: Known for its ease of use and excellent customer support.
- Shockbyte: Offers affordable plans and a wide range of features.
- MCProHosting: Provides high-performance servers and advanced customization options.
7.2 Virtual Private Servers (VPS)
A VPS is a virtualized server that runs on a physical machine shared with other users. VPS hosting offers more flexibility and control than shared Minecraft hosting, but requires more technical knowledge to manage.
-
Advantages:
- Customization: Full control over the server environment, allowing you to install custom software and configure settings.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down as needed.
- Cost-Effective: VPS hosting can be more cost-effective than dedicated servers for medium-sized servers.
-
Considerations:
- Technical Knowledge: Requires more technical knowledge to manage than shared Minecraft hosting.
- Maintenance: Responsible for server maintenance, security, and updates.
-
Popular Providers:
- DigitalOcean: Offers simple and scalable VPS hosting with a wide range of features.
- Vultr: Provides high-performance VPS hosting with global data center locations.
- Linode: Known for its developer-friendly tools and excellent performance.
7.3 Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting offers the ultimate scalability and flexibility for Minecraft server hosting. Cloud servers are hosted on a network of virtual machines, allowing resources to be scaled dynamically as needed.
-
Advantages:
- Scalability: Resources can be scaled instantly to accommodate changing player counts and traffic patterns.
- Reliability: Cloud hosting offers high availability and redundancy.
- Global Reach: Deploy servers in multiple data center locations around the world to reduce latency for players.
-
Considerations:
- Cost: Cloud hosting can be more expensive than other hosting options, especially for high-traffic servers.
- Complexity: Requires more technical knowledge to manage than shared Minecraft hosting.
-
Popular Providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers a wide range of cloud services, including EC2 for virtual servers.
- Microsoft Azure: Provides scalable cloud hosting solutions for Minecraft servers.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Offers high-performance cloud hosting with global data center locations.
7.4 Choosing the Right Solution
The best hosting solution for your Minecraft Bedrock server depends on your specific needs and budget.
- Minecraft Server Hosting Providers: Ideal for beginners who want a hassle-free hosting experience with excellent support.
- VPS Hosting: A good option for those who want more control and customization options, but are comfortable with basic server management.
- Cloud Hosting: Best for large servers with high traffic and demanding performance requirements.
By exploring these alternative hosting solutions, you can find the perfect option for your Minecraft Bedrock server and provide a seamless gaming experience for your community.
8. Ensuring Server Security: Best Practices
How can you ensure the security of your Bedrock server and protect it from threats? Let’s look at essential security practices.
Securing your Minecraft Bedrock server is crucial to protect your players, prevent griefing, and maintain a safe and enjoyable environment. Here are some best practices to ensure your server’s security:
8.1 Strong Passwords and Access Control
- Admin Password: Set a strong, unique password for the server admin account. Avoid using common passwords or personal information.
- Operator Permissions: Grant operator (op) permissions only to trusted players. Limit the number of players with admin privileges to minimize the risk of abuse.
- Regular Audits: Regularly review the list of operators and remove permissions from players who no longer need them.
8.2 Whitelisting
- Enable Whitelisting: Enable the server’s whitelist to restrict access to only approved players. This prevents unknown or malicious users from joining the server.
- Manage Whitelist: Regularly update the whitelist to add new players and remove those who are no longer active or trusted.
8.3 Firewall Configuration
- Firewall: Configure your firewall to allow traffic only on the necessary ports. The default Minecraft Bedrock server port is 19132.
- Restrict Access: Restrict access to the server from specific IP addresses or ranges to further limit exposure to potential threats.
8.4 Monitoring and Logging
- Server Logs: Regularly review server logs for suspicious activity, such as unusual login attempts, unauthorized command usage, or signs of griefing.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track server performance and identify any anomalies that may indicate a security breach.
8.5 Regular Backups
- Automated Backups: Implement an automated backup system to regularly back up the server’s world files. Store backups in a secure location, separate from the server.
- Test Restores: Periodically test the backup restore process to ensure it works correctly and that you can recover data in case of a security incident.
8.6 Plugin Security
- Trusted Sources: Only install plugins from trusted sources to minimize the risk of malware or vulnerabilities.
- Regular Updates: Keep plugins up to date with the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Permissions Management: Configure plugin permissions carefully to limit the functionality available to players.
8.7 DDoS Protection
- DDoS Mitigation: Implement DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) mitigation measures to protect the server from attacks that can disrupt service and make it unavailable to players.
- Cloudflare: Use Cloudflare or other DDoS protection services to filter malicious traffic and ensure the server remains accessible.
8.8 Player Education
- Security Awareness: Educate players about security best practices, such as using strong passwords and avoiding suspicious links or downloads.
- Reporting Mechanisms: Provide players with a clear and easy way to report suspicious activity or security concerns.
By implementing these security best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of security breaches and maintain a safe and enjoyable Minecraft Bedrock server environment for your players. According to a report by IBM, implementing strong access controls and regular security audits can reduce the risk of data breaches by up to 60%.
9. Joining the Bedrock Server Community
How can you engage with the Bedrock server community and learn from other server owners? Let’s explore community resources and platforms.
Engaging with the Minecraft Bedrock server community is a great way to learn best practices, troubleshoot issues, and discover new ideas for your server. Here are some community resources and platforms you can join:
9.1 Minecraft Forums
- Official Minecraft Forums: The official Minecraft forums (minecraftforum.net) are a valuable resource for finding information, asking questions, and connecting with other server owners and players.
- Server Administration Subforum: Look for a subforum dedicated to server administration, where you can find discussions on topics such as server setup, configuration, security, and troubleshooting.
9.2 Reddit
- r/Minecraft: The main Minecraft subreddit (reddit.com/r/Minecraft) is a large and active community where you can find news, discussions, and helpful resources related to Minecraft.
- r/MinecraftServers: A subreddit specifically for Minecraft server owners and players (reddit.com/r/MinecraftServers). You can use this subreddit to advertise your server, find players, and ask for advice from other server owners.
- r/Admincraft: A subreddit for Minecraft server administrators (reddit.com/r/Admincraft). This subreddit is focused on more technical aspects of server administration, such as plugin development, server optimization, and security.
9.3 Discord Servers
- Minecraft Official Discord: The official Minecraft Discord server is a great place to connect with other players and get help with the game.
- Server-Specific Discord Servers: Many Minecraft servers have their own Discord servers where you can connect with the server community, get support, and participate in events.
9.4 Online Communities
- Planet Minecraft: A website dedicated to Minecraft content, including servers, maps, skins, and mods (planetminecraft.com). You can use Planet Minecraft to advertise your server and connect with potential players.
- Minecraft Server Lists: Several websites list Minecraft servers, allowing players to find and join new servers. Some popular server lists include:
- MinecraftServers.org: A popular server list with a large selection of servers.
- Top Minecraft Servers: A server list that ranks servers based on popularity and player reviews.
- Minecraft Server List: A comprehensive server list with a variety of filters and search options.
9.5 Social Media
- Twitter: Use Twitter to connect with other Minecraft server owners and players, share updates about your server, and promote your community.
- YouTube: Create videos about your server to showcase its features, events, and community. Use YouTube to attract new players and engage with your existing community.
- Twitch: Stream gameplay from your server on Twitch to attract viewers and promote your community.
By joining these community resources and platforms, you
