Are you looking for the best Aws Storage Server options to power your business? At rental-server.net, we understand that choosing the right storage solution is crucial for performance, cost-efficiency, and scalability. This guide explores various AWS storage services to help you make an informed decision and optimize your infrastructure with AWS cloud storage solutions.
1. What is an AWS Storage Server and Why is it Important?
An AWS storage server refers to the range of storage solutions provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) to store and manage data in the cloud. AWS provides various options such as Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon EFS, each designed for different use cases and performance needs.
Choosing the right storage server is crucial because it directly impacts your application’s performance, data durability, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. According to Gartner, by 2025, 80% of enterprises will have shut down their traditional data centers, relying instead on cloud services like AWS.
1.1 What are the Key Benefits of Using an AWS Storage Server?
Using an AWS storage server provides numerous advantages, making it a compelling choice for businesses of all sizes.
- Scalability: AWS storage solutions can easily scale to accommodate growing data needs without requiring significant upfront investment in hardware.
- Durability: AWS storage services like Amazon S3 offer exceptional data durability, ensuring that your data is protected against loss or corruption.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With AWS, you only pay for the storage you use, eliminating the need for costly infrastructure maintenance and upgrades.
- Accessibility: AWS storage servers provide secure and reliable access to your data from anywhere in the world, enabling seamless collaboration and remote work.
- Integration: AWS storage services integrate seamlessly with other AWS services, such as EC2, Lambda, and RDS, enabling you to build powerful and flexible cloud-based applications.
1.2 How Does AWS Storage Server Improve Business Operations?
AWS storage servers improve business operations by providing a reliable, scalable, and cost-effective way to store and manage data. This enables businesses to:
- Enhance Data Security: AWS provides robust security features, including encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications, to protect your data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Streamline Data Management: AWS storage services offer centralized management tools that simplify data organization, backup, and recovery, reducing administrative overhead and improving operational efficiency.
- Enable Data-Driven Decision Making: With AWS storage, you can easily store and analyze large volumes of data, gaining valuable insights that can inform business decisions and drive innovation.
- Support Business Continuity: AWS storage solutions offer high availability and disaster recovery capabilities, ensuring that your data is always accessible, even in the event of an outage or natural disaster.
 aws-storage-options
aws-storage-options
2. What are the Different Types of AWS Storage Servers Available?
AWS offers a variety of storage services, each designed to meet specific requirements for performance, durability, and cost. Understanding these options is crucial for selecting the right storage solution for your business.
2.1 Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
Amazon S3 is an object storage service designed to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere. It is highly scalable, durable, and secure, making it ideal for a wide range of use cases, including backup and storage, application hosting, and media hosting. According to Amazon, S3 is designed for 99.999999999% durability.
2.1.1 What are the Key Features and Benefits of Amazon S3?
- Scalability and Durability: S3 can store virtually unlimited amounts of data and is designed for high durability, ensuring that your data is protected against loss or corruption.
- Cost-Effectiveness: S3 offers various storage classes, allowing you to optimize costs based on access frequency and storage duration.
- Security: S3 provides comprehensive security features, including access controls, encryption, and compliance certifications, to protect your data from unauthorized access.
- Integration: S3 integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, enabling you to build powerful and flexible cloud-based applications.
- Query-in-Place Functionality: S3 allows you to run powerful analytics directly on your data at rest, eliminating the need to move data to a separate analytics platform.
2.1.2 What are the Different S3 Storage Classes and Their Use Cases?
S3 offers several storage classes, each optimized for different access patterns and storage durations. Here’s an overview of the most common S3 storage classes:
| Storage Class | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| S3 Standard | Durable, immediately available storage for frequently accessed data. | Active workloads, content distribution, mobile and gaming applications, big data analytics. |
| S3 Intelligent-Tiering | Automatically moves data to the most cost-effective tier based on access patterns. | Applications with changing access patterns, data with unknown or unpredictable access patterns. |
| S3 Standard-IA | Durable, immediately available storage for infrequently accessed data. | Long-term storage, backup and disaster recovery, data archiving. |
| S3 One Zone-IA | Lower cost option for infrequently accessed data with less resilience (stored in a single Availability Zone). | Secondary backups, easily re-creatable data, data with lower availability requirements. |
| S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval | Low-cost storage for data that is rarely accessed and requires retrieval in milliseconds. | Archival data, compliance archives, long-term backups. |
| S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval | Lowest cost storage for archived data, with retrieval times in minutes or hours. | Long-term data archiving, digital preservation, compliance retention. |
| S3 Glacier Deep Archive | Lowest cost storage class for long-term retention of data that is rarely accessed, with retrieval times in hours. | Data that must be retained for regulatory or compliance reasons, long-term archival data. |
