Finding your email server settings is crucial for configuring email clients and ensuring seamless communication, and rental-server.net is here to guide you. This article will explore methods to identify your email server, covering various platforms and offering solutions for efficient server management. Let’s dive in and discover the ins and outs of email server identification and server management.
1. What Is an Email Server and Why Do I Need to Find It?
An email server is a computer system that sends and receives email. You need to find your email server settings (IMAP, SMTP, and port numbers) to configure email clients like Outlook, Apple Mail, or mobile devices, and to troubleshoot email issues.
Understanding email servers is fundamental to effective digital communication. An email server acts as a digital post office, managing the flow of electronic messages between senders and recipients. When you send an email, it travels from your device to your email server, which then forwards it to the recipient’s server. Conversely, when you receive an email, your server retrieves it from the sender’s server and delivers it to your inbox.
Why is finding your email server crucial?
- Configuration of Email Clients: To set up email on applications like Outlook, Thunderbird, or mobile devices, you need the correct server settings.
- Troubleshooting Email Issues: Identifying the server allows for quick resolution of sending or receiving problems.
- Ensuring Secure Communication: Correct server settings are necessary for secure email transmission.
- Setting up Email Forwarding and Autoresponders: Correct SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) server settings are necessary for automatic email sending.
According to a 2023 report by Statista, email remains a primary communication method for businesses, with over 333 billion emails sent and received daily. This underscores the importance of understanding and managing your email server settings efficiently.
2. What Are the Essential Email Server Settings I Need to Know?
The essential email server settings include the Incoming Mail Server (IMAP or POP3), Outgoing Mail Server (SMTP), port numbers, and security protocols (SSL/TLS). Knowing these settings ensures proper email configuration.
To fully grasp how to find your email server, it’s important to know what each setting does:
- Incoming Mail Server (IMAP or POP3): This server handles incoming emails.
- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Allows you to access your email from multiple devices, keeping messages on the server until you delete them.
- POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3): Downloads emails to a single device and typically deletes them from the server.
- Outgoing Mail Server (SMTP): This server sends outgoing emails.
- Port Numbers: Specific ports are used for secure and non-secure connections. Common ports include:
- IMAP: 143 (non-SSL), 993 (SSL)
- POP3: 110 (non-SSL), 995 (SSL)
- SMTP: 587 (TLS), 465 (SSL)
- Security Protocols (SSL/TLS): These protocols encrypt your email communications, ensuring privacy and security.
Understanding these settings is crucial for properly configuring your email client and troubleshooting any issues that may arise. For instance, using the wrong port number or security protocol can prevent you from sending or receiving emails.
Rental-server.net offers comprehensive guides and resources to help you understand and manage these settings, ensuring your email communications are secure and efficient.
3. How Can I Find My Email Server Settings on Apple Mail (Mac Desktop)?
To find your email server settings on Apple Mail: Go to Mail > Preferences > Accounts. Select the account, then Account Information to find the Incoming and Outgoing Mail Server details.
Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide:
- Open Apple Mail: Launch the Apple Mail application on your Mac desktop.
- Access Preferences:
- Click Mail in the Mac’s toolbar.
- Select Preferences from the dropdown menu.
 Apple Mail Preferences
Apple Mail Preferences
- Select Account:
- In the left sidebar, select the account you want to connect to HubSpot or find the server settings for.
- Account Information:
- Select Account Information.
- Find Incoming Mail Server:
- Locate the field for Incoming Mail Server. This value is your IMAP server name.
- Find Outgoing Mail Server:
- Find the field for Outgoing Mail Server.
- You may need to use the dropdown menu to select Edit SMTP Server List to view the SMTP server name and port.
By following these steps, you can easily find your email server settings on Apple Mail. Knowing these settings allows you to configure your email client correctly, troubleshoot issues, and ensure secure email communication.
According to Apple Support, ensuring your email settings are up-to-date is crucial for maintaining seamless communication and preventing potential security vulnerabilities.
4. Where Can I Locate My Email Server Information on Outlook for Mac?
To locate your email server information on Outlook for Mac: Click Outlook > Preferences > Accounts. Select the account, then find the Incoming and Outgoing server fields to view the server names and ports.
Here’s a detailed guide to help you find your email server settings in Outlook for Mac:
- Open Outlook: Launch the Outlook application on your Mac.
