A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, enhancing security, privacy, and control over network traffic; rental-server.net can help you understand and implement proxy servers for optimal performance. Think of it as a go-between that shields your IP address and filters web content. Explore advanced proxy configurations and server proxy options to unlock the full potential of your network.
1. Understanding Proxy Servers: The Basics
1.1. What is a Proxy Server? Defining the Intermediary
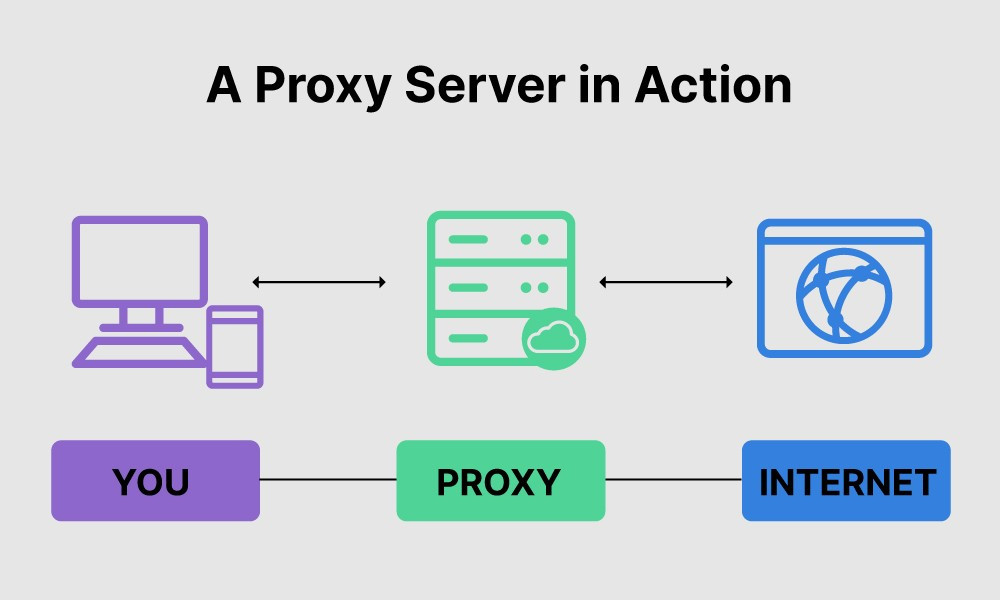
A proxy server is a dedicated computer system or software application acting as an intermediary between an endpoint device (like your computer) and another server. It essentially stands as a gateway, forwarding requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. In simpler terms, when you use a proxy server, your internet traffic flows through the proxy server on its way to the address you requested. The response then comes back through the same proxy server, which forwards it to you.
1.2. How Does a Proxy Server Work? The Mechanics Explained
When you initiate a request to access a website, your request is first routed to the proxy server. The proxy server then makes the request to the destination server on your behalf. The destination server responds to the proxy server, which then forwards the response back to your computer. This process effectively masks your IP address and location, making it appear as though the request originated from the proxy server itself.
To illustrate:
- User Request: You type a URL into your browser.
- Proxy Interception: Your request is intercepted by the proxy server.
- Request Forwarding: The proxy server forwards the request to the web server.
- Response Receipt: The proxy server receives the response from the web server.
- Response Delivery: The proxy server sends the response back to your computer.
1.3. Why Use a Proxy Server? Benefits and Advantages
Using a proxy server offers several significant advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Proxy servers act as a buffer between your computer and the internet, protecting your device from direct exposure to malicious websites and attackers.
- Improved Privacy: By masking your IP address, proxy servers make it more difficult for websites and advertisers to track your online activity.
- Content Filtering: Proxy servers can be configured to block access to specific websites or types of content, enhancing productivity and security.
- Bypass Geo-Restrictions: Proxy servers can allow you to access content that is restricted in your geographic location.
- Caching: Proxy servers can cache frequently accessed content, reducing bandwidth usage and improving website loading times.
- Load Balancing: Proxy servers can distribute network traffic across multiple servers, improving performance and reliability.