2.1.3 How Does S3 Integrate with Other AWS Services?
S3 integrates seamlessly with a wide range of AWS services, enabling you to build powerful and flexible cloud-based applications. Here are some examples of how S3 integrates with other AWS services:
- Amazon EC2: S3 can be used to store and retrieve data for EC2 instances, such as application code, configuration files, and media assets.
- AWS Lambda: S3 can trigger Lambda functions when objects are created, updated, or deleted, enabling you to automate data processing and workflow orchestration.
- Amazon RDS: S3 can be used to store database backups and snapshots, providing a cost-effective and durable solution for disaster recovery.
- Amazon CloudFront: S3 can be used as the origin for CloudFront distributions, enabling you to deliver content to users with low latency and high transfer speeds.
- AWS Glue: S3 can be used as a data source for AWS Glue, enabling you to extract, transform, and load data for analytics and data warehousing.
2.2 Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
Amazon EBS provides persistent block storage volumes for use with Amazon EC2 instances. EBS volumes are automatically replicated within their Availability Zone to protect you from component failure, offering high availability and durability.
2.2.1 What are the Different Types of EBS Volumes and Their Performance Characteristics?
EBS offers several volume types, each optimized for different workloads and performance requirements.
| Volume Type | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| EBS Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1/io2) | Highest performance SSD volume designed for latency-sensitive transactional workloads. | I/O-intensive NoSQL and relational databases. |
| EBS General Purpose SSD (gp2/gp3) | General Purpose SSD volume that balances price performance for a wide variety of transactional workloads. | Boot volumes, low-latency interactive apps, dev & test. |
| Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) | Low-cost HDD volume, designed for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads. | Big-data, data warehouses, log processing. |
| Cold HDD (sc1) | Lowest cost HDD volume designed for less frequently accessed workloads. | Colder data requiring fewer scans per day. |
2.2.2 How Does EBS Ensure Data Durability and Availability?
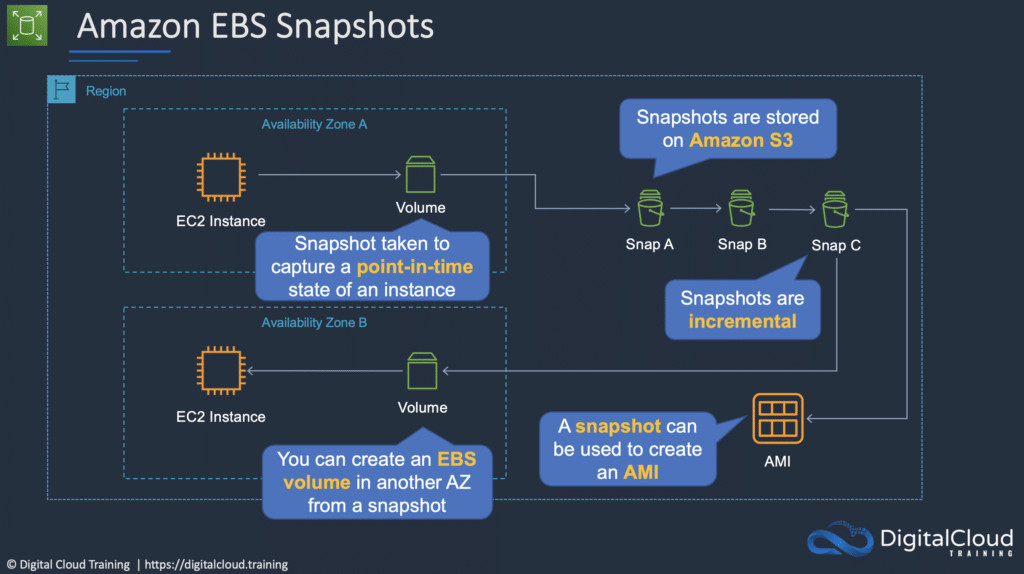
EBS ensures data durability and availability through automatic replication within its Availability Zone. Each EBS volume is replicated multiple times to protect against component failure, ensuring that your data remains accessible even in the event of an outage. Additionally, EBS supports snapshots, which are point-in-time backups of your data that can be stored in S3 for long-term durability.