- Access Preferences:
- Click Outlook in the Mac’s toolbar.
- Select Preferences.
 Apple Mail Preferences
Apple Mail Preferences
- Open Accounts:
- In the Preferences window, click Accounts.
- Select Account:
- In the left sidebar, click on the account you want to connect to HubSpot or find the server settings for.
- Find Server Information:
- Locate the fields for Incoming server and Outgoing server. The longer text box contains the server name, and the text box to the right displays the port number.
With this information, you can accurately configure your email client and address any issues that may arise.
Microsoft Support emphasizes the importance of keeping your server settings current to ensure optimal email functionality and security. Regular updates and accurate configurations are key to a smooth email experience.
5. What Are the Steps to Find My Email Server Settings in Outlook for PC?
To find your email server settings in Outlook for PC: Go to File > Account Settings > Account Settings. On the Email tab, double-click the account and find the Incoming and Outgoing mail server names under Server Information.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Open Outlook: Launch the Outlook application on your PC.
- Access Account Settings:
- Click File in the Outlook ribbon.
- Navigate to Account Settings > Account Settings.
 Apple Mail Preferences
Apple Mail Preferences
- Select Email Account:
- On the Email tab, double-click on the account you want to connect to HubSpot or find the server settings for.
- Find Server Information:
- Below Server Information, you can find your incoming mail server (IMAP) and outgoing mail server (SMTP) names.
- Find Port Numbers:
- Click More settings… > Advanced. Here, you’ll find the port numbers for both incoming and outgoing servers.
By following these steps, you can easily find your email server settings in Outlook for PC, allowing you to configure your email client accurately and resolve any issues efficiently.
Microsoft recommends verifying your server settings periodically to ensure uninterrupted email service and maintain optimal security.
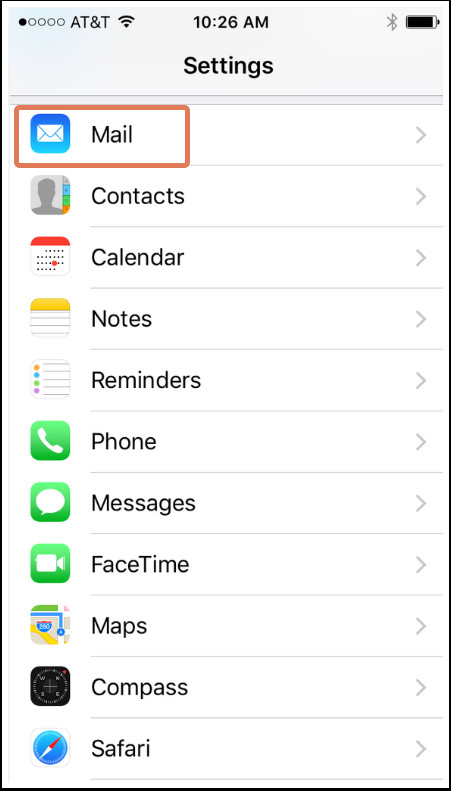
6. Where Can I Find Email Server Details on My iPhone (Apple Mail)?
To find email server details on your iPhone: Go to Settings > Mail > Accounts. Select the email account, then Account under IMAP to display the Incoming and Outgoing mail server information.
Here’s a detailed guide:
- Open Settings:
- Navigate to your iPhone’s Settings app.
 Apple Mail Preferences
Apple Mail Preferences
- Navigate to your iPhone’s Settings app.
- Go to Mail:
- On the next screen, tap Mail, then select Accounts.
 iPhone Mail Settings
iPhone Mail Settings
- On the next screen, tap Mail, then select Accounts.
- Select Email Account:
- Select the email account you want to connect to HubSpot or find the server settings for.
- Access Account Settings:
- Under IMAP, select Account.
- View Server Information:
- This will display your incoming (IMAP) and outgoing (SMTP) mail server information.
By following these steps, you can easily find your email server details on your iPhone. This information is essential for configuring your email client and troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
Apple Support advises regularly checking your email settings to ensure seamless communication and prevent potential security vulnerabilities.