2. Types of Proxy Servers: Choosing the Right Fit
2.1. Transparent Proxies: Unseen Intermediaries
Transparent proxies inform websites that they are proxies and pass your IP address along with the request, while still offering caching benefits. They are often used in corporate environments for content filtering and monitoring.
2.2. Anonymous Proxies: Hiding Your Identity
Anonymous proxies identify themselves as proxies but do not reveal your original IP address. This provides a moderate level of privacy by preventing websites from identifying your specific location.
2.3. Distorting Proxies: Providing Misleading Information
Distorting proxies pass along a false IP address, further obscuring your identity. These proxies make it more difficult for websites to track your online activity, offering an additional layer of privacy.
2.4. High Anonymity Proxies (Elite Proxies): Maximum Privacy
High anonymity proxies, also known as elite proxies, do not identify themselves as proxies and do not reveal your original IP address. This type of proxy offers the highest level of privacy, making it nearly impossible for websites to track your online activity.
2.5. Reverse Proxies: Protecting Web Servers
Unlike forward proxies, which protect clients, reverse proxies protect web servers. They sit in front of web servers, intercepting requests and forwarding them to the appropriate server. This enhances security, load balancing, and caching capabilities.
2.6. Shared vs. Dedicated Proxies: Understanding the Difference
- Shared Proxies: Multiple users share the same proxy server and IP address, making them more affordable but potentially slower due to shared resources.
- Dedicated Proxies: You have exclusive use of the proxy server and IP address, providing better performance and reliability, but at a higher cost.
2.7. Datacenter Proxies: High Speed, Lower Anonymity
Datacenter proxies originate from data centers, offering high speed and reliability. However, they are often easily detected by websites due to their association with data centers, making them less suitable for tasks requiring high anonymity.
2.8. Residential Proxies: Real IP Addresses for Authenticity
Residential proxies use IP addresses assigned to real residential users, making them appear more legitimate to websites. This type of proxy is ideal for tasks requiring high authenticity, such as social media management and ad verification.
3. Use Cases for Proxy Servers: Real-World Applications
3.1. Enhancing Security: Protecting Your Network
Proxy servers provide a valuable layer of security by acting as a barrier between your network and the internet. They can be configured to filter traffic, block malicious websites, and prevent unauthorized access. According to a report by Cisco, organizations using proxy servers experience a 30% reduction in malware infections.
3.2. Improving Privacy: Masking Your IP Address
By masking your IP address, proxy servers make it more difficult for websites and advertisers to track your online activity. This is particularly useful for individuals concerned about their online privacy.
3.3. Bypassing Geo-Restrictions: Accessing Blocked Content
Proxy servers can allow you to access content that is restricted in your geographic location. By connecting to a proxy server in a different country, you can bypass these restrictions and access the content you want.
3.4. Content Filtering: Managing Internet Access
Proxy servers can be configured to block access to specific websites or types of content. This is particularly useful in corporate and educational environments for managing internet access and ensuring compliance with acceptable use policies.
3.5. Load Balancing: Distributing Network Traffic
Proxy servers can distribute network traffic across multiple servers, improving performance and reliability. This is particularly useful for websites with high traffic volumes, ensuring that users experience fast loading times and minimal downtime.
3.6. Caching: Speeding Up Website Loading Times
Proxy servers can cache frequently accessed content, reducing bandwidth usage and improving website loading times. This is particularly useful for websites with a large number of static assets, such as images and videos.
3.7. Web Scraping: Automating Data Collection
Proxy servers are essential for web scraping, allowing you to automate the collection of data from websites without being blocked or rate-limited. By rotating through multiple proxy servers, you can avoid detection and ensure the continuous collection of data.
3.8. Ad Verification: Ensuring Ad Placement and Compliance
Proxy servers are used in ad verification to ensure that ads are being displayed correctly and in compliance with advertising guidelines. By using proxy servers in different geographic locations, advertisers can verify that their ads are being displayed to the correct audience.
3.9. Social Media Management: Managing Multiple Accounts
Proxy servers are used in social media management to manage multiple accounts without being flagged for suspicious activity. By using different proxy servers for each account, you can avoid detection and ensure that your accounts remain active.