2.2.3 What are EBS Snapshots and How Do They Work?
EBS snapshots are incremental backups of your EBS volumes that are stored in S3. When you create a snapshot, only the blocks on the volume that have changed since the last snapshot are saved, reducing storage costs and backup times. Snapshots can be used to create new EBS volumes or restore existing volumes to a previous state, providing a flexible and reliable solution for data protection and disaster recovery.
2.3 Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)
EFS provides a fully managed file system service that makes it easy to set up and scale file storage in the Amazon Cloud. EFS is elastic, growing and shrinking as you add and remove data, and can concurrently connect 1 to 1000s of EC2 instances from multiple Availability Zones.
2.3.1 What are the Key Features and Benefits of Amazon EFS?
- Scalability and Elasticity: EFS can scale up to petabytes and automatically grows and shrinks as you add and remove data, eliminating the need for pre-provisioning.
- Shared File System: EFS provides a shared file system that can be accessed concurrently by multiple EC2 instances, making it ideal for applications that require shared storage.
- High Availability: EFS stores data across multiple Availability Zones within a region, ensuring high availability and durability.
- Performance: EFS offers two performance modes, General Purpose and Max I/O, allowing you to optimize performance based on your application’s requirements.
- Integration: EFS integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, such as EC2, Lambda, and ECS, enabling you to build powerful and flexible cloud-based applications.
2.3.2 How Does EFS Differ From EBS and S3?
EFS differs from EBS and S3 in several key ways:
- EBS: EBS is a block storage service designed for use with EC2 instances. It provides persistent storage volumes that can be attached to a single EC2 instance at a time.
- S3: S3 is an object storage service designed for storing and retrieving any amount of data from anywhere. It is highly scalable, durable, and secure, making it ideal for a wide range of use cases, including backup and storage, application hosting, and media hosting.
- EFS: EFS is a file system service that provides a shared file system that can be accessed concurrently by multiple EC2 instances. It is elastic, growing and shrinking as you add and remove data, and offers high availability and durability.
| Feature | EBS | S3 | EFS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Block Storage | Object Storage | File System |
| Access | Single EC2 Instance | Anywhere via HTTP/HTTPS | Multiple EC2 Instances |
| Scalability | Limited to Volume Size | Virtually Unlimited | Elastic, Grows and Shrinks |
| Durability | High (Replication within AZ) | Extremely High (99.999999999% designed) | High (Replication across AZs) |
| Use Cases | Boot Volumes, Databases | Backup, Media Storage, Static Websites | Shared File Storage, Content Mgmt |
2.3.3 What are the Performance Modes and Throughput Options for EFS?
EFS offers two performance modes:
- General Purpose: Appropriate for most file systems and provides good performance for a wide range of workloads.
- Max I/O: Optimized for applications where tens, hundreds, or thousands of EC2 instances are accessing the file system.
EFS also offers two throughput options:
- Bursting Throughput: Allows your file system to burst to higher throughput levels for periods of time.
- Provisioned Throughput: Allows you to provision a specific amount of throughput for your file system, ensuring consistent performance for demanding workloads.
2.4 AWS Snow Family
The AWS Snow Family is a collection of physical devices designed to move large amounts of data into and out of AWS. The Snow Family includes AWS Snowball, AWS Snowcone, and AWS Snowmobile, each designed for different use cases and data transfer volumes.
2.4.1 What are AWS Snowball, Snowcone, and Snowmobile and Their Primary Use Cases?
- AWS Snowball: A portable storage and compute device designed to transfer hundreds of terabytes or petabytes of data between your on-premises data centers and AWS. It is ideal for large-scale data migrations, disaster recovery, and edge computing.
- AWS Snowcone: A small, rugged, and secure edge computing and data transfer device designed for use in harsh environments. It is ideal for IoT data collection, mobile data acquisition, and edge analytics.
- AWS Snowmobile: A literal shipping container full of storage (up to 100PB) and a truck to transport it. It is ideal for extremely large-scale data migrations, such as migrating an entire data center to AWS.
