If you’re experiencing lag in Fortnite, or are simply curious about how the game connects you to its online world, understanding Fortnite Server Locations is key. Knowing where these servers are geographically located can shed light on your connection quality and potentially help you optimize your gameplay experience.
In the past, connecting to online games often involved manually selecting servers from lists, sometimes leading to a gamble for the best connection. Choosing the right server meant the difference between smooth gameplay and a frustrating, lag-filled experience.
Modern games like Fortnite utilize sophisticated client-server architectures to streamline this process. Your game client automatically assesses available servers and connects you to the one that offers the quickest and most stable connection, measured by ‘ping’ – the round-trip time for data packets. Typically, this is the server closest to your physical location. However, network conditions or infrastructure issues can sometimes lead you to connect to a server further away. Some games even attempt to group players with similar, even if poor, connections together for a more balanced (albeit laggy for everyone) match.
For players in regions with less developed internet infrastructure, such as parts of Africa or the Middle East, latency can be a persistent challenge. This raises a crucial question: where exactly are the Fortnite servers located around the globe?
 Fortnite battle bus soaring through the sky
Fortnite battle bus soaring through the sky
The straightforward answer is that Fortnite servers are globally distributed. However, the more detailed explanation lies in understanding that Fortnite leverages Amazon Web Services (AWS), a vast and distributed cloud infrastructure, to host its game servers.
Delving Deeper: The Public Cloud and Fortnite
To fully grasp Fortnite server locations, it’s essential to understand the concept of the public cloud. Unlike older online games that relied on single physical servers, Fortnite operates on a network of virtual servers. When you play Fortnite, you’re likely interacting with multiple servers simultaneously. Some servers handle user authentication and account management, others manage in-game transactions, and load balancers intelligently distribute players across different server instances based on player density.
Crucially, there are the backend game servers – the ones you directly play on. You might be connected to authentication servers in one location and game servers in another. The power of AWS lies in its interconnected global network of data centers. These data centers, massive facilities housing the cloud’s hardware, are linked by a vast network of private fiber optic cables spanning thousands of miles.
The public internet typically involves numerous ‘hops’ between different networks and providers to reach a destination, each hop adding to latency. However, once you connect to Amazon’s network, the internal connectivity between AWS data centers via their private fiber network is incredibly fast and low latency.
Essentially, you need to connect to the AWS network through the nearest access point, and from there, your connection to Fortnite servers and services within the AWS infrastructure should be optimized for speed. This type of global cloud infrastructure is also the backbone for other demanding online services, including game streaming platforms.
Furthermore, cloud infrastructure provides Epic Games with immense scalability. They can rapidly expand Fortnite server capacity on demand to accommodate player surges, without the delays associated with ordering and installing physical hardware. Epic Games essentially pays for the server resources they consume, allowing costs to scale up or down with player activity, network bandwidth, and data storage needs.
Now that we understand the cloud infrastructure powering Fortnite, let’s pinpoint the physical locations of these servers, or rather, the AWS data centers hosting them.
According to a report from 2018, Fortnite servers were operating across “24 of the 55 availability zones” within AWS at that time. An availability zone is essentially a data center or a cluster of data infrastructure within an AWS region. For example, the US East (N. Virginia) AWS region comprises multiple availability zones located near Dulles airport, a global hub for fiber optic connectivity, attracting numerous data centers and service providers, including AWS.
To determine your connected Fortnite server location, you can utilize the in-game ping tool. Navigate to the ‘settings’ menu, then the ‘game’ tab, and find the ‘matchmaking region’ option. This displays your ping and the server region you are connected to. You can even enable a setting to show this information on your game HUD during matches.
Leveraging this in-game tool, dedicated players have compiled lists of Fortnite server locations, allowing for the monitoring of server availability, response times, and potential game issues. Online tools like pingtestlive.com track server status for Fortnite and other games. Based on such tools and publicly available information, we can compile a list of known Fortnite server locations as of May 2019:
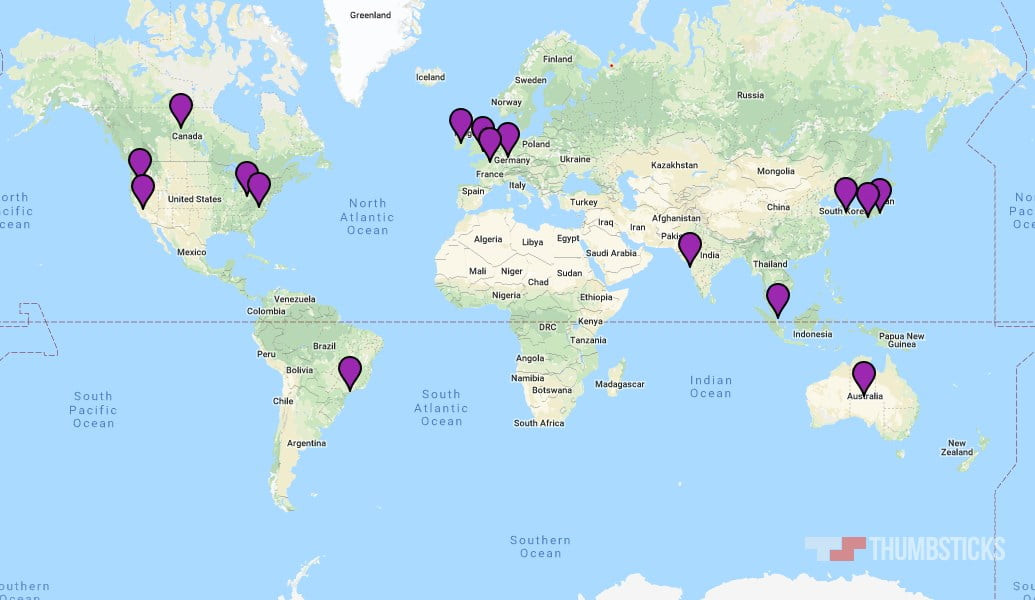 Map showing approximate Fortnite server locations around the world
Map showing approximate Fortnite server locations around the world
It’s important to note that these locations are approximate. For example, while a server location is indicated in Australia, there isn’t necessarily a data center in the exact center of the continent. Instead, the location represents the general region where AWS data centers hosting Fortnite servers are situated. The list of Fortnite server locations includes:
- Ohio, USA
- Virginia, USA
- California, USA
- Oregon, USA
- Tokyo, Japan
- South Korea
- Osaka, Japan
- Mumbai, India
- Singapore
- Australia
- Canada
- Frankfurt, Germany
- Ireland
- London, UK
- Paris, France
- Sao Paulo, Brazil
This list, reflecting server locations in May 2019, reveals some gaps in coverage, notably in Africa, the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and Russia. Players in these regions may experience higher latency as their connections are routed to more distant servers. For instance, for players in Dubai, the nearest server might be in Mumbai, India, a considerable distance away.
However, the landscape of Fortnite server locations is not static. As Fortnite’s popularity persists and Amazon’s AWS infrastructure expands globally, there is a strong possibility that Epic Games will deploy servers in more regions to meet player demand and improve latency for underserved areas. The flexibility of public cloud infrastructure makes expanding server presence relatively straightforward.
Understanding Fortnite server locations and the underlying cloud infrastructure empowers players to better comprehend their connection quality and the factors influencing their online gaming experience. As Fortnite evolves, so too will its server infrastructure, hopefully leading to a smoother, lower-latency experience for players worldwide.
