We recently explored the evolution of cloud computing over six decades. However, it was around 2002 that cloud computing began to take its current form, driven by Amazon’s need for a more scalable infrastructure for its online marketplace.
It’s therefore not surprising that Amazon’s cloud services arm, Amazon Web Services (AWS), launched in 2006, has become the dominant Cloud Service Provider (CSP) today.
This guide will delve into the cloud infrastructure market, highlight the major players, and help you understand how to choose the Top Cloud Server for your needs.
Understanding Cloud Service Providers and Cloud Servers
A cloud service provider essentially rents out a combination of technology, infrastructure, and expertise to businesses and individuals. This enables cloud computing, encompassing online storage, computing power, and networking capabilities accessible via the internet.
Cloud service providers maintain and operate numerous data centers globally. These facilities house the physical infrastructure essential for cloud computing, including servers, storage devices, and cooling systems.
Users can access this cloud infrastructure from anywhere, at any time, by connecting to these data centers. They can then procure the required capacity on a flexible, pay-as-you-go basis, often referred to as usage-based pricing.
CSPs offer a range of benefits beyond just infrastructure.
Are you struggling with cloud costs and visibility? Discover cloud cost management tools to gain better control over your cloud expenditure.
 A playbook depicting cloud cost management strategies
A playbook depicting cloud cost management strategies
Benefits of Choosing a Top Cloud Server Over On-Premises Solutions
Companies often opt for cloud servers from CSPs rather than building their own on-premises infrastructure due to the high costs, specialized expertise needed, and continuous maintenance demands associated with in-house solutions. Utilizing a reputable cloud service provider for your server needs offers several advantages:
- Reduced Capital Expenditure: Customers avoid substantial upfront investments in infrastructure. Instead, they pay a predictable, ongoing fee based on their usage.
- Accelerated Time-to-Market: By bypassing the lengthy process of procuring, installing, configuring, and optimizing server infrastructure, businesses can launch products and services much faster.
- Enhanced Agility: Cloud servers enable businesses to adapt and pivot more rapidly. They eliminate the need to liquidate existing infrastructure and invest in new hardware when exploring new markets or business ventures.
- Comprehensive Cloud Computing Services: CSPs provide a wide array of services, including Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), and Serverless Computing options.
- Flexible Cloud Deployment Models: Businesses can select from various cloud server deployment models offered by CSPs, such as public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments.
- Pay-As-You-Go Pricing for Servers: You only pay for the server resources you consume. There are no provisioning charges, upfront payments, or long-term contracts typically required.
- Managed Server Services: CSPs offer varying levels of management over the rented server infrastructure. You can choose fully managed services or options that allow your engineers greater configuration control.
- Robust Disaster Recovery for Servers and Data: CSPs can replicate your server data across multiple geographic regions, ensuring data redundancy and enabling recovery in case of data center failures or on-premises system disruptions.
Furthermore, CSPs handle the testing, updates, security, and optimization of server infrastructure and related services. This allows your organization to concentrate resources on core business activities. However, the cloud server model also presents certain challenges.
Key Challenges of Utilizing a Cloud Server from a CSP
While cloud servers offer numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of the potential challenges:
Data Confidentiality on Shared Servers
Public cloud environments rely on a network of shared, third-party owned servers to process, store, and manage data. This differs from on-premises solutions where a single customer owns and controls the storage devices and servers within their own data center or office. This shared infrastructure model can raise concerns for businesses handling sensitive business secrets, customer data, and compliance-related information.
Data Security Risks on Cloud Servers
Cloud computing via a CSP’s server infrastructure involves transmitting data remotely and accessing it from various devices with internet connectivity. While CSPs invest heavily in security, they are not immune to breaches. Hackers can potentially infiltrate their systems and compromise customer data residing on cloud servers, leading to reputational damage, customer attrition, and potential legal repercussions.
Limited Infrastructure Control Over Servers
Some organizations require greater control over the backend server infrastructure to optimize performance and meet specific requirements. However, the level of control can vary depending on the cloud service provider and the type of server service selected. Certain CSPs may offer limited configuration options compared to on-premises setups.
Vendor Lock-in with Specific Server Technologies
Over-reliance on a single cloud service provider for your server needs can create vendor lock-in. If your chosen CSP alters its pricing structure or implements unfavorable changes, migrating your server infrastructure and applications to another provider can be complex, costly, and time-consuming.
Considering migration options, let’s examine the current market landscape for cloud servers.
Market Share of the Leading Cloud Server Providers: AWS, Azure, and GCP
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are the dominant cloud service providers in the market today. Collectively, these “big three” capture approximately 66% of the global cloud infrastructure market, increasing from 63% the previous year, according to Synergy Research Group data.