2.4.2 How Do AWS Snow Family Devices Ensure Data Security During Transfer?
AWS Snow Family devices ensure data security during transfer through several measures:
- Encryption: All data transferred to Snow Family devices is automatically encrypted using 256-bit encryption.
- Tamper-Resistance: Snow Family devices are tamper-resistant and include a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) that detects any unauthorized modifications to the hardware or software.
- Physical Security: Snow Family devices are physically secured and tracked throughout the data transfer process.
- Data Wipe: Once the data transfer is complete, AWS securely wipes the data from the Snow Family device before returning it to you.
2.4.3 What are the Benefits of Using AWS Snow Family for Data Migration?
Using AWS Snow Family for data migration offers several benefits:
- Faster Data Transfer: Snow Family devices can transfer data much faster than traditional network-based methods, especially for large datasets.
- Reduced Network Costs: By transferring data offline, Snow Family devices can significantly reduce network costs associated with data migration.
- Improved Security: Snow Family devices provide a secure and tamper-resistant way to transfer data, reducing the risk of data loss or corruption.
- Simplified Migration Process: AWS provides tools and services to simplify the data migration process using Snow Family devices, making it easier to move your data to the cloud.
2.5 AWS Storage Gateway
AWS Storage Gateway is a hybrid cloud storage service that gives you on-premises access to virtually unlimited cloud storage. Storage Gateway connects your on-premises applications to AWS storage services, enabling you to seamlessly integrate your on-premises and cloud environments.
2.5.1 What are the Different Types of AWS Storage Gateway and Their Use Cases?
AWS Storage Gateway offers three different types of gateways:
- File Gateway: Provides file system interfaces to on-premises servers, allowing you to store files in S3 via NFS or SMB. It is ideal for file sharing, backup, and archiving.
- Volume Gateway: Provides block-based access for on-premises servers, allowing you to store block data in AWS via iSCSI. It is ideal for backup and disaster recovery.
- Tape Gateway: Provides a virtual tape library that is compatible with common backup software, allowing you to archive your data to AWS using virtual tapes. It is ideal for long-term data retention and compliance.
2.5.2 How Does AWS Storage Gateway Facilitate Hybrid Cloud Storage?
AWS Storage Gateway facilitates hybrid cloud storage by providing a seamless connection between your on-premises applications and AWS storage services. It allows you to store data in AWS while maintaining local access to that data, enabling you to take advantage of the scalability, durability, and cost-effectiveness of AWS storage without disrupting your existing on-premises workflows.
2.5.3 What are the Benefits of Using AWS Storage Gateway for On-Premises Data Storage?
Using AWS Storage Gateway for on-premises data storage offers several benefits:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Storage Gateway allows you to reduce on-premises storage costs by leveraging the cost-effective storage services of AWS.
- Scalability: Storage Gateway provides virtually unlimited storage capacity, allowing you to scale your storage infrastructure without investing in additional hardware.
- Durability: Storage Gateway stores your data in highly durable AWS storage services, ensuring that your data is protected against loss or corruption.
- Integration: Storage Gateway integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, enabling you to build powerful and flexible hybrid cloud applications.
3. How to Choose the Right AWS Storage Server for Your Needs?
Choosing the right AWS storage server for your needs requires careful consideration of your application’s requirements, data characteristics, and budget constraints. Here are some factors to consider when selecting an AWS storage server:
3.1 Understanding Your Storage Requirements
Before selecting an AWS storage server, it is important to understand your storage requirements, including:
- Data Volume: How much data do you need to store?
- Access Frequency: How often will your data be accessed?
- Performance Requirements: What are the latency and throughput requirements for your application?
- Durability Requirements: How important is it to protect your data against loss or corruption?
- Compliance Requirements: Do you have any regulatory or compliance requirements for data storage?
3.2 Considering Performance, Durability, and Cost
When selecting an AWS storage server, it is important to consider the trade-offs between performance, durability, and cost. Here’s a general guideline:
- Performance: If your application requires low latency and high throughput, consider using EBS or EFS.
- Durability: If data durability is critical, consider using S3 or EFS, which offer high levels of data protection.
- Cost: If cost is a primary concern, consider using S3 Glacier or S3 One Zone-IA, which offer lower storage costs for infrequently accessed data.
