Determining “How Much Is A Serving Of Alcohol” is crucial for making informed choices about your health, especially when enjoying beverages on servers you’re hosting. At rental-server.net, we understand the importance of responsible server management and a balanced lifestyle, so let’s delve into what constitutes a standard drink and its implications. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of alcohol servings, empowering you with the knowledge to make responsible decisions and ensuring you’re well-informed about the impacts of alcohol consumption.
1. What Defines a Standard Serving of Alcohol?
A standard serving of alcohol contains roughly 14 grams (0.6 fluid ounces) of pure alcohol. This amount is found in:
- 12 ounces of regular beer (about 5% alcohol).
- 5 ounces of wine (about 12% alcohol).
- 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits (about 40% alcohol).
Understanding these measurements helps you monitor your alcohol consumption accurately. It’s important to note that these are standardized amounts, while actual serving sizes can vary, potentially leading to overconsumption if not carefully observed.
1.1 Why is a Standard Serving Important?
Standard servings help individuals track alcohol consumption and adhere to health guidelines. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) uses these standards to provide recommendations for moderate alcohol consumption, which differ for men and women.
1.2 How Do Different Beverages Compare?
Different alcoholic beverages contain varying amounts of alcohol, influencing the number of standard servings in a single drink. For example, craft beers often have a higher alcohol content than regular beers, meaning a single bottle can contain more than one standard serving. Similarly, wines can vary significantly in alcohol percentage, affecting how much you’re actually consuming.
2. Decoding Alcohol Content: ABV and Proof
Alcohol content is typically expressed in two ways: Alcohol By Volume (ABV) and proof. Understanding these terms is essential for calculating the amount of alcohol in a drink.
2.1 Alcohol By Volume (ABV)
ABV indicates the percentage of alcohol in a beverage. For instance, a beer with 5% ABV contains 5% pure alcohol. It is a straightforward way to understand how potent a drink is and helps in comparing different beverages.
2.2 Proof
Proof is twice the ABV. Therefore, a spirit with 40% ABV is 80 proof. The term “proof” has historical roots, dating back to when spirits were tested for alcohol content using gunpowder. If the gunpowder ignited, the spirit was “proof” of containing a sufficient amount of alcohol.
2.3 Converting ABV to Standard Servings
To calculate the number of standard servings in a drink, use this formula:
(Volume in ounces x ABV x 0.0338) / 0.6 = Number of Standard Drinks
For example, a 16-ounce beer with 6% ABV would contain approximately 1.6 standard servings.
3. The Impact of Different Types of Alcohol on Your Body
Different alcoholic beverages can affect the body differently, due to variations in alcohol content and additional ingredients. Understanding these nuances can help you make better choices.
3.1 Beer
Beer is often carbonated, which can speed up alcohol absorption. It also contains carbohydrates, which can affect blood sugar levels. Craft beers with higher ABVs can lead to quicker intoxication compared to light beers.
3.2 Wine
Wine contains antioxidants, particularly red wine, which some studies suggest may have cardiovascular benefits. However, wine can also contain sulfites, which may cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
3.3 Spirits
Spirits have the highest concentration of alcohol and are absorbed rapidly into the bloodstream. Mixing spirits with sugary drinks can further accelerate absorption and increase the risk of overconsumption.
3.4 Liqueurs and Cordials
Liqueurs and cordials often contain high amounts of sugar, which can mask the effects of alcohol and lead to increased calorie intake. They may also contain various additives and flavorings that can affect how the body processes the alcohol.
4. Factors Influencing Alcohol Absorption
Several factors can influence how quickly your body absorbs alcohol, including weight, gender, food consumption, and medication. These factors can significantly alter the effects of alcohol and should be considered.
4.1 Body Weight and Composition
Individuals with lower body weights generally experience the effects of alcohol more quickly because they have less body mass to distribute the alcohol. Body composition also plays a role; those with a higher percentage of body fat tend to absorb alcohol faster, as fat does not absorb alcohol like muscle tissue does.
4.2 Gender Differences
Women typically have a lower tolerance for alcohol than men due to differences in body composition and enzyme activity. Women generally have a higher percentage of body fat and less of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, which breaks down alcohol in the stomach.
4.3 Food Consumption
Eating before or while drinking slows down alcohol absorption. Food, especially foods high in protein and fat, creates a barrier that prevents alcohol from being absorbed quickly into the bloodstream.
4.4 Medications and Health Conditions
Certain medications can interact with alcohol, increasing its effects or causing adverse reactions. Health conditions, such as liver disease, can also impair the body’s ability to process alcohol, leading to higher blood alcohol concentrations.