4. Setting Up a Proxy Server: A Step-by-Step Guide
4.1. Choosing a Proxy Server Provider: Factors to Consider
When choosing a proxy server provider, consider the following factors:
- Reliability: Choose a provider with a proven track record of uptime and performance.
- Speed: Look for providers with fast connection speeds and low latency.
- Location: Select a provider with proxy servers in the locations you need.
- Anonymity: Ensure that the provider offers the level of anonymity you require.
- Price: Compare pricing plans and choose a provider that fits your budget.
- Support: Look for providers with responsive and helpful customer support.
4.2. Configuring Your Browser to Use a Proxy Server: Basic Steps
Configuring your browser to use a proxy server is a relatively simple process. Here are the basic steps:
- Open Your Browser Settings: Access your browser’s settings menu.
- Find Proxy Settings: Search for “proxy” in the settings or look under “Advanced” or “Network” settings.
- Enter Proxy Details: Enter the proxy server’s address and port number provided by your proxy server provider.
- Save Changes: Save the changes and restart your browser.
4.3. Setting Up a Proxy Server on Your Operating System: Advanced Configuration
Setting up a proxy server on your operating system allows you to route all network traffic through the proxy server, providing a higher level of privacy and security. The steps vary depending on your operating system:
- Windows: Go to “Settings” > “Network & Internet” > “Proxy” and enter the proxy server details.
- macOS: Go to “System Preferences” > “Network” > “Advanced” > “Proxies” and enter the proxy server details.
- Linux: Configure the proxy settings in your network configuration file or use a graphical network manager.
4.4. Testing Your Proxy Server Connection: Ensuring Proper Functionality
After setting up your proxy server, it’s important to test the connection to ensure that it is working properly. You can use online tools to check your IP address and verify that it matches the proxy server’s IP address.
4.5. Proxy Server Software: Options and Features
Several proxy server software options are available, each with its own features and capabilities. Some popular options include:
- Squid: A popular open-source proxy server for caching and content filtering.
- NGINX: A high-performance web server and reverse proxy server.
- Apache: A widely used web server with proxy server capabilities.
- HAProxy: A reliable and high-performance load balancer and proxy server.
 Proxy server setup illustration
Proxy server setup illustration
5. Proxy Servers and Security: Best Practices
5.1. Choosing a Secure Proxy Server: Encryption and Protocols
When choosing a proxy server, it’s important to ensure that it uses secure protocols such as HTTPS and supports encryption to protect your data from interception. Look for providers that offer SSL/TLS encryption to secure your connection.
5.2. Avoiding Free Proxy Servers: Risks and Limitations
Free proxy servers often come with risks, such as malware infections, data logging, and slow connection speeds. It’s generally recommended to avoid free proxy servers and opt for a reputable paid provider.
5.3. Regularly Updating Your Proxy Server Software: Patching Vulnerabilities
Regularly updating your proxy server software is essential for patching vulnerabilities and ensuring that your server is protected against the latest threats. Keep your software up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
5.4. Monitoring Your Proxy Server Logs: Detecting Suspicious Activity
Monitoring your proxy server logs can help you detect suspicious activity and identify potential security breaches. Regularly review your logs for unusual traffic patterns or unauthorized access attempts.
5.5. Combining Proxy Servers with VPNs: Enhanced Security and Privacy
Combining proxy servers with VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) can provide an enhanced level of security and privacy. A VPN encrypts all of your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, while a proxy server masks your IP address and filters content.
6. Proxy Servers vs. VPNs vs. Tor: Understanding the Differences
6.1. Proxy Servers: Basic Intermediaries
Proxy servers act as intermediaries between your computer and the internet, masking your IP address and providing some level of privacy. However, they typically do not encrypt your traffic, making them less secure than VPNs.
6.2. VPNs: Encrypted Tunnels
VPNs encrypt all of your internet traffic and route it through a secure server, providing a high level of security and privacy. They are ideal for protecting your data from interception and bypassing geo-restrictions.