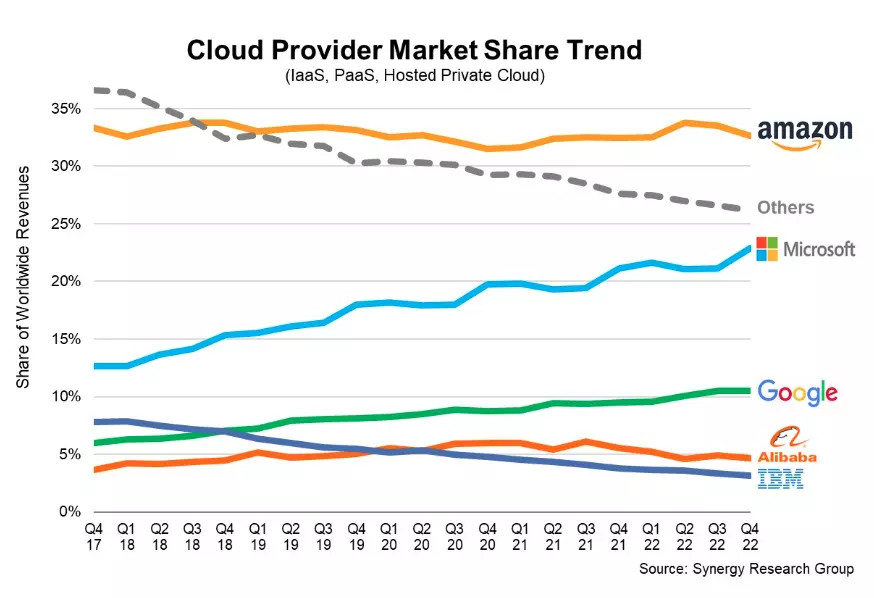 Line graph showing cloud service provider market share trends Credit: Cloud service providers market share at the beginning of 2023 – Synergy Research Group
Line graph showing cloud service provider market share trends Credit: Cloud service providers market share at the beginning of 2023 – Synergy Research Group
Research indicates that the total cloud computing market generated over $227 billion in revenue in the preceding 12 months.
Furthermore, forecasts from Grand View Research project a robust 13.1% CAGR for the US cloud computing market between 2023 and 2030.
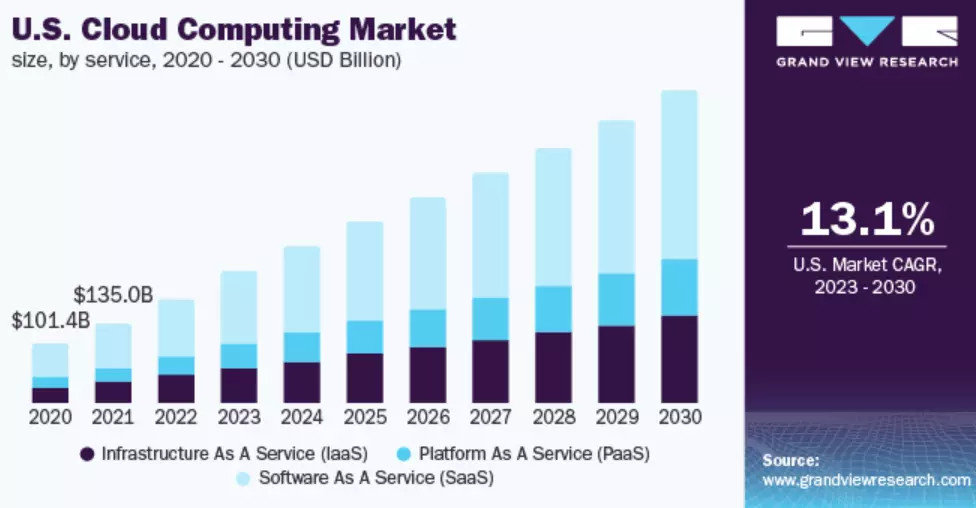 Bar chart illustrating cloud service provider market share in the US Credit: Cloud computing marketshare in the US – Grand View Research
Bar chart illustrating cloud service provider market share in the US Credit: Cloud computing marketshare in the US – Grand View Research
This growth trajectory suggests that these major players, along with other emerging providers, will continue to expand and innovate in the cloud server space. Let’s explore some of the top cloud service providers offering leading cloud server solutions in 2024.
Top 13 Cloud Server Providers in 2024
The following cloud providers are powering some of the world’s most innovative companies, providing the server infrastructure for their cloud operations.