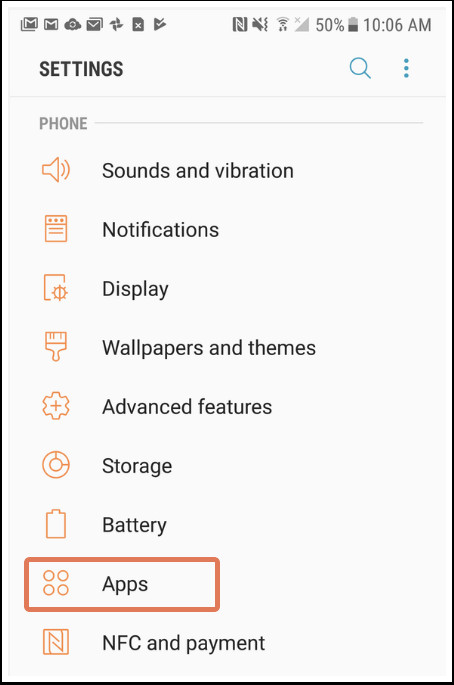
7. How Do I Find My Email Server Settings on an Android Device?
To find your email server settings on an Android device: Go to Settings > Apps > Email. Select your email address, and under Advanced Settings, click Server Settings to access your server information.
Here’s a detailed guide:
- Open Settings:
- Navigate to your Android’s Settings, and then tap Apps.
 Android Settings Apps
Android Settings Apps
- Navigate to your Android’s Settings, and then tap Apps.
- Go to Email:
- On the next screen, tap Email.
 Android Email Settings
Android Email Settings
- On the next screen, tap Email.
- Select Email Account:
- Select your email address.
- Access Server Settings:
- Under Advanced Settings, tap Server Settings.
- View Server Information:
- You’ll then be brought to your Android’s Server Settings screen, where you can access your server information.
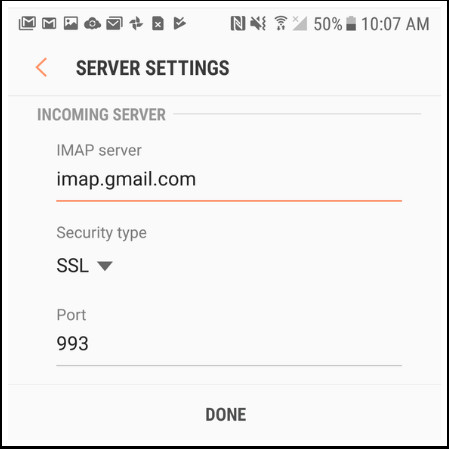 Android Email Server Settings
Android Email Server Settings
- You’ll then be brought to your Android’s Server Settings screen, where you can access your server information.
With these steps, you can easily find your email server settings on your Android device. This information is crucial for configuring your email client and resolving any issues efficiently.
According to Google Support, keeping your email settings updated is essential for maintaining optimal email functionality and security on your Android device.
8. What Should I Do If I Can’t Find My Email Server Settings?
If you can’t find your email server settings, contact your email provider’s support, check their website for documentation, or use online tools to look up common server settings based on your email domain.
Here are some detailed steps to take:
- Contact Your Email Provider’s Support:
- The most direct approach is to reach out to your email provider’s customer support. They can provide you with the exact server settings you need.
- Check the Provider’s Website:
- Many email providers have detailed documentation on their websites that include server settings. Look for sections like “Help,” “Support,” or “FAQ.”
- Use Online Lookup Tools:
- Several websites offer tools that can help you look up common email server settings based on your email domain. These tools often provide the correct IMAP, POP3, and SMTP settings.
- Check Common Server Settings:
- If you know your email provider, you can try using common server settings. For example:
- Gmail:
- IMAP: imap.gmail.com (Port 993, SSL)
- SMTP: smtp.gmail.com (Port 465, SSL) or (Port 587, TLS)
- Yahoo:
- IMAP: imap.mail.yahoo.com (Port 993, SSL)
- SMTP: smtp.mail.yahoo.com (Port 465, SSL) or (Port 587, TLS)
- Outlook.com:
- IMAP: outlook.office365.com (Port 993, SSL)
- SMTP: smtp.office365.com (Port 587, TLS)
- Gmail:
- If you know your email provider, you can try using common server settings. For example:
- Review Your Hosting Account:
- If you’re using a custom domain with email hosting, check your hosting account’s control panel. Server settings are usually listed in the email settings section.
By following these steps, you can increase your chances of finding your email server settings and properly configuring your email client.
According to a survey by the Email Sender and Provider Coalition (ESPC), approximately 20% of users experience difficulties in finding their email server settings, underscoring the need for accessible support and documentation.