3.3 Matching Storage Solutions to Specific Use Cases
To help you choose the right AWS storage server for your needs, here are some common use cases and the recommended storage solutions:
| Use Case | Recommended Storage Solution(s) |
|---|---|
| Web Hosting | S3 |
| Database Storage | EBS |
| Shared File Storage | EFS |
| Backup and Disaster Recovery | S3, EBS Snapshots, Storage Gateway |
| Archiving | S3 Glacier |
| Big Data Analytics | S3, EFS |
| Content Delivery | S3, CloudFront |
| Hybrid Cloud Storage | Storage Gateway |
4. Optimizing AWS Storage Server Costs
Optimizing AWS storage server costs is crucial for maximizing your return on investment. Here are some strategies for reducing your AWS storage costs:
4.1 Utilizing S3 Storage Classes Effectively
Leverage S3 storage classes to optimize costs based on access frequency. Move infrequently accessed data to lower-cost storage classes like S3 Standard-IA, S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval, or S3 Glacier Deep Archive.
4.2 Implementing Lifecycle Policies
Implement lifecycle policies to automatically transition objects between storage classes based on age and access patterns. This can help you reduce storage costs by moving older, less frequently accessed data to lower-cost storage classes.
4.3 Compressing Data Before Storing
Compress data before storing it in S3 or EBS to reduce storage costs and improve transfer speeds. Use compression algorithms like gzip or zstd to reduce the size of your data.
4.4 Deleting Unnecessary Data
Regularly review your storage and delete unnecessary data to reduce storage costs. Identify and remove old backups, log files, and other data that is no longer needed.
4.5 Monitoring Storage Usage and Costs
Monitor your storage usage and costs using AWS Cost Explorer and CloudWatch to identify areas where you can optimize costs. Set up alerts to notify you when your storage costs exceed a certain threshold.
According to a study by Flexera, organizations waste an average of 30% of their cloud spending. By implementing these cost optimization strategies, you can significantly reduce your AWS storage costs and improve your overall cloud ROI.
5. Securing Your AWS Storage Server
Securing your AWS storage server is essential for protecting your data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Here are some best practices for securing your AWS storage server:
5.1 Implementing Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Bucket Policies
Use ACLs and bucket policies to control access to your S3 buckets and objects. Grant the minimum necessary permissions to users and applications to prevent unauthorized access.
5.2 Enabling Encryption at Rest and in Transit
Enable encryption at rest and in transit to protect your data from unauthorized access. Use server-side encryption (SSE) or client-side encryption to encrypt your data at rest, and use HTTPS to encrypt your data in transit.
5.3 Using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Use IAM to manage access to your AWS storage server. Create IAM users and roles with specific permissions to access your storage resources.
5.4 Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Enable MFA for all IAM users who have access to your AWS storage server. This adds an extra layer of security to your account and helps protect against unauthorized access.
5.5 Regularly Auditing Security Settings
Regularly audit your security settings to ensure that your AWS storage server is properly secured. Use AWS Trusted Advisor and AWS Security Hub to identify security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
By implementing these security best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and protect your valuable data in the cloud.
6. Managing and Monitoring Your AWS Storage Server
Effective management and monitoring of your AWS storage server are crucial for ensuring optimal performance, availability, and security. Here are some best practices for managing and monitoring your AWS storage server:
6.1 Using AWS CloudWatch for Monitoring
Use AWS CloudWatch to monitor your storage server’s performance, availability, and security. Set up alarms to notify you when certain metrics exceed a threshold.
6.2 Implementing Logging and Auditing
Implement logging and auditing to track access to your storage server and identify potential security threats. Use AWS CloudTrail to log all API calls made to your storage resources.
6.3 Automating Tasks with AWS Lambda
Automate common management tasks with AWS Lambda. Use Lambda functions to automatically create backups, delete old data, and perform other routine tasks.
6.4 Using AWS Backup for Centralized Backup Management
Use AWS Backup for centralized backup management across your AWS storage resources. AWS Backup allows you to create backup policies and schedules to automatically back up your data.
6.5 Regularly Reviewing Performance and Security
Regularly review your storage server’s performance and security to identify areas for improvement. Use AWS Trusted Advisor and AWS Security Hub to identify security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
7. Future Trends in AWS Storage Servers
The landscape of AWS storage servers is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time. Here are some future trends to watch out for:
7.1 Increased Use of NVMe Storage
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) storage is becoming increasingly popular for high-performance applications. AWS is likely to offer more NVMe-based storage options in the future.