6.3. Tor: The Onion Router
Tor (The Onion Router) is a decentralized network that routes your traffic through multiple relays, providing a high level of anonymity. However, Tor can be slow and is not suitable for all types of traffic.
6.4. Key Differences: A Comparison Table
| Feature | Proxy Server | VPN | Tor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Typically No | Yes | Yes (Multiple Layers) |
| Anonymity | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate | Slow |
| Use Cases | Content Filtering, Bypassing Geo-Restrictions | Securing Public Wi-Fi, Bypassing Geo-Restrictions | Anonymizing Sensitive Communications |
| Complexity | Simple | Moderate | Complex |
7. Choosing the Right Proxy Server for Your Needs: A Decision Guide
7.1. Identifying Your Requirements: Security, Privacy, Speed, Location
Before choosing a proxy server, it’s important to identify your specific requirements. Consider the following factors:
- Security: Do you need a high level of security to protect your data from interception?
- Privacy: Do you need to mask your IP address and prevent websites from tracking your online activity?
- Speed: Do you need a fast connection speed for streaming and downloading content?
- Location: Do you need proxy servers in specific geographic locations?
7.2. Matching Proxy Types to Use Cases: A Practical Guide
| Proxy Type | Use Cases | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transparent Proxy | Content Filtering, Monitoring | Easy to Implement | Limited Privacy |
| Anonymous Proxy | Basic Privacy, Bypassing Geo-Restrictions | Hides IP Address | May Be Slow |
| Distorting Proxy | Enhanced Privacy | Provides False IP Address | May Be Unreliable |
| High Anonymity Proxy | Maximum Privacy | Does Not Identify as Proxy | Can Be Expensive |
| Reverse Proxy | Load Balancing, Web Server Security | Improves Performance, Protects Servers | Requires Server Configuration |
| Datacenter Proxy | High-Speed Tasks | Fast Connection Speed | Easily Detected |
| Residential Proxy | High Authenticity Tasks | Appears as Real User | Can Be Expensive and Slower |
7.3. Budget Considerations: Free vs. Paid Proxy Servers
Free proxy servers may be tempting, but they often come with risks and limitations. Paid proxy servers offer better reliability, speed, and security, but they can be more expensive. Consider your budget and choose a proxy server that meets your needs without breaking the bank.
7.4. Long-Term vs. Short-Term Use: Adapting Your Proxy Strategy
If you only need a proxy server for a short period of time, you may be able to get away with a cheaper option. However, if you plan to use a proxy server for the long term, it’s worth investing in a more reliable and secure solution.
8. Proxy Server Providers: A Comprehensive Comparison
8.1. Popular Proxy Server Providers: Overview and Features
Several reputable proxy server providers are available, each offering a range of features and pricing plans. Some popular options include:
- Smartproxy: Offers residential and datacenter proxies with a focus on reliability and performance.
- Oxylabs: Provides a wide range of proxy types, including residential, datacenter, and mobile proxies.
- Bright Data (formerly Luminati): Offers a large network of residential proxies with advanced targeting capabilities.
- Soax: Provides residential and mobile proxies with a focus on affordability and ease of use.
- NetNut: Offers datacenter and residential proxies with a focus on speed and reliability.
8.2. Pricing Plans: Comparing Costs and Value
Compare the pricing plans of different proxy server providers to find the best value for your money. Consider the number of proxies included in each plan, the bandwidth limits, and any additional features that may be important to you.
8.3. Customer Support: Responsiveness and Helpfulness
Look for providers with responsive and helpful customer support. Check online reviews to see what other users have to say about their experiences with the provider’s support team.
8.4. User Reviews and Ratings: Gauging Satisfaction
Read user reviews and ratings to get a sense of the overall satisfaction level of different proxy server providers. Pay attention to both positive and negative reviews to get a balanced perspective.
8.5. Free Trials: Testing Before Committing
Many proxy server providers offer free trials, allowing you to test their services before committing to a paid plan. Take advantage of these free trials to see if the provider meets your needs.
