VMware Vcenter Server stands as the cornerstone of efficient and streamlined management for VMware vSphere virtual environments. It is designed as a robust, centralized platform that empowers administrators to configure, control, and monitor their entire virtual infrastructure from a single pane of glass. Implemented as a prepackaged virtual appliance, vCenter Server is optimized for performance and ease of deployment, encapsulating not only the core server software but also essential supporting services like licensing, authentication, and certificate management.
For organizations leveraging VMware virtualization, vCenter Server provides a critical single point of administration for VMware ESXi hosts and their virtual machines (VMs). Administrators gain granular control over resource provisioning, proactive performance monitoring, workflow automation, and user privilege management, among a host of other capabilities. To underpin these comprehensive operations, vCenter Server is equipped with a suite of key features, including vCenter High Availability (HA), vCenter Hybrid Linked Mode for hybrid cloud environments, and vCenter Server Profiles for consistent configurations.
Diving into VMware vCenter Server Components
The vCenter Server appliance is more than just the central server software; it’s a comprehensive package that includes the vCenter Server application and a range of supporting components vital for its operation. A single instance of vCenter Server is capable of managing up to 2,000 ESXi hosts and an impressive 35,000 virtual machines, showcasing its scalability for even large-scale deployments.
Beyond the vCenter Server itself, the appliance bundles two distinct sets of services: core server services and authentication services, each playing a crucial role in the platform’s functionality.
The core services suite includes integral components such as:
- vSphere Client: This is the modern, web-based interface built on Hypertext Markup Language 5 (HTML5). It provides administrators with a user-friendly portal to connect to and manage their vSphere environments. Replacing the older vSphere Web Client since vSphere 7.0, the HTML5 vSphere Client offers enhanced performance and compatibility across browsers.
- vSphere Auto Deploy: Designed for rapid and consistent ESXi host provisioning, vSphere Auto Deploy is a powerful management tool for deploying and configuring hundreds of ESXi hosts efficiently. Administrators can pre-define the ESXi image and host configurations to ensure uniform deployments at scale.
- vSphere ESXi Dump Collector: This configuration tool is essential for diagnosing system failures. It allows administrators to configure ESXi hosts to automatically save VMkernel memory dumps to a designated network server when critical errors occur. This centralized collection of diagnostic information streamlines troubleshooting and root cause analysis.
- vSphere Lifecycle Manager: A centralized automation engine, vSphere Lifecycle Manager (vLCM) simplifies and automates the management of patches, updates, and upgrades across ESXi hosts, virtual machines, and virtual appliances. vLCM ensures environments are consistently up-to-date and compliant with organizational standards.
- PostgreSQL Relational Database System: At the heart of vCenter Server is the PostgreSQL database, which serves as the repository for storing critical status information about every host, VM, user, and configuration element within the vCenter Server environment. This robust database ensures data integrity and accessibility for vCenter operations.
VMware ESXi management interface showcasing CPU, memory, and storage statistics alongside various host settings.
These core components are intrinsically linked to the vCenter installation and are not available as separate installations, emphasizing the integrated nature of the vCenter Server appliance.
Complementing these core services are a set of critical authentication services, ensuring secure access and management:
- vCenter Single Sign-On (SSO): vCenter SSO is the security backbone of vSphere, providing robust authentication capabilities across the virtual environment. It enables users to authenticate seamlessly using external identity providers or vCenter’s built-in identity provider, enhancing security and simplifying access management.
- vSphere License Service: This service centralizes and simplifies license management across all vCenter instances within a vCenter SSO domain. Administrators can efficiently manage and allocate licenses, ensuring compliance and optimal resource utilization.
- VMware Certificate Authority (VMCA): VMCA plays a vital role in securing vSphere communications. It provisions each ESXi host with a signed certificate, designating VMCA as the default root certificate authority. This ensures secure and trusted communication within the vSphere infrastructure.
VMware has meticulously optimized the vCenter Server appliance for peak performance and reliability. It operates on the Photon operating system, a lightweight, Linux-based, open-source OS specifically tailored for cloud and edge computing environments, further enhancing the appliance’s efficiency and security.
Obtaining vCenter Server: Understanding the Licensing Shift
Historically, vCenter Server was available as a standalone product, offering flexibility in procurement. However, significant changes were introduced in December 2023, following Broadcom Inc.’s acquisition of VMware. VMware transitioned from a perpetual licensing model to a subscription-based model and streamlined its product offerings, impacting how vCenter Server is obtained.
The product portfolio consolidation resulted in two primary platforms: VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) and VMware vSphere Foundation (VVF). vCenter Server is now exclusively available as part of these comprehensive platforms or within specific vSphere product editions geared toward smaller deployments, such as vSphere Essentials Plus Kit and vSphere Standard edition, which are now part of the VVF package.
