The office of the Governor of Georgia is a powerful and influential position, leading the state’s executive branch. Understanding the parameters of this role, especially concerning term limits, is crucial for anyone interested in Georgia politics. This article delves into the specifics of how long a governor can serve in Georgia, alongside other key aspects of the office, providing a comprehensive overview for those seeking to understand this important state leadership position.
Term Limits for Georgia’s Governor: Understanding the Constraints
One of the first questions many have about gubernatorial roles is regarding term limits. In Georgia, the term length for a governor is four years. However, to ensure a balance of power and prevent any individual from holding office indefinitely, Georgia, like many other states, has implemented term limits for its governor.
According to the Georgia Constitution, a governor is limited to serving two consecutive terms. This means that after serving two full four-year terms, an individual cannot immediately run for reelection as governor. They must step aside, and another person must take office.
This provision is clearly outlined in the Georgia Constitution, Article V, Section 1, Paragraph 1, which states that governors “may succeed themselves for one four-year term of office. Persons who have held the office of Governor and have succeeded themselves as herein before provided shall not again be eligible to be elected to that office until after the expiration of four years from the conclusion of their term as Governor.”
To put it simply, a governor can serve a maximum of eight consecutive years. After that, they must wait at least one full gubernatorial term (four years) before they are eligible to run for governor again. This ensures a rotation of leadership while still allowing experienced individuals to potentially return to office after a break.
The Length of a Governor’s Term in Georgia
As mentioned, the standard term for a Georgia governor is four years. This is comparable to the presidential term in the United States and is a common term length for governors across the states. This four-year period provides sufficient time for a governor to implement policies, address state issues, and lead the executive branch effectively.
Governors in Georgia are elected in midterm election years, meaning in even-numbered years that are not presidential election years. This election cycle is designed to keep state elections somewhat separate from the national presidential campaigns, allowing state-level issues and candidates to receive more focused attention from voters. Georgia gubernatorial elections take place in years like 2018, 2022, 2026, and so on, every four years.
Who Can Become Governor? Qualifications to Serve
Beyond term limits, there are specific qualifications outlined in the Georgia Constitution that an individual must meet to be eligible to hold the office of governor. These qualifications ensure that candidates have sufficient experience, residency, and commitment to the state and the nation.
According to Article V, Section 1 of the Georgia Constitution, a candidate for governor must meet the following criteria:
- Age: Must be at least 30 years old by the date they assume office.
- Citizenship: Must have been a citizen of the United States for at least 15 years by the day of election.
- Residency: Must have been a legal resident of Georgia for at least six years immediately preceding the election.
These qualifications are designed to ensure that the governor is mature, experienced, and deeply familiar with the state of Georgia and its people.
The Election Process for Georgia’s Governor
Georgia’s governor is elected through a popular vote by the citizens of Georgia. The election process involves primary elections and a general election:
-
Primary Elections: Candidates from each political party (typically Republican and Democratic) compete in primary elections to become their party’s nominee for governor. These primaries usually occur in the spring or early summer of the election year. In Georgia, if no candidate receives a majority of the votes in a primary, a runoff election is held between the top two candidates.
-
General Election: The winners of the primary elections from each party, along with any independent or third-party candidates, then compete in the general election. This election is held in November. The candidate who receives a plurality of the votes in the general election wins the governorship.
The inauguration of the newly elected governor in Georgia is legally set for the same day the Georgia General Assembly convenes. This ensures a smooth transition of power and alignment with the legislative calendar.
Recent Gubernatorial Elections in Georgia
To illustrate the election process, let’s look at some recent Georgia gubernatorial elections:
2022 Election:
In the 2022 general election, incumbent Republican Governor Brian Kemp successfully defended his seat against Democratic challenger Stacey Abrams.
| Candidate | Party | Percentage | Votes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brian Kemp | Republican | 53.4% | 2,111,572 |
| Stacey Abrams | Democratic | 45.9% | 1,813,673 |
| Shane Hazel | Libertarian | 0.7% | 28,163 |
| David Byrne | Independent | 0.0% | 18 |
| Milton Lofton | Independent | 0.0% | 7 |
 Brian Kemp, current Governor of Georgia
Brian Kemp, current Governor of Georgia
2018 Election:
In 2018, Brian Kemp was first elected governor, again in a closely watched race against Stacey Abrams.
| Candidate | Party | Percentage | Votes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brian Kemp | Republican | 50.2% | 1,978,408 |
| Stacey Abrams | Democratic | 48.8% | 1,923,685 |
| Ted Metz | Libertarian | 0.9% | 37,235 |
2014 Election:
In 2014, incumbent Republican Governor Nathan Deal won reelection against Democratic challenger Jason Carter.
| Candidate | Party | Vote % | Votes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nathan Deal | Republican | 52.7% | 1,345,237 |
| Jason Carter | Democratic | 44.9% | 1,144,794 |
| Andrew Hunt | Libertarian | 2.4% | 60,185 |
These election results illustrate the competitive nature of gubernatorial races in Georgia and the importance of each election cycle in determining the state’s leadership.
Authority and Duties of the Governor
The Governor of Georgia holds significant authority and a wide range of duties as the head of the executive branch. These responsibilities are primarily defined in Article V, Section II of the Georgia Constitution. Key duties and powers include:
- Chief Executive Powers: The governor is vested with the chief executive powers of the state, responsible for implementing and enforcing state laws.
- Proposing Legislation and Budget: The governor proposes new programs and laws to the Georgia General Assembly and is responsible for submitting a state budget for the legislature’s consideration. This budget proposal is a critical part of the state’s financial planning and policy direction.
- Veto Power: The governor has the power to veto legislation passed by the General Assembly. This veto can be overridden by a two-thirds majority vote in both chambers of the legislature, providing a check and balance on power.
- Appointments: The governor appoints members to numerous state boards and commissions, influencing policy and administration across various state departments. Many executive departments are headed by policy-making boards whose members are gubernatorial appointees.
- Commander-in-Chief: The governor serves as the commander-in-chief of the military forces of Georgia, including the National Guard, when they are not federalized.
- Conservator of Peace: The governor is considered the “conservator of peace” within Georgia, responsible for maintaining order and enforcing laws throughout the state.
- State of the State Address: Each year, the governor delivers a ‘State of the State’ address to the General Assembly, outlining the current condition of the state and recommending legislative priorities.
- Convening the Legislature: The governor can convene extraordinary sessions of the General Assembly, not exceeding 40 days, and also emergency sessions when necessary.
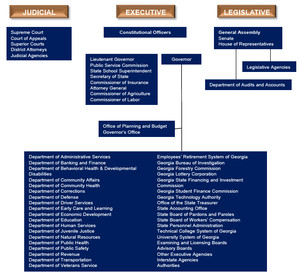 Organizational chart of Georgia state government
Organizational chart of Georgia state government
Gubernatorial Vacancies and Succession
In the event of a vacancy in the office of Governor, whether due to death, resignation, or removal, the line of succession is clearly defined in the Georgia Constitution.
If the governor is temporarily or permanently unable to discharge the duties of office, the Lieutenant Governor assumes the office. If the vacancy is permanent, the Lieutenant Governor serves as acting governor, typically until the next general election.
However, specific rules apply depending on the timing of the vacancy:
- Vacancy in the Last Year of Term: If the governorship becomes vacant in the last year of the term, especially close to a general election (less than 90 days before or less than 30 days before a general election), the Lieutenant Governor typically completes the remainder of the term without a special election.
- Vacancy Earlier in the Term: If the vacancy occurs earlier in the term, the Lieutenant Governor serves as acting governor until a special election can be held to fill the office for the remainder of the four-year term.
If both the Governor and Lieutenant Governor positions are vacant, the Speaker of the House of Representatives schedules a special election and serves as acting governor until the special election is held.
The Georgia Constitution also outlines a process for removing a governor (or other constitutional officers) due to disability. This involves a petition to the Georgia Supreme Court by four constitutional officers and a hearing with medical evaluations to determine fitness for office.
Compensation and Budget of the Governor’s Office
The Governor of Georgia receives a salary determined by state law, as mandated by the Georgia Constitution. The General Assembly is responsible for setting the compensation for the governor, lieutenant governor, and other elected executive officials.
In 2023, the Governor’s salary was $180,000 annually. This figure has seen increases over the years. For example, it was $175,000 in the years 2019-2022 and $139,339 in 2018.
The budget for the Governor’s Office is also a significant aspect of state finances. In Fiscal Year 2025, the budget allocated for the Office of the Governor was $6,904,362. This budget covers the operational costs of the governor’s office and its staff, enabling the governor to carry out their duties effectively.
Historical Perspective and Partisan Balance
Historically, Georgia has seen a shift in partisan control of the governorship. For a significant period, particularly from 1992 to 2002, Georgia had Democratic governors. However, starting in 2003 with Sonny Perdue, the state shifted towards Republican leadership in the governor’s office. This Republican trend has continued through Nathan Deal and current Governor Brian Kemp.
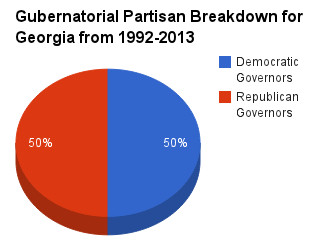 Pie chart of Georgia gubernatorial partisan balance from 1992-2013
Pie chart of Georgia gubernatorial partisan balance from 1992-2013
This partisan shift reflects broader political trends in the Southern United States. From 1992-2013, while nationally there was a slight Republican advantage in gubernatorial years, Georgia transitioned from a Democratic to a Republican stronghold. This change also coincided with Georgia becoming a Republican trifecta state, where the Republican party controls the governorship and both chambers of the state legislature.
Conclusion: Term Limits and the Dynamics of Georgia’s Governorship
In summary, a governor in Georgia can serve a maximum of two consecutive four-year terms. This term limit is a key feature of the state’s governance structure, designed to promote democratic principles and prevent long-term entrenchment of power. Beyond term limits, the office of the Governor of Georgia is defined by specific qualifications, a robust election process, significant duties and powers, and a clear line of succession. Understanding these aspects provides valuable insight into the leadership and governance of the state of Georgia.
For further information, you can refer to the official website of the Governor of Georgia or consult resources like the Georgia Constitution and Ballotpedia for detailed information on Georgia state government and elections.
Contact Information for the Governor’s Office:
Mailing address: 206 Washington Street Suite 203, State Capitol Atlanta, GA 30334
Phone: 404-656-1776