7.2 Greater Integration with Machine Learning
AWS is likely to continue to integrate its storage services with its machine learning services, enabling you to easily analyze and process data stored in S3 and other storage resources.
7.3 Enhanced Data Management Capabilities
AWS is likely to add more data management capabilities to its storage services, making it easier to organize, classify, and govern your data.
7.4 Serverless Storage Solutions
Serverless storage solutions, such as AWS Lambda-backed S3 buckets, are likely to become more popular in the future. These solutions offer greater scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
8. How Can Rental-Server.net Help You with AWS Storage Servers?
At rental-server.net, we provide comprehensive solutions to help you with your AWS storage needs. Whether you’re looking for information, guidance, or managed services, we have you covered.
8.1 Our Services and Expertise
We offer a range of services to help you with your AWS storage server needs, including:
- Consulting: We can help you assess your storage requirements and choose the right AWS storage solutions for your business.
- Implementation: We can help you implement and configure your AWS storage servers, ensuring that they are properly secured and optimized for performance.
- Management: We can provide managed services to monitor and maintain your AWS storage servers, freeing you up to focus on your core business.
- Optimization: We can help you optimize your AWS storage costs and performance, ensuring that you are getting the most out of your cloud investment.
8.2 Case Studies and Success Stories
We have helped numerous clients successfully implement and manage their AWS storage servers. Here are a few examples:
- Case Study 1: We helped a large e-commerce company migrate their product catalog to S3, resulting in a 50% reduction in storage costs and improved website performance.
- Case Study 2: We helped a financial services firm implement a secure and compliant backup solution using EBS snapshots and S3 Glacier, ensuring that their critical data is protected against loss or corruption.
- Case Study 3: We helped a media company implement a shared file storage solution using EFS, enabling their video editors to collaborate more efficiently and improve their workflow.
8.3 Contact Us for a Free Consultation
Ready to take your AWS storage to the next level? Contact us today for a free consultation. Our team of experts can help you assess your storage needs, choose the right AWS storage solutions, and optimize your cloud infrastructure for performance, cost, and security.
Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States
Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000
Website: rental-server.net
9. FAQs About AWS Storage Servers
Here are some frequently asked questions about AWS storage servers:
9.1 What is the difference between S3 and EBS?
S3 is object storage for unstructured data, while EBS is block storage for EC2 instances, offering different performance and use cases.
9.2 How do I choose the right S3 storage class?
Consider data access frequency and storage duration when selecting an S3 storage class for cost optimization.
9.3 Can I use EBS volumes with multiple EC2 instances?
No, EBS volumes can only be attached to one EC2 instance at a time. Use EFS for shared file storage across multiple instances.
9.4 What is AWS Storage Gateway used for?
AWS Storage Gateway connects on-premises applications to AWS storage services, facilitating hybrid cloud storage solutions.
9.5 How do I secure my AWS storage server?
Implement ACLs, bucket policies, encryption, and IAM to protect your data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
9.6 What are the benefits of using AWS Snow Family?
AWS Snow Family offers faster data transfer, reduced network costs, and improved security for large-scale data migrations.
9.7 How do I optimize my AWS storage costs?
Utilize S3 storage classes effectively, implement lifecycle policies, compress data, and delete unnecessary data to reduce storage costs.
9.8 What is the role of AWS CloudWatch in storage management?
AWS CloudWatch monitors storage server performance, availability, and security, helping you optimize your cloud infrastructure.
9.9 Can Rental-Server.net help me with my AWS storage needs?
Yes, rental-server.net provides consulting, implementation, management, and optimization services to help you with your AWS storage needs.
9.10 What are the future trends in AWS storage servers?
Future trends include increased use of NVMe storage, greater integration with machine learning, enhanced data management capabilities, and serverless storage solutions.
10. Conclusion
Choosing the right AWS storage server is crucial for optimizing your cloud infrastructure for performance, cost, and security. By understanding the different storage options available and carefully considering your application’s requirements, you can select the ideal storage solutions for your business. At rental-server.net, we are committed to providing you with the expertise and services you need to succeed in the cloud. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you optimize your AWS storage and achieve your business goals.