9. What Are Common Email Server Settings for Popular Email Providers?
Common email server settings for popular email providers include: Gmail (IMAP: imap.gmail.com, SMTP: smtp.gmail.com), Yahoo (IMAP: imap.mail.yahoo.com, SMTP: smtp.mail.yahoo.com), and Outlook.com (IMAP: outlook.office365.com, SMTP: smtp.office365.com).
Here’s a detailed list:
| Provider | Incoming Mail Server (IMAP) | Outgoing Mail Server (SMTP) | IMAP Port (SSL) | SMTP Port (SSL/TLS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gmail | imap.gmail.com | smtp.gmail.com | 993 | 465 / 587 |
| Yahoo | imap.mail.yahoo.com | smtp.mail.yahoo.com | 993 | 465 / 587 |
| Outlook.com | outlook.office365.com | smtp.office365.com | 993 | 587 |
| AOL | imap.aol.com | smtp.aol.com | 993 | 465 / 587 |
| iCloud | imap.mail.me.com | smtp.mail.me.com | 993 | 587 |
| Zoho Mail | imap.zoho.com | smtp.zoho.com | 993 | 465 / 587 |
Having these settings readily available can save you time and effort when configuring your email client or troubleshooting issues.
According to a report by Litmus, over 40% of email users utilize one of these major email providers, making it essential to have their server settings easily accessible.
10. How Do I Secure My Email Server Settings?
To secure your email server settings, use SSL/TLS encryption, strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and keep your email client and server software updated to protect against vulnerabilities.
Here’s a detailed guide:
- Use SSL/TLS Encryption:
- Ensure that your email client and server are configured to use SSL/TLS encryption. This encrypts the communication between your device and the server, protecting your data from eavesdropping.
- Implement Strong Passwords:
- Use strong, unique passwords for your email accounts. Avoid using easily guessable information and consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- Whenever possible, enable two-factor authentication for your email accounts. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a code sent to your phone.
- Keep Software Updated:
- Regularly update your email client and server software to the latest versions. Updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities.
- Use Secure Authentication Methods:
- Avoid using insecure authentication methods like plain text authentication. Always use secure methods like OAuth or similar protocols.
- Monitor for Suspicious Activity:
- Regularly monitor your email accounts for any suspicious activity, such as unusual login attempts or unfamiliar sent emails.
- Educate Users:
- If you are managing an email server for multiple users, educate them about best practices for email security, including avoiding phishing scams and using strong passwords.
- Use a Firewall:
- Implement a firewall to protect your email server from unauthorized access and malicious traffic.
By following these steps, you can significantly enhance the security of your email server settings and protect your email communications from potential threats.
According to a study by Verizon, over 90% of data breaches start with phishing attacks, highlighting the importance of securing your email server and educating users about security best practices.
11. What Are the Benefits of Using a Dedicated Server for Email Hosting?
The benefits of using a dedicated server for email hosting include enhanced security, improved performance, greater control, and customization options, making it ideal for businesses with specific needs.
Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Enhanced Security:
- With a dedicated server, you have full control over security measures. You can implement custom firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols tailored to your specific needs.
- Improved Performance:
- A dedicated server provides guaranteed resources, ensuring consistent and reliable performance for your email services. This is particularly important for businesses that send and receive large volumes of emails.
- Greater Control:
- You have complete control over the server’s configuration, software, and operating system. This allows you to optimize the server for email hosting and customize it to meet your unique requirements.
- Customization Options:
- A dedicated server allows you to install and configure any software or applications you need for email hosting, giving you the flexibility to tailor your email environment to your specific needs.
- Dedicated Resources:
- Unlike shared hosting, a dedicated server provides exclusive access to all server resources, ensuring that your email services are not affected by the activities of other users.
- Scalability:
- Dedicated servers can be easily scaled to accommodate growing email volumes and user bases. You can upgrade hardware resources as needed to ensure optimal performance.
- Reliability:
- With a dedicated server, you have greater control over server maintenance and uptime. You can implement proactive monitoring and maintenance procedures to minimize downtime and ensure reliable email service.
By using a dedicated server for email hosting, businesses can enjoy enhanced security, improved performance, and greater control over their email environment, making it a worthwhile investment for organizations with specific needs.