Here’s a comparison table of some popular proxy providers:
| Provider | Proxy Types | Pricing | Customer Support | User Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smartproxy | Residential, Datacenter | From $75/month | Excellent | High |
| Oxylabs | Residential, Datacenter, Mobile | From $180/month | Good | High |
| Bright Data | Residential, Datacenter, Mobile | From $300/month | Good | High |
| Soax | Residential, Mobile | From $75/month | Good | Moderate |
| NetNut | Datacenter, Residential | From $20/month (Datacenter), From $250/month (Residential) | Good | Moderate |
9. Advanced Proxy Server Configurations: Optimizing Performance
9.1. Proxy Chaining: Routing Through Multiple Servers
Proxy chaining involves routing your traffic through multiple proxy servers, providing an enhanced level of anonymity and security. This can make it more difficult for websites to track your online activity.
9.2. Load Balancing with Proxy Servers: Distributing Traffic Efficiently
Proxy servers can be used to load balance traffic across multiple servers, improving performance and reliability. This is particularly useful for websites with high traffic volumes, ensuring that users experience fast loading times and minimal downtime.
9.3. Caching Strategies: Optimizing Content Delivery
Proxy servers can be configured to cache frequently accessed content, reducing bandwidth usage and improving website loading times. Experiment with different caching strategies to optimize content delivery for your specific needs.
9.4. Using Proxy Servers with Command-Line Tools: Automation and Scripting
Proxy servers can be used with command-line tools such as curl and wget to automate tasks and scripts. This can be particularly useful for web scraping and other data collection activities.
9.5. Integrating Proxy Servers with APIs: Advanced Functionality
Proxy servers can be integrated with APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to add advanced functionality to your applications. This can allow you to programmatically manage your proxy servers and automate tasks.
10. Proxy Server FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
10.1. What is the difference between a proxy server and a VPN?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your computer and the internet, masking your IP address, while a VPN encrypts all of your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server.
10.2. Are proxy servers legal?
Yes, proxy servers are legal in most jurisdictions. However, using a proxy server to engage in illegal activities is not legal.
10.3. Can proxy servers be hacked?
Yes, proxy servers can be hacked if they are not properly secured. It’s important to choose a reputable proxy server provider and keep your software up to date with the latest security patches.
10.4. How do I find a good proxy server?
Look for providers with a proven track record of uptime, performance, and security. Read user reviews and ratings to get a sense of the overall satisfaction level of different providers.
10.5. What is a residential proxy?
A residential proxy uses IP addresses assigned to real residential users, making them appear more legitimate to websites.
10.6. What is a datacenter proxy?
Datacenter proxies originate from data centers, offering high speed and reliability but are often easily detected by websites.
10.7. How do I set up a proxy server on my router?
The process for setting up a proxy server on your router varies depending on the router model. Consult your router’s documentation for specific instructions.
10.8. Can I use a proxy server on my phone?
Yes, you can use a proxy server on your phone by configuring the proxy settings in your phone’s Wi-Fi settings or using a proxy server app.
10.9. What is a reverse proxy server used for?
A reverse proxy server protects web servers by intercepting requests and forwarding them to the appropriate server, enhancing security and load balancing.
10.10. How do I test if my proxy server is working?
You can use online tools to check your IP address and verify that it matches the proxy server’s IP address.
Proxy servers are powerful tools that can enhance your security, privacy, and control over network traffic. By understanding the different types of proxy servers and how they work, you can choose the right solution for your needs. Whether you’re looking to protect your network, bypass geo-restrictions, or optimize content delivery, a proxy server can help you achieve your goals.
Ready to explore the world of proxy servers and find the perfect solution for your needs? Visit rental-server.net today to discover a wide range of server options, compare prices, and find the ideal server to meet your specific requirements in the USA. Our experts are available to provide personalized guidance and support, ensuring you make the right choice for your business or personal use. Contact us at Address: 21710 Ashbrook Place, Suite 100, Ashburn, VA 20147, United States, Phone: +1 (703) 435-2000, or visit our website rental-server.net to get started. Unlock the full potential of your network with rental-server.net today.