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Premier Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) Cloud Servers
 Amazon Web Services (AWS) logo Amazon Web Services (AWS) delivers a comprehensive suite of over 200 cloud services spanning diverse industries and technology domains.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) logo Amazon Web Services (AWS) delivers a comprehensive suite of over 200 cloud services spanning diverse industries and technology domains.
AWS is particularly renowned for its robust Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) offerings, anchored by services like Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) for compute servers, Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) for storage, and Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for databases. AWS EC2 provides a vast range of server instance types optimized for various workloads, from general-purpose computing to memory-intensive and accelerated computing tasks.
With a global footprint of over 100 Availability Zones across 31 geographic regions, AWS currently commands over 34% of the global cloud computing market share, making it a leading provider of cloud servers.
While AWS is best known for its highly scalable public cloud servers, it also supports on-premises, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and multi-cloud server deployments. AWS offers a mix of free-tier, cost-effective, and premium server options, known for its rapid setup and deployment processes.
Explore further: “The 25+ Best AWS Cost Optimization Tools (Organized By Category)”
2. Microsoft Azure – Enterprise-Grade and Hybrid Cloud Servers
 Microsoft Azure logo Microsoft Intelligent Cloud delivers AWS-comparable cloud computing services through the Azure Cloud, operating across more than 116 Availability Zones globally.
Microsoft Azure logo Microsoft Intelligent Cloud delivers AWS-comparable cloud computing services through the Azure Cloud, operating across more than 116 Availability Zones globally.
The Azure cloud offers over 200 cloud services, including Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), as well as Edge and Serverless computing solutions. Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) provide a wide selection of server options, including Windows and Linux-based VMs, catering to enterprise needs and hybrid cloud strategies.
Launched in 2010, two years after AWS, Azure has steadily grown to capture a 23% market share. Its appeal lies in its strong integration with enterprise environments, hybrid cloud capabilities, and seamless compatibility with Microsoft product ecosystems, including Office 365, making it a top choice for businesses seeking robust cloud servers.
Related reading: “The 15 Best Azure Cost Management Tools”
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – Innovative Cloud Servers for AI, ML, and Kubernetes
 Google Cloud Platform (GCP) logo The Google Cloud Platform provides a similar range of services to Azure and AWS. However, GCP has distinguished itself through innovation in areas like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Data Analytics, and Kubernetes, the widely adopted container management platform. Google Compute Engine offers high-performance virtual machines and specialized server instances optimized for data-intensive workloads and advanced analytics, positioning GCP as a leader in cloud servers for cutting-edge applications.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) logo The Google Cloud Platform provides a similar range of services to Azure and AWS. However, GCP has distinguished itself through innovation in areas like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Data Analytics, and Kubernetes, the widely adopted container management platform. Google Compute Engine offers high-performance virtual machines and specialized server instances optimized for data-intensive workloads and advanced analytics, positioning GCP as a leader in cloud servers for cutting-edge applications.
GCP is also favored by smaller companies that frequently utilize Alphabet’s services, such as Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Gmail, etc.), Google Drive, YouTube, and Google Console.
Further insights: “The 15 Best GCP Cost Optimization Tools For Google Cloud”
4. Alibaba Cloud – Leading Cloud Server Provider in Asia
 Alibaba Cloud logo For businesses operating in Southeast Asia considering cloud adoption, Alibaba Cloud is a primary contender. Similar to AWS’s origin within Amazon, Alibaba Cloud evolved from the Alibaba e-commerce ecosystem. Since 2009, it has grown to command approximately 5% of the global cloud services market, becoming a major cloud server provider in the Asian region.
Alibaba Cloud logo For businesses operating in Southeast Asia considering cloud adoption, Alibaba Cloud is a primary contender. Similar to AWS’s origin within Amazon, Alibaba Cloud evolved from the Alibaba e-commerce ecosystem. Since 2009, it has grown to command approximately 5% of the global cloud services market, becoming a major cloud server provider in the Asian region.
Alibaba Cloud supports critical operations for a diverse clientele, including large enterprises, SMEs, government agencies, and non-profit organizations, offering a comprehensive suite of cloud server solutions.
5. IBM Cloud – Multi-Cloud Focused Server Solutions
 IBM Cloud logo IBM Cloud Services assists businesses seeking to transition to digital platforms while maintaining familiarity with on-premises environments. IBM Cloud supports about 4% of the cloud computing services market, offering over 170 products across on-premises, hybrid cloud, and multi-cloud server deployments. IBM Cloud Virtual Servers are designed for enterprise workloads, emphasizing security and compliance.