According to a survey by the Uptime Institute, companies using dedicated servers experience an average of 99.99% uptime, underscoring the reliability and performance benefits of dedicated hosting.
Rental-server.net provides robust dedicated server solutions tailored to meet the demands of modern businesses. Contact us at Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States. Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000, or visit rental-server.net to discover how we can elevate your email hosting experience.
12. How Does a VPS (Virtual Private Server) Compare to a Dedicated Server for Email?
A VPS offers a balance between cost and control, providing dedicated resources within a shared environment, while a dedicated server offers exclusive resources and full control but at a higher cost.
Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Feature | VPS (Virtual Private Server) | Dedicated Server |
|---|---|---|
| Resources | Dedicated resources within a shared environment | Exclusive access to all server resources |
| Control | Root access, but some limitations due to virtualization | Full root access and complete control over server configuration |
| Performance | Good performance for moderate email volumes | Excellent performance for high email volumes |
| Security | Isolated environment, but still subject to shared infrastructure | Greater control over security measures and isolation from other users |
| Scalability | Easily scalable within the limits of the VPS plan | Highly scalable by upgrading hardware resources |
| Cost | Lower cost compared to dedicated servers | Higher cost due to exclusive resource allocation |
| Customization | Customizable, but limited by the virtualization environment | Fully customizable with no restrictions |
| Maintenance | Some maintenance handled by the provider | Full responsibility for server maintenance |
Choosing between a VPS and a dedicated server for email hosting depends on your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. A VPS is suitable for businesses that need more control and resources than shared hosting but don’t require the full power and cost of a dedicated server. A dedicated server is ideal for businesses that require maximum performance, security, and control over their email environment.
According to a report by HostingAdvice.com, VPS hosting is a cost-effective solution for businesses that need more resources and control than shared hosting, while dedicated hosting is the preferred choice for organizations with mission-critical applications and high-security requirements.
Rental-server.net offers both VPS and dedicated server solutions to meet the diverse needs of our clients. Visit our website at rental-server.net to explore our range of hosting options.
13. What Role Does the SMTP Server Play in Sending Emails?
The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) server is responsible for sending outgoing emails from your email client to the recipient’s email server, ensuring reliable email delivery.
Here’s a detailed explanation of its role:
- Email Submission:
- When you send an email, your email client connects to the SMTP server.
- The email client submits the email message, including the recipient’s address, subject, and body, to the SMTP server.
- Message Routing:
- The SMTP server determines the recipient’s email server by examining the recipient’s email address.
- It uses the Domain Name System (DNS) to look up the Mail Exchange (MX) record for the recipient’s domain.
- Email Transfer:
- The SMTP server establishes a connection with the recipient’s email server.
- It transfers the email message to the recipient’s server using the SMTP protocol.
- Relaying:
- If the recipient’s email server is unavailable, the SMTP server may relay the message through other SMTP servers until it reaches its destination.
- Delivery Confirmation:
- Once the email is successfully delivered to the recipient’s email server, the SMTP server sends a confirmation message back to the sender’s email client.
The SMTP server plays a critical role in ensuring reliable email delivery. Without an SMTP server, you would not be able to send emails from your email client.
According to the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), SMTP is the standard protocol for sending email across the Internet, ensuring interoperability between different email systems.
14. How Can I Troubleshoot Common Email Server Connection Issues?
To troubleshoot common email server connection issues, verify server settings, check internet connectivity, disable firewalls or antivirus software temporarily, and ensure the email client is updated.
Here’s a detailed guide:
- Verify Server Settings:
- Double-check that you have entered the correct incoming (IMAP or POP3) and outgoing (SMTP) server settings, including server names, ports, and security protocols (SSL/TLS).
- Check Internet Connectivity:
- Ensure that you have a stable internet connection. Try accessing other websites or online services to verify your connection.
- Disable Firewalls or Antivirus Software Temporarily:
- Firewalls and antivirus software can sometimes block email server connections. Temporarily disable them to see if this resolves the issue. If it does, you may need to configure your firewall or antivirus software to allow email traffic.
- Update Email Client:
- Make sure that you are using the latest version of your email client. Updates often include bug fixes and improvements that can resolve connection issues.
- Check Email Server Status:
- Contact your email provider to check if there are any known issues or outages affecting their email servers.