Within the vSphere product line, vSphere Essentials Plus Kit represents the entry-level option, vSphere Standard offers a mid-range feature set, and vSphere Foundation provides the most comprehensive capabilities. While vSphere Foundation shares many features with VCF, VCF is designed to support the demands of large enterprise workloads with additional advanced features.
Irrespective of the specific platform or edition, vCenter Server is a consistent inclusion. However, it’s important to note that the Essentials Plus Kit includes vCenter Essentials, a scaled-down version of vCenter Server. The vSphere Standard and Foundation editions, along with VCF, include vCenter Standard, the full-featured version capable of managing larger and more complex environments. The key takeaway is that vCenter Server is no longer sold as a standalone product and is exclusively accessed through these bundled offerings.
 virtualization benefits diagram
virtualization benefits diagram
Key Features and Benefits of VMware vCenter Server
VMware vCenter Server is packed with features designed to simplify operations, enhance visibility, and optimize virtual environments. Here are some of the standout features that contribute to its value:
- vCenter Lifecycle Management Service: Extends lifecycle management to vCenter instances themselves, simplifying the scheduling and execution of updates and upgrades for vCenter Server, ensuring the management platform remains healthy and current.
- vCenter Server Profiles: Enables administrators to define, validate, and apply consistent configuration settings across multiple vCenter Server instances. This is particularly beneficial for large deployments, ensuring uniformity and reducing configuration drift.
- vCenter Server Update Planner: Provides administrators with a crucial tool for managing compatibility and interoperability concerns when upgrading vCenter Server instances. It helps assess dependencies and potential issues before initiating updates, minimizing risks.
- Virtual Volumes (vVols): vVols virtualize external storage, offering VM-aware, policy-based storage management capabilities directly within vCenter. This granular control optimizes storage utilization and simplifies storage provisioning for virtual machines.
- vCenter HA (High Availability): A critical feature for business continuity, vCenter HA automatically restarts virtual machines within a cluster if a physical host failure occurs. This minimizes downtime and ensures application availability.
- vCenter Backup and Restore: Provides native backup and restore capabilities for vCenter Server itself, safeguarding the management platform and enabling rapid recovery in case of failures or data loss.
- vCenter Hybrid Linked Mode: Extends management visibility and control to hybrid cloud environments. It provides administrators with a unified view of their vSphere deployments spanning on-premises data centers and vSphere-enabled public clouds, simplifying hybrid cloud management.
- vCenter Extensibility: Offers a comprehensive set of representational state transfer (REST) APIs for seamless communication and integration between vCenter Server and third-party software solutions. VMware partners also provide a variety of plugins to further extend vCenter functionality and integrate with their ecosystems.
These features represent a subset of the extensive capabilities offered by vCenter Server. It’s important to remember that feature availability may vary across different VMware editions, with vCenter Essentials in the Essentials Plus Kit being more limited compared to vCenter Standard.
Weighing the Pros and Cons of vCenter Server
VMware vCenter Server delivers significant advantages, primarily through automation, comprehensive visibility, and high scalability. Its robust toolset facilitates the automation of numerous administrative tasks and supports proactive management strategies. The platform’s extensive visibility across the virtual environment simplifies the configuration and maintenance of host servers and VMs, as well as performance monitoring. Furthermore, vCenter Server’s scalability is a major strength, amplified by vCenter Hybrid Linked Mode for managing large, distributed environments.
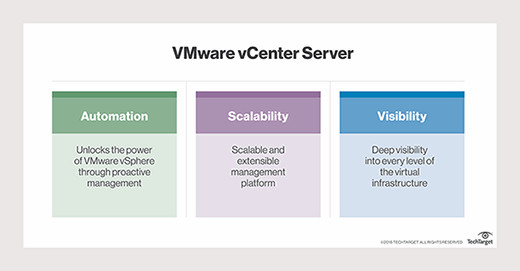 vCenter Server benefits diagram
vCenter Server benefits diagram
VMware emphasizes that vCenter Server streamlines VM deployments, enables continuous performance monitoring, and enhances security by controlling access to resources. Additional benefits include workflow automation, reduced impact of system failures through HA, and simplified integration with a wide range of third-party products.
However, the impressive scalability can also present a potential challenge. Because the vCenter Server database centralizes all server data, managing an exceptionally large number of VMs on a single vCenter instance can increase the risk of approaching database limitations. This might necessitate the deployment of additional vCenter instances to distribute the load, adding to infrastructure complexity and cost.
In conclusion, vCenter Server is an indispensable tool for organizations committed to VMware virtualization, offering a powerful centralized management platform. While it introduces a subscription-based licensing model and is no longer available standalone, its inclusion in VMware’s core platforms underscores its critical role in modern virtualized and hybrid cloud infrastructures. For organizations seeking efficient management, scalability, and comprehensive control over their VMware environments, vCenter Server remains the definitive solution.