IBM Cloud logo IBM Cloud Services assists businesses seeking to transition to digital platforms while maintaining familiarity with on-premises environments. IBM Cloud supports about 4% of the cloud computing services market, offering over 170 products across on-premises, hybrid cloud, and multi-cloud server deployments. IBM Cloud Virtual Servers are designed for enterprise workloads, emphasizing security and compliance.
Like the top four providers, IBM Cloud is also heavily invested in managed Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and cloud migration services, providing robust server solutions for diverse business needs.
6. DigitalOcean Cloud – Developer-Centric Cloud Servers for SMBs
 DigitalOcean Cloud logo The DigitalOcean Cloud platform provides developers with a streamlined platform for deploying and scaling projects across multiple servers concurrently. It ranks as the third-largest hosting company globally and primarily offers compute and storage products. DigitalOcean Droplets are virtual servers known for their simplicity and developer-friendliness, targeting small to medium businesses and individual developers.
DigitalOcean Cloud logo The DigitalOcean Cloud platform provides developers with a streamlined platform for deploying and scaling projects across multiple servers concurrently. It ranks as the third-largest hosting company globally and primarily offers compute and storage products. DigitalOcean Droplets are virtual servers known for their simplicity and developer-friendliness, targeting small to medium businesses and individual developers.
DigitalOcean delivers IaaS, focusing on small and medium businesses with a pay-as-you-go pricing model for its cloud server offerings.
7. Salesforce Cloud – Cloud-Hosted Servers for SaaS and CRM
 Salesforce Cloud logo Salesforce pioneered the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model in its modern form in the late 1990s. Today, Salesforce Cloud offers various cloud types, including cloud-based applications for marketing, sales, customer experience, analytics, commerce, and services. While not directly offering general-purpose cloud servers like AWS or Azure, Salesforce’s infrastructure powers its extensive suite of SaaS applications, including its flagship customer relationship management (CRM) tools.
Salesforce Cloud logo Salesforce pioneered the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model in its modern form in the late 1990s. Today, Salesforce Cloud offers various cloud types, including cloud-based applications for marketing, sales, customer experience, analytics, commerce, and services. While not directly offering general-purpose cloud servers like AWS or Azure, Salesforce’s infrastructure powers its extensive suite of SaaS applications, including its flagship customer relationship management (CRM) tools.
Salesforce Cloud services are the backbone for the company’s renowned customer relationship management (CRM) suite of tools.
8. Tencent Cloud – Expanding Global Cloud Server Footprint
 Tencent Cloud logo Tencent Cloud offers a wide array of cloud computing services, from cloud virtual machines to cloud file storage and more. Similar to Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud is a major player in China. However, Tencent Cloud operates across 26 regions, with over 70 Availability Zones spanning Northeast and Southeast Asia, South Asia, Oceania, Europe, and North and South America, expanding its global cloud server presence.
Tencent Cloud logo Tencent Cloud offers a wide array of cloud computing services, from cloud virtual machines to cloud file storage and more. Similar to Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud is a major player in China. However, Tencent Cloud operates across 26 regions, with over 70 Availability Zones spanning Northeast and Southeast Asia, South Asia, Oceania, Europe, and North and South America, expanding its global cloud server presence.
9. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) – Versatile Cloud Servers with Database Focus
 Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) logo Oracle was the first vendor to provide IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS cloud deployment models within a unified platform. With OCI, users can access a broad spectrum of cloud services globally. Oracle cloud services encompass on-premises, hybrid cloud, public cloud, and dedicated Cloud@Customer options. OCI Compute offers virtual machines and bare metal servers, with a strong emphasis on database performance and integration with Oracle’s database solutions.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) logo Oracle was the first vendor to provide IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS cloud deployment models within a unified platform. With OCI, users can access a broad spectrum of cloud services globally. Oracle cloud services encompass on-premises, hybrid cloud, public cloud, and dedicated Cloud@Customer options. OCI Compute offers virtual machines and bare metal servers, with a strong emphasis on database performance and integration with Oracle’s database solutions.
Like the leading CSPs, OCI’s distributed cloud portfolio is available across numerous regions worldwide and supports pay-as-you-go pricing.
10. Huawei Cloud – Globally Expanding Cloud Server Options
 Huawei Cloud logo After capturing a significant 18% share of the Chinese cloud market, Huawei is focused on delivering a broad range of cloud computing services across 170 countries. This global expansion strategy positions Huawei Cloud as a growing contender for providing cloud server solutions in the future.