5. Identifying High-Risk Drinking Patterns
Recognizing high-risk drinking patterns is essential for preventing alcohol-related problems. These patterns include binge drinking and heavy drinking, both of which can have serious health consequences.
5.1 Binge Drinking
Binge drinking is defined as consuming a large amount of alcohol in a short period, typically resulting in a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.08% or higher. For men, this usually means consuming five or more drinks in about two hours, and for women, four or more drinks.
5.2 Heavy Drinking
Heavy drinking is defined as consuming more than one drink per day for women and more than two drinks per day for men. This pattern of drinking can lead to long-term health problems, including liver disease, heart disease, and certain cancers.
5.3 The Risks of High-Risk Drinking
High-risk drinking patterns increase the risk of accidents, injuries, violence, and alcohol poisoning. They can also contribute to chronic health problems, mental health issues, and social problems.
6. Health Guidelines for Alcohol Consumption
Following health guidelines for alcohol consumption is crucial for minimizing the risks associated with drinking. These guidelines provide recommendations for moderate alcohol consumption to help individuals make informed decisions.
6.1 Moderate Drinking
Moderate drinking is defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. These guidelines are based on research indicating that moderate alcohol consumption may have some health benefits for certain individuals, such as reducing the risk of heart disease.
6.2 When to Avoid Alcohol
There are certain situations in which alcohol should be avoided altogether, such as when driving, operating machinery, or taking medications that interact with alcohol. Pregnant women and individuals with certain health conditions should also avoid alcohol.
6.3 The Importance of Responsible Drinking
Responsible drinking involves making informed decisions about alcohol consumption, pacing yourself, and avoiding situations that could lead to overconsumption. It also includes being aware of your own limits and knowing when to stop.
7. Tools for Tracking Alcohol Consumption
Various tools can help you track your alcohol consumption, including mobile apps, online calculators, and drink journals. These tools can provide valuable insights into your drinking habits and help you stay within recommended limits.
7.1 Mobile Apps
Mobile apps like DrinkControl, AlcoTrack, and EasyQuit Drinking allow you to log your drinks, calculate your BAC, and track your progress over time. These apps can also provide personalized feedback and support to help you achieve your drinking goals.
7.2 Online Calculators
Online calculators, such as the one available on the NIAAA website, can help you estimate your BAC based on factors like weight, gender, and the number of drinks consumed. These calculators can provide a quick and easy way to assess your level of intoxication.
7.3 Drink Journals
Keeping a drink journal can help you become more aware of your drinking habits. By recording each drink you consume, along with the time, type of beverage, and amount, you can identify patterns and make informed decisions about your alcohol consumption.
8. Alcohol and Server Management: A Delicate Balance
Managing servers requires a clear mind and responsible decision-making, qualities that can be compromised by excessive alcohol consumption. At rental-server.net, we advocate for a balanced approach.
8.1 The Impact of Alcohol on Cognitive Functions
Alcohol impairs cognitive functions such as judgment, decision-making, and reaction time. These impairments can negatively impact server management tasks, leading to errors, downtime, and security vulnerabilities.
8.2 Best Practices for Responsible Server Management
To ensure responsible server management, it’s crucial to avoid alcohol consumption while performing critical tasks. Schedule maintenance and updates during periods when you are sober and alert.
8.3 Utilizing Technology for Enhanced Monitoring
Leverage server monitoring tools to track performance metrics and identify potential issues proactively. These tools can provide early warnings of problems, allowing you to address them before they escalate, even if you are not at peak performance.
9. Debunking Common Myths About Alcohol
Several myths surround alcohol consumption, leading to misconceptions about its effects and risks. It’s essential to debunk these myths with accurate information.
9.1 Myth: Eating Before Drinking Prevents Intoxication
While eating before drinking slows down alcohol absorption, it does not prevent intoxication entirely. Alcohol will still enter the bloodstream, just at a slower rate.
9.2 Myth: Mixing Drinks is More Intoxicating
Mixing different types of alcoholic beverages does not inherently make you more intoxicated. The total amount of alcohol consumed is the primary factor determining intoxication levels.
9.3 Myth: Coffee Can Sober You Up
Coffee is a stimulant that can make you feel more alert, but it does not reduce your blood alcohol concentration. The only thing that can sober you up is time.
9.4 Myth: Tolerance Means You Can Drink More
Developing a tolerance to alcohol means your body has adapted to its effects, but it does not mean you can drink more without experiencing negative consequences. Tolerance can mask the effects of alcohol, leading to overconsumption and increased health risks.
10. Strategies for Reducing Alcohol Consumption
If you’re looking to reduce your alcohol consumption, several strategies can help you achieve your goals. These strategies include setting limits, pacing yourself, and finding alternative activities.