- Test with Different Ports:
- Try using different port numbers for your email server connections. Common ports include:
- IMAP: 143 (non-SSL), 993 (SSL)
- POP3: 110 (non-SSL), 995 (SSL)
- SMTP: 587 (TLS), 465 (SSL)
- Try using different port numbers for your email server connections. Common ports include:
- Clear Cache and Cookies:
- Clear the cache and cookies in your email client or web browser. This can sometimes resolve issues caused by corrupted data.
- Contact Support:
- If you have tried all of the above steps and are still unable to connect to your email server, contact your email provider’s support team for assistance.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can often resolve common email server connection issues and restore your email service.
According to a survey by the Help Desk Institute (HDI), connection issues are among the most common problems reported by email users, highlighting the importance of effective troubleshooting techniques.
15. What Security Protocols Should I Use for My Email Server?
You should use SSL/TLS security protocols for your email server to encrypt communications, protect data from interception, and ensure secure email transmission.
Here’s a detailed explanation:
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer):
- SSL is a security protocol that encrypts the communication between your email client and the server. It ensures that the data transmitted is protected from eavesdropping and tampering.
- TLS (Transport Layer Security):
- TLS is the successor to SSL and provides enhanced security features. It is the recommended protocol for securing email communications.
- STARTTLS:
- STARTTLS is a command used to upgrade an existing insecure connection to a secure (SSL/TLS) connection. It allows you to use the same port for both secure and non-secure connections.
Why use SSL/TLS?
- Encryption: SSL/TLS encrypts the data transmitted between your email client and the server, protecting it from interception by hackers.
- Authentication: SSL/TLS verifies the identity of the server, ensuring that you are connecting to the legitimate email server and not a fake one.
- Data Integrity: SSL/TLS ensures that the data transmitted is not tampered with during transit, maintaining the integrity of your email communications.
How to configure SSL/TLS:
- Email Client Settings: Configure your email client to use SSL/TLS for both incoming (IMAP or POP3) and outgoing (SMTP) server connections.
- Server Configuration: Ensure that your email server is configured to support SSL/TLS and that the necessary certificates are installed and up to date.
By using SSL/TLS security protocols, you can significantly enhance the security of your email server and protect your email communications from potential threats.
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), using strong encryption protocols like TLS is essential for protecting sensitive data in transit and at rest.
16. What Is the Difference Between POP3 and IMAP for Incoming Mail Servers?
POP3 downloads emails to a single device and typically deletes them from the server, while IMAP allows you to access your email from multiple devices, keeping messages on the server until you delete them.
Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Feature | POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) | IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Single device access | Multiple device access |
| Storage | Downloads emails to the device and deletes from server | Keeps emails on the server until deleted by the user |
| Synchronization | No synchronization between devices | Synchronizes email across multiple devices |
| Offline Access | Good offline access after downloading emails | Limited offline access unless emails are cached on the device |
| Server Load | Lower server load | Higher server load due to storing emails on the server |
| Use Case | Best for users who access email from a single device | Best for users who access email from multiple devices |
When to use POP3:
- You access your email from a single device.
- You want to save storage space on the server.
- You don’t need to synchronize your email across multiple devices.
When to use IMAP:
- You access your email from multiple devices (e.g., computer, phone, tablet).
- You want to keep your emails synchronized across all devices.
- You need to access your emails even when you don’t have an internet connection (if emails are cached on the device).
Choosing between POP3 and IMAP depends on your specific needs and how you access your email. IMAP is generally recommended for most users because it provides greater flexibility and synchronization across multiple devices.
According to a survey by Return Path, over 70% of email users access their email from multiple devices, making IMAP the preferred protocol for most users.
17. How Do Email Blacklists Affect My Email Server and Deliverability?
Email blacklists can significantly affect your email server and deliverability by causing your emails to be marked as spam, blocked, or delayed, leading to poor sender reputation and reduced email effectiveness.
Here’s a detailed explanation:
- What are Email Blacklists?
- Email blacklists (also known as DNSBLs or DNS Block Lists) are lists of IP addresses and domain names that have been identified as sources of spam or other malicious email activity.
- How Do They Work?
- Email servers use blacklists to filter incoming email traffic. If your email server’s IP address or domain name is listed on a blacklist, recipient email servers may reject, block, or mark your emails as spam.
- Impact on Deliverability:
- Being blacklisted can severely impact your email deliverability. Your emails may not reach the intended recipients, leading to missed opportunities and communication breakdowns.