Huawei Cloud logo After capturing a significant 18% share of the Chinese cloud market, Huawei is focused on delivering a broad range of cloud computing services across 170 countries. This global expansion strategy positions Huawei Cloud as a growing contender for providing cloud server solutions in the future.
11. Dell Technologies Cloud – VMware-Powered Virtualized Cloud Servers
 Dell Technologies Cloud logo Utilizing VMware software and Dell Technologies infrastructure, Dell provides an integrated multi-cloud platform. As a hybrid and multi-cloud provider, Dell Technologies Cloud emphasizes storage and data protection services, offering enterprise-grade, highly scalable, and secure cloud server solutions based on VMware virtualization.
Dell Technologies Cloud logo Utilizing VMware software and Dell Technologies infrastructure, Dell provides an integrated multi-cloud platform. As a hybrid and multi-cloud provider, Dell Technologies Cloud emphasizes storage and data protection services, offering enterprise-grade, highly scalable, and secure cloud server solutions based on VMware virtualization.
12. Cisco Cloud Solutions – Hybrid Cloud Servers with Strong Networking
Cisco, a long-established player in networking, entered the cloud market later with its Global InterCloud solution in 2014. While having a smaller market share compared to the top three, Cisco Cloud Solutions offers valuable options, particularly for organizations prioritizing hybrid cloud strategies. Cisco’s cloud servers benefit from its networking expertise, providing strong integration capabilities for hybrid environments.
Cisco’s multi-cloud solutions facilitate seamless integration and management, optimizing workloads and enhancing operational efficiency. Their user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive support services simplify cloud resource deployment and management, easing cloud migration complexities. Cisco is particularly recognized for its robust security protocols, ensuring data integrity and privacy across diverse environments.
13. Rackspace – Managed Cloud Servers for Flexible Needs
 Rackspace, known for its robust infrastructure and high-performance cloud solutions, offers a mix of public, private, and hybrid cloud environments tailored to diverse customer needs. Rackspace Managed Cloud Services are a key differentiator, providing businesses with expert support and management, streamlining operations and reducing demands on internal IT teams. Rackspace servers are backed by their “Fanatical Experience®” customer service approach, emphasizing responsiveness and customer success.
Rackspace, known for its robust infrastructure and high-performance cloud solutions, offers a mix of public, private, and hybrid cloud environments tailored to diverse customer needs. Rackspace Managed Cloud Services are a key differentiator, providing businesses with expert support and management, streamlining operations and reducing demands on internal IT teams. Rackspace servers are backed by their “Fanatical Experience®” customer service approach, emphasizing responsiveness and customer success.
While Rackspace’s market share is smaller, it provides valuable managed cloud server options, though some users note that its pricing can be higher compared to other cloud service providers.
Honorary Mentions: Emerging Cloud Server Providers
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) services: HPE is focusing on Edge-to-Cloud computing and hybrid cloud server deployments, offering solutions for modern distributed infrastructure.
- Linode Cloud services: Linode specializes in providing virtual machines, managed databases, Kubernetes, and cloud storage, offering developer-friendly cloud server options.
Next Steps: Gain Visibility and Control Over Your Cloud Server Costs with CloudZero
Many cloud cost management tools struggle with accurate cost data collection, often relying too heavily on manual tagging, which is frequently incomplete.
As companies increasingly deploy workloads across multiple cloud service providers’ platforms, the need for a cloud cost intelligence platform that delivers clear, actionable cost insights becomes critical.
CloudZero’s cloud cost intelligence approach empowers you to:
- Access, enrich, analyze, and act on comprehensive cost data from leading cloud service providers.
- Collect, analyze, and share hourly cost information across hybrid/multi-cloud server deployments (AWS, Azure, GCP).
- Measure costs for cloud services like Snowflake, MongoDB, Databricks, New Relic, and Kubernetes with business context.
- Measure and track server costs associated with specific customers, products, features, projects, environments, and other relevant dimensions.
- Utilize CloudZero Advisor to optimize instance selection for your AWS, GCP, or Azure server workloads.
- Analyze individual tenant costs in multi-tenant server environments.
- Ensure your engineers receive timely Slack alerts about unusual cost trends in their systems, enabling proactive intervention to prevent overspending.
Experiencing CloudZero firsthand is more impactful than simply reading about it. Discover why brands like Drift (who saved $2.4 million), MalwareBytes, and Remitly trust CloudZero to enhance their cloud spend understanding, management, and control.
Author: Cody Slingerland
Cody Slingerland, a FinOps certified practitioner, is a content creator with over a decade of experience in SaaS and technology content. Cody collaborates with team members and experts to produce authoritative content on the CloudZero blog.