10.1 Setting Limits
Establish clear limits for how much alcohol you will consume before you start drinking. This can help you avoid overconsumption and stay within recommended guidelines.
10.2 Pacing Yourself
Drink slowly and alternate alcoholic beverages with non-alcoholic drinks. This can help you pace yourself and avoid drinking too much too quickly.
10.3 Finding Alternative Activities
Engage in alternative activities that do not involve alcohol, such as exercise, hobbies, or social events. This can help you reduce your reliance on alcohol and find healthier ways to relax and socialize.
10.4 Seeking Support
If you’re struggling to reduce your alcohol consumption on your own, seek support from friends, family, or a healthcare professional. Support groups and counseling can provide valuable resources and guidance.
11. The Long-Term Effects of Alcohol on Health
Chronic alcohol consumption can have significant long-term effects on your health, including liver damage, heart disease, and an increased risk of certain cancers. Understanding these risks can help you make informed decisions about your drinking habits.
11.1 Liver Damage
The liver is responsible for processing alcohol, and chronic alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, including fatty liver disease, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. These conditions can impair liver function and lead to serious health complications.
11.2 Heart Disease
Heavy alcohol consumption can increase the risk of heart disease, including high blood pressure, cardiomyopathy, and stroke. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some cardiovascular benefits for certain individuals, excessive drinking is detrimental to heart health.
11.3 Cancer
Alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers, including breast cancer, colon cancer, liver cancer, and esophageal cancer. The risk of cancer increases with the amount of alcohol consumed.
11.4 Mental Health Issues
Chronic alcohol consumption can contribute to mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and alcohol dependence. Alcohol can alter brain chemistry and disrupt neurotransmitter function, leading to mood disturbances and addiction.
12. Resources for Alcohol-Related Issues
If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol-related issues, numerous resources are available to provide support and guidance. These resources include hotlines, support groups, and treatment centers.
12.1 SAMHSA National Helpline
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline is a confidential resource that provides information and referrals for individuals and families facing mental health and/or substance use disorders.
12.2 Alcoholics Anonymous (AA)
Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is a peer support group for individuals recovering from alcohol dependence. AA provides a safe and supportive environment for sharing experiences and working towards sobriety.
12.3 National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) is a research institute that provides information and resources on alcohol-related issues. The NIAAA website offers publications, tools, and treatment options for individuals and families affected by alcohol abuse.
13. Safe Alcohol Consumption: Guidelines
Safe alcohol consumption involves drinking responsibly and adhering to health guidelines. Here are some key tips to ensure you’re drinking safely:
13.1 Stick to Standard Servings
Be mindful of the size and alcohol content of your drinks. Adhere to standard serving sizes to avoid overconsumption.
13.2 Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Alcohol can dehydrate the body, leading to headaches and other unpleasant symptoms.
13.3 Avoid Drinking Games
Avoid participating in drinking games that encourage rapid alcohol consumption. These games can lead to intoxication and increase the risk of alcohol poisoning.
13.4 Never Drink and Drive
Never drink and drive or operate machinery. Alcohol impairs judgment and reaction time, making it dangerous to drive or operate equipment.
14. The Role of Legislation in Alcohol Consumption
Legislation plays a significant role in regulating alcohol consumption and reducing alcohol-related harm. These laws include minimum drinking age laws, drunk driving laws, and regulations on alcohol sales and advertising.
14.1 Minimum Drinking Age Laws
Minimum drinking age laws prohibit the sale and consumption of alcohol to individuals under a certain age, typically 21. These laws are intended to reduce alcohol-related deaths and injuries among young people.
14.2 Drunk Driving Laws
Drunk driving laws prohibit operating a vehicle with a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) above a certain level, typically 0.08%. These laws are designed to reduce alcohol-related traffic accidents and fatalities.
14.3 Alcohol Sales and Advertising Regulations
Regulations on alcohol sales and advertising aim to control the availability and promotion of alcoholic beverages. These regulations may include restrictions on hours of sale, advertising content, and the placement of alcohol products in stores.
15. Future Trends in Alcohol Consumption
The landscape of alcohol consumption is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging. These trends include the rise of non-alcoholic beverages, the increasing popularity of craft beverages, and the use of technology to promote responsible drinking.
15.1 Non-Alcoholic Beverages
Non-alcoholic beverages are becoming increasingly popular as consumers seek healthier alternatives to traditional alcoholic drinks. These beverages include non-alcoholic beers, wines, and spirits that offer the same flavors and experiences without the alcohol content.
15.2 Craft Beverages
Craft beverages, such as craft beers and artisanal spirits, are gaining popularity as consumers seek unique and high-quality drinking experiences. These beverages are often produced in small batches using traditional methods and premium ingredients.
15.3 Technology and Responsible Drinking
Technology is being used to promote responsible drinking through mobile apps, online calculators, and virtual reality simulations. These tools can help individuals track their alcohol consumption, assess their level of intoxication, and practice safe drinking behaviors.
Understanding “how much is a serving of alcohol” is just the beginning. By educating yourself on the factors influencing alcohol absorption, recognizing high-risk drinking patterns, and following health guidelines, you can make informed decisions and minimize the risks associated with alcohol consumption. At rental-server.net, we encourage our users to prioritize their health and well-being while managing their servers responsibly.
Remember, responsible server management and a healthy lifestyle go hand in hand.
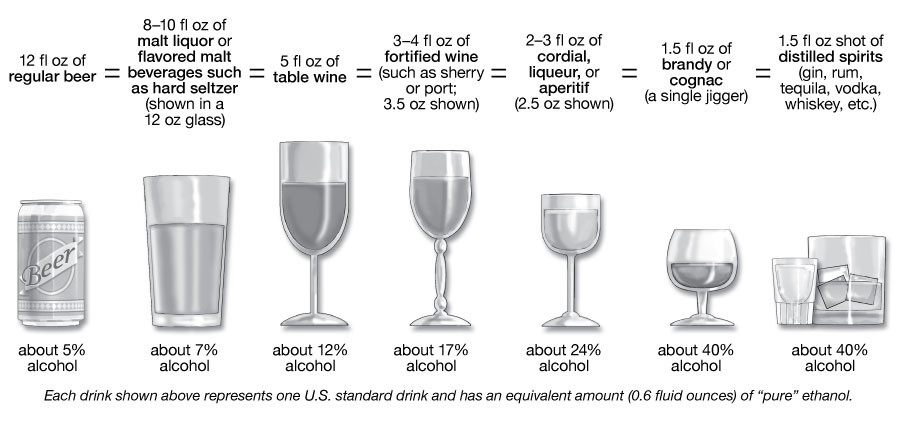 Standard Drink Sizes for Alcohol
Standard Drink Sizes for Alcohol
Each beverage displayed represents one standard drink, containing 0.6 fl oz or 14 grams of pure alcohol in the United States. The percentage of pure alcohol, expressed as alcohol by volume (alc/vol), differs across beverage types.
FAQ: Common Questions About Alcohol Servings
1. How many standard drinks are in a pint of beer?
A pint (16 ounces) of regular beer (5% ABV) contains about 1.33 standard drinks. This calculation helps you keep track of your intake when enjoying larger servings.
2. Is a glass of wine always one standard drink?
Not necessarily. A standard drink of wine is 5 ounces. If your glass is larger, or if the wine has a higher ABV, it could contain more than one standard drink.
3. What is considered a “light” beer? Does it have fewer standard drinks?
Light beers typically have a lower calorie count but may have a similar alcohol content to regular beers. Always check the ABV to determine the number of standard drinks.
4. How does the alcohol content in craft beers affect serving sizes?
Craft beers often have a higher ABV, meaning a smaller volume can contain more alcohol. Always check the label for the ABV to calculate the number of standard servings.
5. Can I accurately estimate my blood alcohol content (BAC) by knowing the number of standard drinks I’ve consumed?
While standard drinks provide a general guideline, BAC can vary based on individual factors like weight, gender, and metabolism. Use online BAC calculators for a more accurate estimate.
6. What are the guidelines for responsible alcohol consumption?
Moderate drinking is defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. Avoid drinking and driving, and be mindful of your personal limits.
7. How does food intake affect the number of standard drinks I can consume safely?
Eating before or while drinking slows down alcohol absorption, allowing your body more time to process the alcohol. This can help you stay within safe limits.
8. What are the long-term health risks associated with exceeding standard drink recommendations?
Exceeding standard drink recommendations can lead to liver damage, heart disease, increased cancer risk, and mental health issues. It’s crucial to drink responsibly.
9. How can I track my alcohol consumption to ensure I stay within healthy limits?
Use mobile apps like DrinkControl or keep a drink journal to track your alcohol consumption and identify patterns. This awareness can help you make informed decisions.
10. Where can I find reliable resources for understanding alcohol consumption guidelines?
Refer to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) for accurate information and resources.
For more information and to explore server solutions that support your balanced lifestyle, visit rental-server.net, or contact us at Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States, Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000. Discover our dedicated server, VPS, and cloud server options tailored to meet your needs.
Ready to find the perfect server solution? Explore our hosting plans, compare prices, and discover exclusive deals. Contact us now for a consultation and let us help you optimize your server experience!