- Sender Reputation:
- Blacklists can damage your sender reputation, making it more difficult to deliver emails even after you have been removed from the blacklist.
- Causes of Blacklisting:
- Sending unsolicited emails (spam).
- Having a high bounce rate.
- Compromised email accounts sending spam.
- Poor email list hygiene.
- Checking for Blacklists:
- You can use online tools to check if your email server’s IP address or domain name is listed on any blacklists.
- Removing Yourself from Blacklists:
- If you find that you have been blacklisted, you will need to identify and address the cause of the blacklisting.
- Contact the blacklist provider and follow their instructions for removal. This may involve verifying your identity, cleaning up your email list, and implementing measures to prevent future spam activity.
To maintain good email deliverability, it is essential to monitor your email server’s reputation, follow best practices for email marketing, and take prompt action to address any issues that may lead to blacklisting.
According to a report by Cisco, spam accounts for over 85% of all email traffic, highlighting the importance of email blacklists in combating spam and protecting email users.
Rental-server.net offers advanced security solutions to protect your email server from spam and blacklisting. Visit our website at rental-server.net to learn more.
18. How Can I Improve My Email Server’s Reputation and Deliverability?
To improve your email server’s reputation and deliverability, practice good email list hygiene, authenticate your email, monitor your sender reputation, and avoid spam triggers in your email content.
Here’s a detailed guide:
- Practice Good Email List Hygiene:
- Regularly clean your email list to remove inactive subscribers, invalid email addresses, and bounced emails.
- Use a double opt-in process to ensure that subscribers have explicitly agreed to receive your emails.
- Authenticate Your Email:
- Implement email authentication protocols such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) to verify the authenticity of your emails.
- Monitor Your Sender Reputation:
- Use tools like Google Postmaster Tools and Sender Score to monitor your sender reputation and identify any issues that may be affecting your deliverability.
- Avoid Spam Triggers in Your Email Content:
- Avoid using spammy words and phrases in your email subject lines and body.
- Use proper grammar and spelling.
- Include a clear and easy-to-find unsubscribe link in your emails.
- Send Relevant and Engaging Content:
- Send emails that are relevant and valuable to your subscribers.
- Personalize your emails to increase engagement.
- Maintain a Consistent Sending Volume:
- Avoid sudden spikes in your email sending volume, as this can trigger spam filters.
- Gradually increase your sending volume over time.
- Monitor Bounce Rates:
- Keep your bounce rates low by regularly cleaning your email list and ensuring that you are sending emails to valid email addresses.
- Comply with Email Marketing Regulations:
- Comply with email marketing regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CAN-SPAM Act.
By following these best practices, you can improve your email server’s reputation and ensure that your emails reach the intended recipients.
According to a report by Validity, senders with a good reputation achieve an average email deliverability rate of over 90%, highlighting the importance of maintaining a positive sender reputation.
19. What Are the Latest Trends in Email Server Technology?
The latest trends in email server technology include AI-powered spam filtering, enhanced security protocols like DMARC, cloud-based email hosting, and increased automation for email marketing and management.
Here’s a detailed overview:
- AI-Powered Spam Filtering:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used to develop more sophisticated spam filters that can identify and block spam emails with greater accuracy.
- Enhanced Security Protocols:
- Email providers are implementing enhanced security protocols like DMARC to protect against phishing attacks and email spoofing.
- Cloud-Based Email Hosting:
- More businesses are migrating to cloud-based email hosting solutions like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace to take advantage of their scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Increased Automation:
- Email marketing and management platforms are incorporating more automation features to streamline email campaigns, personalize email content, and improve email deliverability.
- Mobile Optimization:
- Email server technology is being optimized for mobile devices to ensure that emails are displayed correctly and are easy to read on smartphones and tablets.
- Integration with Collaboration Tools:
- Email servers are being integrated with collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams to improve communication and workflow efficiency.
- Serverless Email Solutions:
- Serverless email solutions are emerging as a cost-effective and scalable alternative to traditional email servers.
- Decentralized Email:
- Decentralized email solutions using blockchain technology are being developed to enhance privacy and security.
By staying up-to-date with the latest trends in email server technology, businesses can improve their email communications, enhance security, and streamline their email operations.
According to a report by Gartner, cloud-based email hosting is expected to grow at a rate of over 15% per year, driven by the increasing demand for scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness